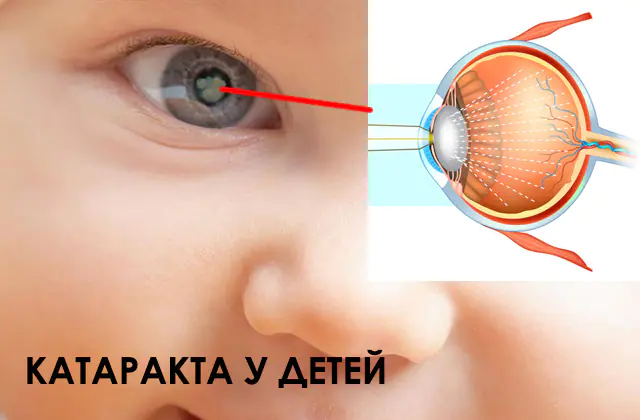
Causes of cataract development in children. Symptoms of congenital and acquired disease. Diagnostic methods for detecting lens opacities. Cataract surgery, features of the recovery period.
The content of the article:- Causes
- Symptoms of cataracts in children
- Diagnostic methods
- How to treat cataracts in a child
- Complications
- Prevention
Cataract is an ophthalmic disease characterized by clouding of the lens. In children it is often congenital. Without treatment, the disease progresses and leads to complete blindness in the affected eye. But surgery to remove and replace the lens can completely restore the visual function of the child’s body.
- Read a separate article if an adult has cataracts
Causes of cataracts in children
The lens is a biological lens located deep in the eyeball opposite the pupil. Its function is to refract light rays to distribute them evenly to the retina. A healthy lens looks like a capsule with transparent jelly-like contents. With the development of cataracts, its structure becomes heterogeneous, thick, and cloudy.
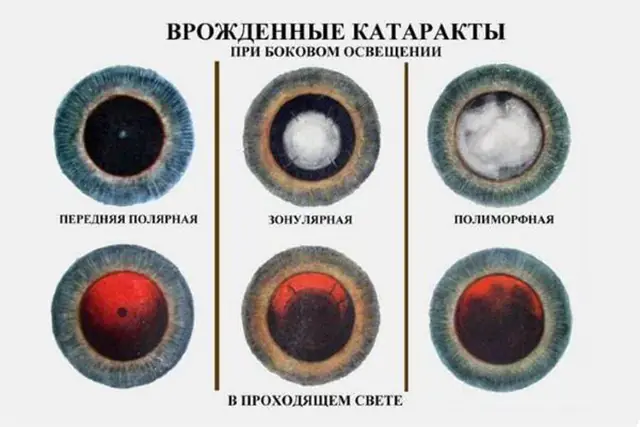
Causes of cataracts in children:
- Hereditary factor. If the baby's parents have a history of congenital cataracts, there is a high probability that the child will also suffer from this disease.
- Chromosomal disorders. Cataracts often develop in children with Down syndrome (presence of chromosome 47), Turner syndrome (absence of the sex chromosome in girls), Lejeune syndrome (absence of a fragment of chromosome 5).
- Intrauterine lesion. Cloudiness of the lens develops in a child in the womb if a woman has suffered from infectious diseases during pregnancy.
- Mechanical damage. Cataracts in children can develop as a result of head trauma, as well as as a complication of unsuccessful surgical and diagnostic procedures on the eye.
- Complication of galactosemia. This hereditary disease is characterized by difficulty converting galactose into glucose, the child’s main source of energy.
Symptoms of cataracts in children
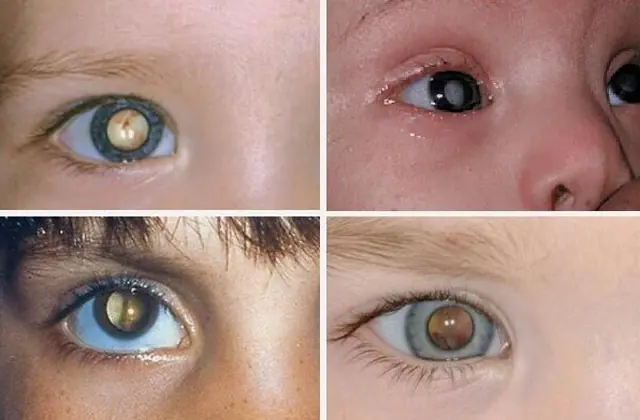
Photo of a child's cataract
The congenital form of cataracts in children is diagnosed in the maternity hospital. If lens opacification develops as a complication of an injury or illness suffered in the first months of life, it is manifested by the following symptoms:
- uncontrolled movements of the pupil;
- inability to focus on an object;
- looking at toys with one eye;
- frequent rubbing of the eyes with hands;
- capriciousness and tearfulness of the baby while playing with objects.
A sign of clouding of the lens in an infant may be an interest in rattles and complete indifference to silent toys.

Symptoms of cataracts in children of preschool and school age:
- rapid fatigue when writing, reading, looking at pictures;
- significant weakening of visual acuity in the dark;
- excessive lacrimation when exposed to bright light;
- complaints about ghosting of objects, blurred images;
- the appearance of white flies and dark spots before the eyes.
Methods for diagnosing cataracts in children
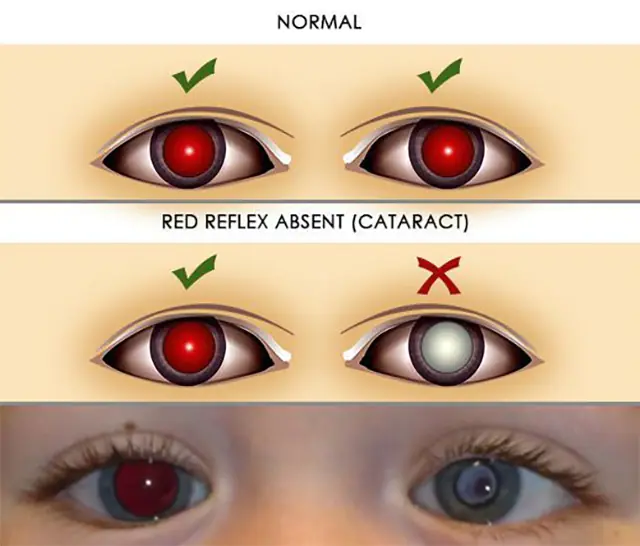
The first diagnostic examination of a newborn is carried out in the maternity hospital by a neonatologist. He identifies cases of congenital cataracts in children and makes recommendations for their treatment.
To confirm the diagnosis, parents visit a pediatric ophthalmologist. He examines the child’s eyes and talks with the parents about the child’s behavioral characteristics. In addition, the doctor will learn about ophthalmological diseases of relatives, the nature of pregnancy and childbirth.
Diagnostic procedures for identifying cataracts in a child:
- Visometry. This method of determining visual acuity is used for children who can speak and follow adult instructions. The doctor points to the image of objects on the table, and the child names them. You can also identify the presence of a problem in a playful way. For example, when playing dominoes with special chips (Lea optotypes). Instead of dots, they depict geometric figures of different sizes.
- Reverse ophthalmoscopy. The child sits with his back to the lighting fixture. The doctor directs a beam of light so that it is reflected from the mirror into the eye. A healthy pupil “burns” red. The absence of redness indicates clouding of the biological lens. During the examination, the ophthalmologist examines not only the lens, but also the elements of the baby’s fundus.
- Autorefractokeratometry. The child sits in front of the device and looks at the image of an object (balloon, Christmas tree) on the screen. At the same time, his gaze is fixed at one point, and the muscles and ligaments relax. The computer examines parts of the baby's eye and displays the result on paper using letters, numbers and symbols. The doctor deciphers these patterns and identifies ophthalmological diseases, including cataracts.
- Ultrasound biometrics. The child lies with his back on the couch and closes his eyes. The doctor moves the nozzle of the device over his eyelids. In this case, ultrasonic waves penetrate into the deep layers of the eye and are partially reflected from its tissues. The scanner processes the information and displays it on the screen in the form of a black and white picture. The procedure is absolutely painless and safe. Its duration is 15-20 minutes.
To perform all diagnostic procedures, it is necessary to ensure that the child remains motionless. Therefore, these methods are carried out only with children over 2 years old. To examine infants, the doctor uses small portable devices. And at this time the parents distract the baby with a rattle.
How to treat cataracts in a child?

If a congenital cataract is detected, the doctor registers the baby. Surgery to remove it is performed later due to the high risk of developing glaucoma. The best age for surgical treatment is 6-12 weeks.
Surgery to remove cataracts in children in the first year of life is called microinvasive vitrectomy. During this procedure, the surgeon makes three small incisions, inserts instruments, and sucks out the cloudy tissue with a vacuum. In the next step, the doctor injects silicone oil or organofluoride liquid into the empty space.
Cataracts can appear in children as a complication of injury or ophthalmic disease. In this case, the doctor conducts an examination and chooses the most effective method of surgical treatment. If bilateral lens opacification is detected, the surgeon performs surgery on both eyes at once so that the visual organs are restored simultaneously.
Methods for removing acquired cataracts:
- Ultrasonic removal. An ultrasound-emitting device is inserted into a small incision in the cornea. Under the influence of the rays, the lens is crushed, after which it is sucked up by a vacuum. An implant made of hypoallergenic material is installed in its place.
- Laser removal. A beam is directed at the lens of the diseased eye, which crushes its tissue. After aspiration, the surgeon installs a prosthesis, which stretches as the child’s body grows. The high temperatures of the laser seal the cut cornea.
- Intracapsular extraction. The surgeon makes a wide incision in the cornea and removes the lens using a cryopencil. The cloudy lens tissue is frozen to the tip of the device and removed without additional incisions.
- Extracapsular extraction. The main difference of this operation is that it is not the entire lens that is removed, but only its anterior and middle part. Thus, the vitreous body of the diseased eye remains protected by the posterior compartment of the biological lens.
After surgery, parents should explain to their child the importance of good hygiene. So, after the procedure, the eyes may water or burn slightly. At this time, they should not be rubbed or scratched with your hands. There should always be a clean handkerchief in your baby's pocket.
In addition, as directed by a doctor, adults should drip anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Visine. The main substance (tetrizoline) has anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictor, and anti-edematous effects. Price - from 270 rubles in Russia (150 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 15 ml.
- Visoptic. This analogue of Visine helps to extinguish the inflammatory process, relieve pain, and moisturize the eyeball. Price - from 198 rubles in Russia (120 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 15 ml.
In addition to anti-inflammatory drops, in the postoperative period it is useful to strengthen the child’s visual system by taking special vitamins. Ophthalmologists often prescribe Vitrum Vision, Lutein Children's, Chernikoezhka and their analogues.
After cataract surgery in a child, the visual acuity of the affected eye is restored within a few weeks. To prevent the development of amblyopia (lazy eye), the doctor prescribes wearing a patch on the healthy eye. This trains the diseased organ and makes it work harder. As a result, the process of overall recovery of the visual system is accelerated.
- Read about the treatment of cataracts with folk remedies
Complications of cataracts in children
Replacing the lens in mature and elderly people often leads to restoration of visual acuity. If a child has congenital cataracts, the doctor must not only eliminate the problem, but also ensure normal development of the visual organs.

Photo of amblyopia in a child before and after treatment
Remember, ignoring symptoms and untimely treatment of cataracts in children can lead to the following complications:
- Obscuration amblyopia. The disease is characterized by a persistent decrease in visual acuity due to the functional inability of the eye to perform normal activities. In childhood, it leads to a delay in the development of the visual analyzer.
- Strabismus. The inability of the eye to respond correctly to light signals leads to asymmetry of the pupils relative to the bridge of the nose. Children feel headaches and have difficulty orienting themselves in space.
- Nystagmus. Disturbance in the functioning of the extraocular muscle leads to uncontrolled sudden movements of the pupils. Due to the inability to focus on objects, children feel dizzy, double vision, general malaise, and weakness.
- Lens luxation. Cataracts that appear as a result of mechanical damage to the eye are sometimes complicated by displacement of the biological lens. The disease can be determined by the yellowness of the lens and trembling of the iris.
- Iridocyclitis. Changes in the structure of the lens sometimes lead to damage to the iris and ciliary body. The inflammatory process is characterized by immobility of the pupil and blue discoloration of the vascular network of the eye.
Measures to prevent cataracts in children

To preserve the health of the fetus, give up bad habits during pregnancy. Eat healthy foods, take vitamins, go for walks, and limit your interactions with sick people as much as possible.
Pay attention to your child's complaints. Bring him to an ophthalmologist if he frequently squints, has watery eyes, or rubs his eyes with his fingers. Do not skip preventive examinations, follow all instructions and recommendations of the doctor.
To prevent senile cataracts from childhood, teach your son/daughter to observe a work and rest schedule, properly illuminate the workplace, and do eye exercises. Make sure that your child does not rub his eyelids with dirty hands, always washes himself, and wears safety goggles for swimming underwater.
How to treat cataracts in children - watch the video:



