Melanoma is a type of cancer that affects melanocytes—pigment cells located in human skin.
Melanoma has a high risk of rapid metastasis, which leads to the development of severe complications and, in severe cases, death of the patient. Every year, about 50 thousand new cases of melanoma are registered in the United States.
The first link in the timely diagnosis of the disease is the patients themselves, since melanomas usually occur on open, visible areas of the skin. This is important because early detection and diagnosis of melanoma ensures rapid cure with minimal surgery.
Disease statistics
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States and Australia. In other countries, this group of diseases is in the top three. Melanoma is the leader among skin cancers in terms of the number of deaths. Every hour in the world one person dies from this disease. In 2013, there were 77 thousand confirmed melanoma diagnoses and 9,500 deaths from it. The share of melanoma in the structure of cancer is only 2.3%, while at the same time being the cause of 75% of deaths from skin cancer.
This form of cancer is not exclusively skin cancer and can affect the eyes, scalp, nails, feet, and oral mucosa (regardless of gender and age). The risk of developing melanoma among Caucasians is 2%, 0.5% among Europeans and 0.1% among Africans.
Causes
- Prolonged exposure to the sun. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, including solariums, can cause the development of melanoma. Excessive sun exposure in childhood significantly increases the risk of disease. Residents of regions with increased solar activity (Florida, Hawaii and Australia) are more susceptible to developing skin cancer.
Burns caused by prolonged exposure to the sun more than double the risk of developing melanoma. A visit to the solarium increases this indicator by 75%. The WHO Cancer Research Agency classifies tanning equipment as an "increased risk factor for skin cancer" and classifies tanning equipment as carcinogenic.
- Moles. There are two types of moles: normal and atypical. The presence of atypical (asymmetrical, raised above the skin) moles increases the risk of developing melanoma. Also, regardless of the type of moles, the more there are, the higher the risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor;
- Skin type. People with more delicate skin (characterized by light hair and eye color) are at increased risk.
- Anamnesis. If you have previously had melanoma or another type of skin cancer and are cured, your risk of developing the disease again increases significantly.
- Weakened immunity. The negative impact of various factors on the immune system, including chemotherapy, organ transplantation, HIV/AIDS and other immunodeficiency conditions, increases the likelihood of developing melanoma.
Heredity plays an important role in the development of cancer, including melanoma. Approximately one in ten patients with melanoma has a close relative who has or has had the disease. A strong family history includes melanoma in parents, siblings, and children. In this case, the risk of melanoma increases by 50%.
Types of melanomas
Based on the type of melanoma, they are divided into 4 categories. Three of them are characterized by a gradual onset with the development of changes in only the superficial layer of the skin. Such forms very rarely become invasive. The fourth type is characterized by a tendency to quickly grow deep into the skin and spread to other parts of the body and internal organs of the patient.
Superficial (superficial) melanomais the most common variant of the disease (70% of cases). This is a melanoma of the skin, the symptoms of which are characterized by the long-term persistence of relatively benign growth in the upper (outer) layer of the skin. Only after a long period of time does superficial melanoma grow into deeper layers.
The first sign of this type of melanoma is the appearance of a flat, asymmetrical spot with uneven borders. The color of the affected area changes to brown (like a tan), black, red, blue, or white. Such melanomas can occur at the site of moles. Although the disease can occur anywhere on the skin, symptoms are more likely to develop on the torso (men) and legs (women), as well as the upper back (regardless of gender).
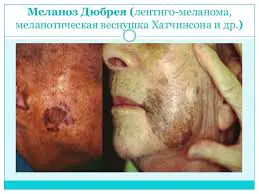
Lentigo malignaits course is similar to superficial melanoma, since it develops in the upper layers of the skin for a long time. Visually, lentigo appears as a flat or slightly raised unevenly colored area of skin. The color of the spot is variegated with brown and dark brown elements. This type of in situ melanoma is more common in older patients due to constant chronic exposure to sunlight and usually develops on the face, ears, arms and upper torso. This is the most common form of melanoma in Hawaii. When it enters the invasive stage, the disease is called lentigo melanoma.
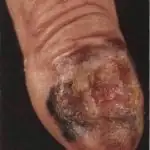
Acral lentiginous melanomaalso develops superficially before continuing to grow deeper into the skin. This form differs from the others in that it appears as black or brown spots under the nails, on the palms of the hands or on the soles of the feet. The disease progresses faster than previous forms and is more likely to affect dark-skinned people. It is the most common form among Africans and Asians, while Caucasians and Europeans are least susceptible to it.
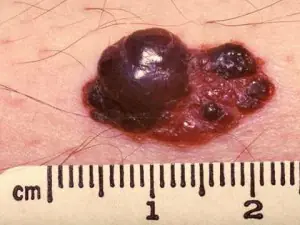
Nodular melanomais an invasive variant of the course. Usually, by the time it is detected, it has already grown quite deeply into the skin. Outwardly, this melanoma resembles a lump. It is usually black in color, but there are other variations (blue, grey, white, brown, red or even unaltered skin colours). It is most often localized on the torso, legs and arms. Mainly affects older people. This is the most aggressive variant of melanoma. It is diagnosed in 10-15% of cases.
Melanoma symptoms
Melanoma can develop from an existing mole or as a result of another skin disease, but it often occurs on normal skin. The most common locations for melanoma are the legs and upper back. Due to the continued production of melanin by the altered cells, the tumor is black or brown, but colorless melanomas are also found.
Less commonly, melanomas occur on the palms, nails, and mucous membranes. In older people, melanomas are more likely to appear on the face, as well as on the neck, scalp and ears.
Early symptoms of melanoma
The main signs of melanoma are changes in the size, shape, color of existing moles or “birthmarks” or the appearance of discomfort in this area. The development of these symptoms may take a long time (several weeks or months). In addition, melanoma may initially be perceived as a new mole, but at the same time have an unpleasant appearance. The appearance of such a subjective symptom should serve as an alarming sign and a reason to visit a doctor.
Early signs of melanoma include:
- Bleeding
- Burning feeling
- Crust formation
- Change in the height of the spots (thickening or raising a mole that was previously flat above the skin)
- Ulceration, itchy skin
- Change in consistency (mole becomes soft)
- The appearance of any discharge in the tumor area
- Increase in the size of the altered lesion
- Redness or swelling of surrounding tissues
- The appearance of new small areas of pigmentation around the main lesion
Late symptoms of melanoma
Further development is characterized by the following symptoms of melanoma:
- Violation of the integrity of the skin
- Bleeding from a mole
- Bleeding from other pigmented areas of the skin
- Pain in the affected area
Symptoms of metastatic melanoma
These symptoms develop when melanoma cancer cells enter the bloodstream and spread to other organs:
- Chronic cough
- Lump under the skin
- Gray skin tone
- Constant headache
- Convulsions
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Unexplained weight loss, exhaustion
You should immediately consult a doctor if you experience:
- Bleeding from moles or areas of pigmentation
- Discoloration of fingernails and toenails not caused by injury
- Asymmetry in the growth of moles or individual areas of skin
- Darkening of the skin not associated with tanning
- The appearance of areas of pigmentation with uneven edges
- The appearance of moles with areas of different colors (the spread of pigmentation from a mole to surrounding tissue is an early sign of melanoma)
- Increase in diameter more than 6mm
Stages of melanoma
According to the new approved international classification, when determining the stage of melanoma, diagnostic criteria are the thickness of the tumor (Breslow thickness), the presence of microscopic ulcerations and the rate of division of cancer cells. Thanks to the new system, it has become possible to make a more accurate diagnosis and plan the most effective treatment.
Breslow thickness is measured in millimeters and characterizes the distance from the upper layer of the epidermis to the deepest point of tumor invasion. The thinner the melanoma, the higher the chance of cure. This indicator is the most important aspect in predicting the course and effectiveness of treatment measures.
- Stages 1 and 2
melanomas are characterized by limited swelling. This means that cancer cells have not yet metastasized to lymph nodes or other organs. At this stage, the risk of recurrence of melanoma or further spread of the tumor is quite low.
Depending on the thickness there are:
- Melanoma “in situ” (“in place”). This is the initial stage, when the tumor has not yet grown deep into the epidermis. This form is still referred to as the zero stage;
- Thin tumors (less than 1 mm). The development of a tumor indicates the initial (first) stage of melanoma;
- Medium thickness (1 – 4 mm). From this moment on, the course of melanoma enters the second stage;
- Thick melanomas (more than 4 mm in thickness).
The presence of microscopic ulcerations aggravates the severity of the disease and means a transition to later stages. The rate of cell division is also an important criterion in determining the prognosis of the course. Even a single confirmed process of dividing a cancer cell culture by one square millimeter characterizes the transition to more severe stages of melanoma and increases the risk of metastasis. In this case, the method of choice is a more aggressive treatment tactic to achieve the desired effect. At the first and second stages, melanoma is characterized by an asymptomatic increase in the size of areas of pigmentation, their elevation above the skin level without bleeding or pain.
At this stage, important changes in the course of the disease are observed. At this stage, the Breslow thickness is no longer taken into account, but the identification of ulcerations becomes indicative.
The third stage is characterized by the spread of tumor cells to the lymph nodes and surrounding areas of the skin. Any spread of the tumor beyond the boundaries of the primary focus is characterized. As a transition to the third stage. This is confirmed by a biopsy of the lymph node closest to the tumor. Now this diagnostic method is indicated when the tumor size increases by more than 1 mm or if there are signs of ulceration. The third stage is characterized by the late symptoms of melanoma described above (pain, bleeding, etc.).
means that tumor cells metastasize to distant organs. Metastases in melanoma spread in (according to the time of involvement in the pathological process):
At this stage, symptoms of metastatic melanoma appear, which depend on the damage to a particular organ. At stage 4, melanoma has a very unfavorable prognosis, the effectiveness of treatment is only 10%.
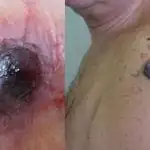
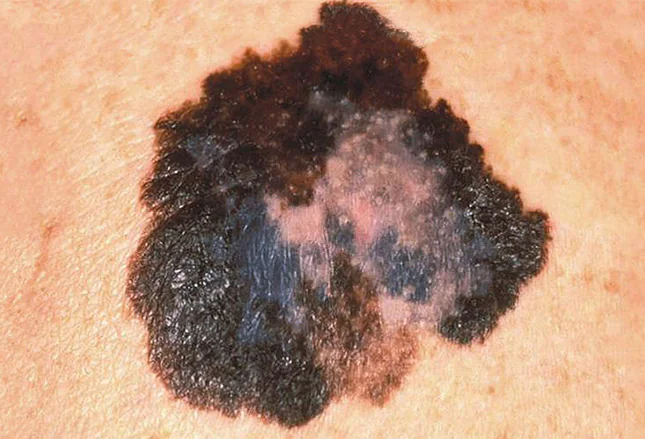
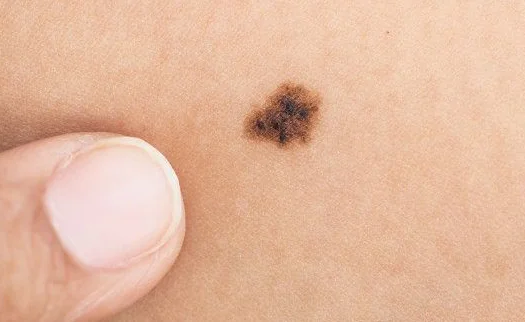
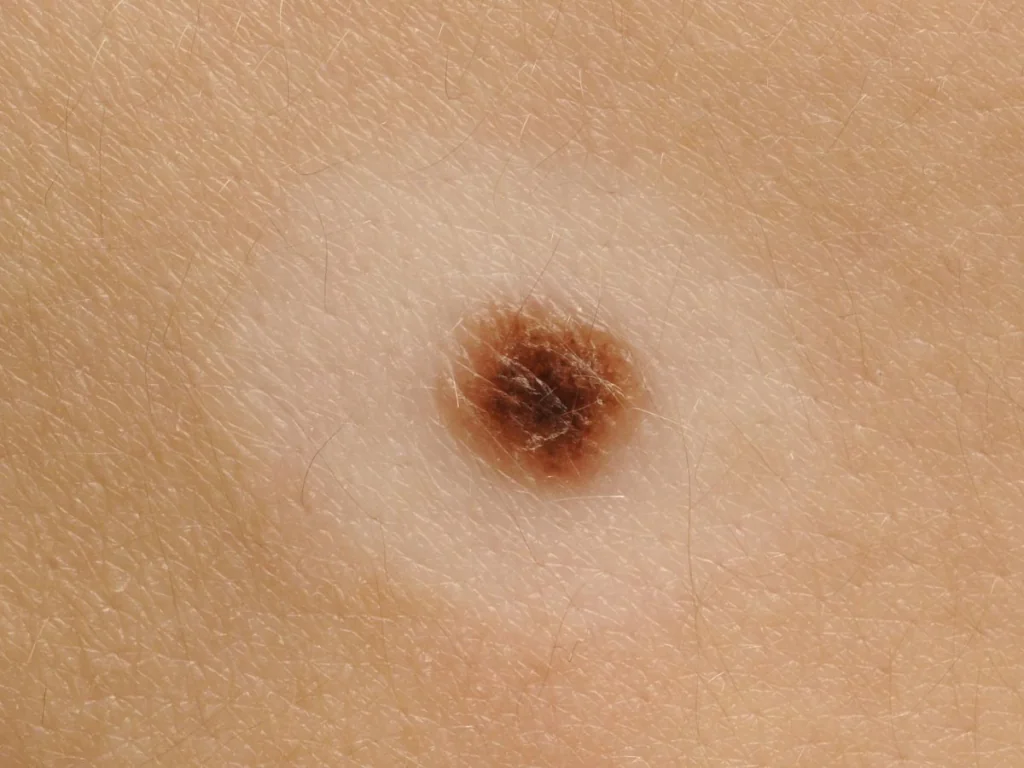
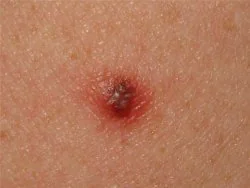
What does melanoma look like - photo
| Malignant melanoma is not always characterized by dark pigmentation. Because of this, it is often difficult to make a correct diagnosis. | Photographs taken at some time interval help to assess the degree of tumor growth and changes in the size of the lesion. |
 |
 |
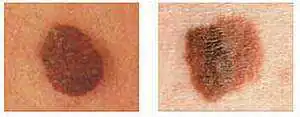
| Left - Plain Right - Color changes within one element |
Left - Smooth edges Right - No clear border |
 |
 |
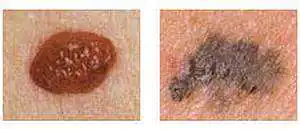
| Left - Common mole Right - Change shape, size and color |
Left - Normal mole (symmetrical) Right - Melanoma (asymmetric) |
 |
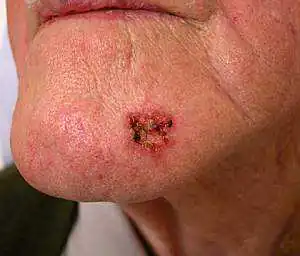 |
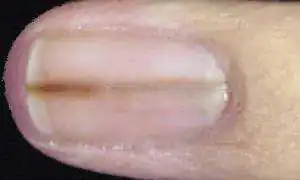
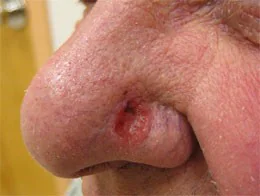
| A brown or dark line along the nail should be considered malignant melanoma, especially if the edges become uneven and gradually thicken. | Melanoma on the face |
Diagnostics
Diagnosing melanoma is quite a difficult task even for an experienced dermatologist. Since characteristic symptoms do not always come first, it is necessary to pay great attention to self-diagnosis and notify the doctor immediately after discovering a suspicious mole or spot. This is especially important if your close relatives have had a similar disease. After an examination, your doctor may order a skin biopsy as well as a lymph node biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. The final diagnosis of melanoma is confirmed only after histological examination of the biopsy specimen. Obtained from a pathological focus.
Early detection of melanoma can save the patient's life. To do this, it is recommended to perform a monthly self-examination to detect skin changes in a timely manner. You don't need any special equipment for this. All you need is a bright lamp, a large mirror, a hand mirror, two chairs and a hairdryer.
- Examine the head and face using one or both mirrors. Use a hair dryer to check the scalp;
- Check the skin of your hands, including your nails. Using mirrors, examine your elbows, shoulders, and armpits;
- Carefully assess the condition of the skin on the neck, chest and torso. For women, it is mandatory to check the skin under the mammary glands;
- Using a mirror, examine your back, buttocks, and the back of your neck, shoulders, and legs;
- Carefully evaluate the condition of the skin on your legs and feet, including your nails. Be sure to examine your knees;
- Using a mirror, inspect the skin on the genitals.
If you find suspicious pigmentation elements, compare them with the photos of melanomas below.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends on the time of detection and the degree of tumor progression. When detected early, most melanomas respond well to treatment.
Melanoma that has grown deeply or has spread to the lymph nodes increases the risk of recurrence after treatment. If the depth of the lesion exceeds 4 mm or there is a lesion in the lymph node, then there is a high probability of metastasis to other organs and tissues. When secondary lesions appear (stages 3 and 4), treatment of melanoma becomes ineffective.
If you have had melanoma and recovered, it is very important to conduct self-examination regularly, since for this category of patients the risk of recurrence of the disease is very high. Melanoma can recur even after several years.
Survival rates for melanoma vary widely depending on the stage of the disease and the treatment provided. In the first stage, cure is most likely. Also, cure can occur in almost all cases of stage 2 melanoma. Patients treated in the first stage have a 95 percent five-year survival rate and 88 percent ten-year survival rate. For the second stage, these figures are 79% and 64%, respectively.
In stages 3 and 4, the cancer has spread to distant organs, resulting in a significantly reduced survival rate. The five-year survival rate of patients with stage 3 melanoma ranges (according to various sources) from 29% to 69%. Ten-year survival is achieved in only 15 percent of patients.
If the disease has progressed to stage 4, then the chance of five-year survival is reduced to 7-19%. There are no 10-year survival statistics for patients with stage 4.
The risk of melanoma recurrence increases in patients with a large tumor thickness, as well as in the presence of ulcerations of melanoma and nearby metastatic skin lesions. Recurrent melanoma can occur either in close proximity to the previous site or at a considerable distance from it.
Despite the fact that this form of cancer looks frightening, the prognosis for its treatment is not always unfavorable. Even if it reoccurs, early treatment leads to cure and ensures long-term survival of patients.
Melanoma or melanoblastoma is a malignant neoplasm (skin cancer) that develops from melanocytes. What is it and what functions does it perform?
Melanocytes are specialized cells that produce melanin, which determines the color of a person’s skin and its ability to tan. Melanocytes also perform a protective function, preventing the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation.
Skin melanoma is considered the most aggressive type of cancer. The tumor process develops very rapidly. It is a mistake to believe that melanoma appears only from moles.
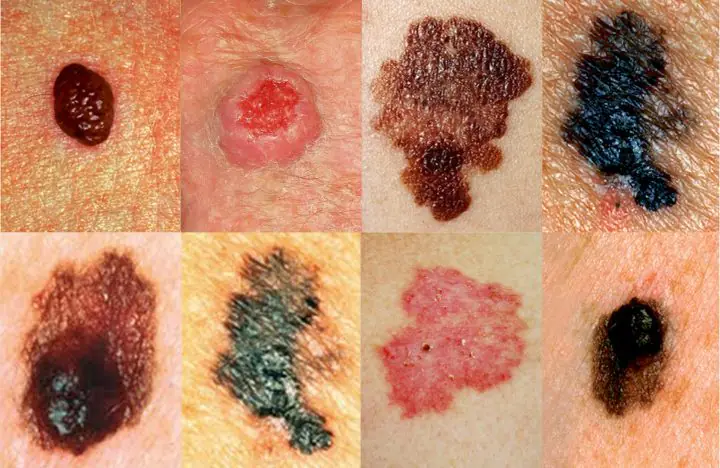
The percentage of development of this type of cancer from moles is only 30%, the rest occurs in clean areas of the skin. Melanoma can even form under the nails.
Despite the fact that for the most part melanoma develops on the skin, it can occur in the rectum, vagina, various structures of the eye, and oral cavity.
Causes of melanoma
There are many theories about the origin of cancer. Science has not yet determined the reasons for the development of the tumor process, however, for each type of tumor there are prerequisites and risk factors. For melanoma it is:
- systematic long-term exposure of the skin to ultraviolet radiation (sunlight, artificial light in solariums);
- chronic burns;
- regular repetitive mechanical trauma to moles, age spots, nevi;
- ionizing radiation;
- chronic electromagnetic radiation;
- predisposition of the skin - low pigmentation (white skin, abundant freckles);
- heredity (the risk of the disease increases if someone in the family has suffered this type of skin cancer);
- immunodeficiency states;
- hormonal disorders (increased levels of sex and melanocyte-stimulating hormones);
- late pregnancy (after 30);
- use of oral contraceptives.
Melanoma symptoms
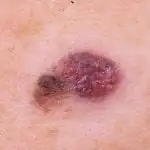
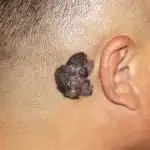
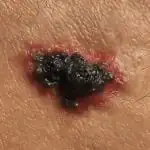
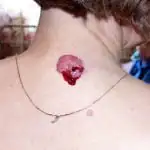
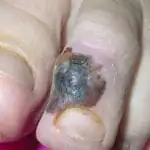
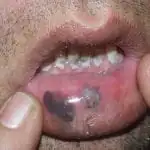
Skin cancer most often occurs on the lower extremities or back, but the location can vary greatly. As was said, it can occur at the site of a mole, in places of injury to the skin, or on ordinary, uninjured, clean skin (see photo above).
A malignant neoplasm changes the melanocyte, but it continues to produce the pigment melanin, so the neoplasm becomes black or brown.
There are also colorless melanomas.
One of the symptoms of melanoma is a black rim around the edge of the tumor on the skin.
A characteristic sign of melanoma is the asymmetry of the formation and its large size. At first, people often don't recognize skin changes as cancer.
At first, melanoma looks like a mole, but of an unusual appearance.
Symptoms of melanoblastoma are divided into early and late:
- Early (first) signs of the disease:
- elevation of previously flat moles;
- itching, burning, bleeding, ulceration;
- change in density (a previously hard mole becomes soft);
- hyperemia and swelling of adjacent tissues;
- growth of the primary tumor focus;
- new areas of pigmentation around the primary focus of the tumor;
- crust formation;
- change in color of the nail plate on the hands and feet;
- darkening of the skin not associated with prolonged exposure to the sun;
Stages of melanoma development
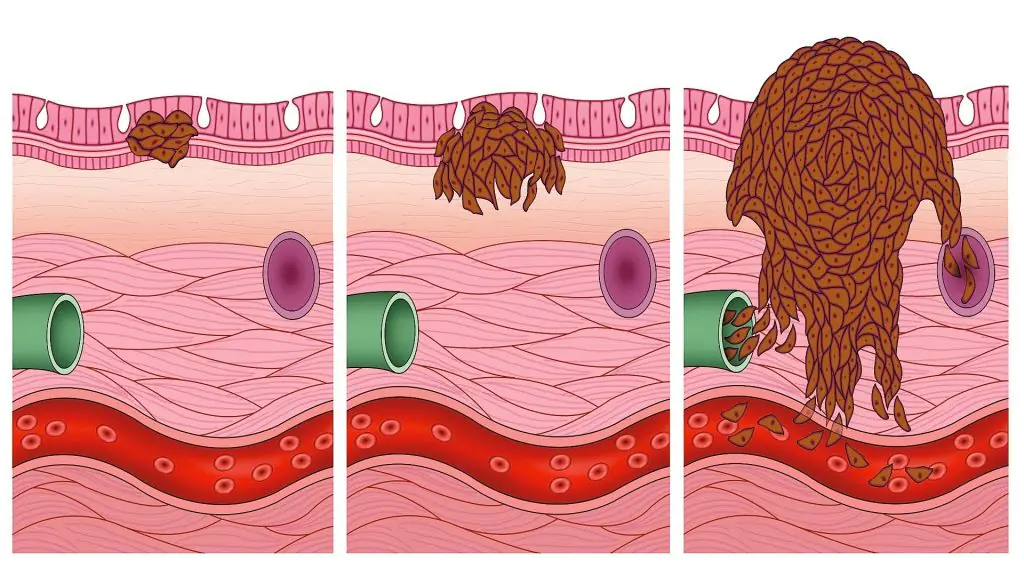
The doctor determines the stage of melanoma development according to the thickness of the tumor:
- Zero stage – “cancer in situ” – at this stage, melanoma has not yet grown into the thickness of the epidermis;
- initial stage – tumor size is less than one millimeter with skin damage or up to two millimeters without damage (see what it looks like in the photo below);
- Second stage – formation thickness up to two millimeters with damaged skin surface or more than two millimeters without damage;
- Third stage – the presence of metastasis in one of the regional lymph nodes (lymphatic vessels);
- Fourth stage – tumor growth and invasion of underlying tissue, the presence of metastases throughout the body.
Melanoma metastases most often occur on the skin, subcutaneous tissues, liver, brain and bones (spine, ribs, cranial and pelvic bones).
Classification
- Superficial spreading melanoma. Typically, this type of melanoma develops on a mole or intact area of skin.
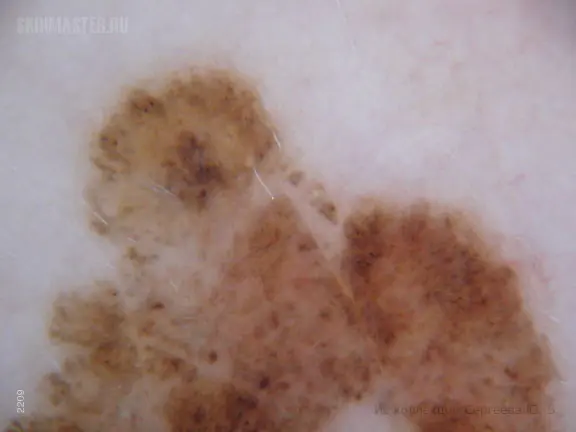
Lentigo maligna (superficial spreading melanoma)
- Nodular melanoma is a more malignant type of the disease.
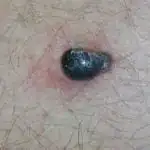
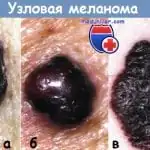
- Lentiginous melanoma (Hutchinson's freckle) develops more often on the face, ears, neck, and hands. It is considered the most favorable form of this pathology (slow growth combined with a low risk of metastasis);
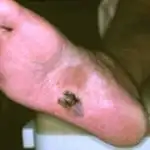
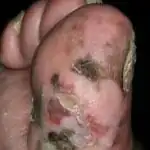
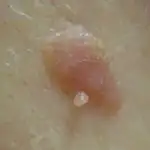
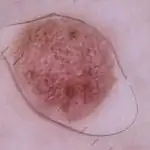
How is diagnostics carried out?
First of all, a specialist doctor examines the affected area of skin.
A thorough visual examination is carried out using a special device - a dermatoscope.
This is an instrumental research device that allows you to examine skin tumors without surgical intervention.
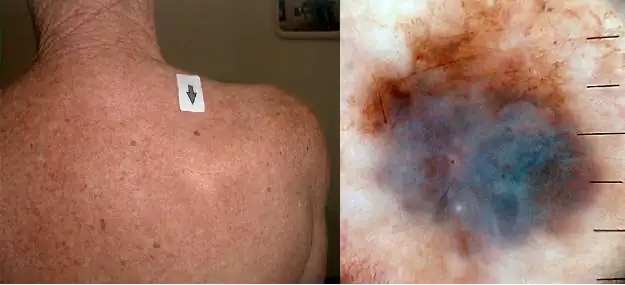
Dermatoscope image
A dermatoscope allows you to see signs of a malignant tumor that are not visible to the naked eye. Scientific progress has contributed to the creation of a digital dermatoscope, thanks to which you can see a three-dimensional image of the pathology on the screen.
It is mandatory for a patient with suspected skin cancer to donate blood to detect tumor markers. Tumor markers are specific substances released by a malignant tumor.
A biopsy is a mandatory diagnostic method if a pathology is suspected of being cancerous.
The material undergoes histological and morphological examination, which allows us to determine the degree of malignancy of the tumor, stage and clinical form of melanoma.
Additional research methods are:
- CT scan;
- scintigraphy;
- Ultrasound of the regional lymph node and internal organs.
These methods are used to detect tumor metastases.
Treatment of melanoma
In the early stages of the disease, surgical treatment is carried out, which is the most effective. Drug therapy may be used. In the later stages of melanoblastoma development, radiation treatment methods are used.
Drug therapy for melanoma
For skin melanoma, three drug treatment regimens are used:
- before surgical excision of the tumor to reduce the size of the melanoma and the defect that remains after (not adjuvant therapy);
- primary therapy when surgery is not possible;
- after surgical removal of the tumor to prevent relapses (adjuvant therapy).
Drug treatments for melanoma include immunotherapy, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy for melanoma is carried out using biological drugs created in the laboratory, but similar to the immune proteins of the human body.
Medicines used:
- Interferon-alpha used in adjuvant therapy, preventing recurrence of the excised tumor;
- Interleukin-2 used to prevent metastasis;
- Peginterferon-alpha-2b provides effective anti-relapse prevention;
- Ipilimumab – a drug created on the basis of monoclonal antibodies; specifically affects the body, increasing the immune response to malignant processes;
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
During chemotherapy for melanoma, the drugs are carried through the blood vessels, penetrate into all organs and tissues and have a systemic effect.
This type of therapy for melanoma is not effective enough; moreover, healthy cells of the body are destroyed, which makes chemotherapy drugs undesirable for use.
Chemotherapy is carried out in combination with immunotherapy in order to reduce the possibility of side effects.
Drugs used in this type of therapy: Dacarbazine, Paclitaxel, Carboplatin.
Chemotherapy causes a number of side effects:
- baldness;
- anemia;
- weakness, loss of appetite;
- increased bleeding;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
Radiotherapy is a treatment method that uses strong radiation to kill tumor-damaged cells. The method is not used for primary melanoma.
Radiotherapy is prescribed after lymph node dissection as a way to prevent relapse.
This type of therapy is accompanied by side effects (hair loss, nausea, vomiting, skin manifestations), however, all unwanted effects from radiotherapy disappear upon completion of treatment.
Surgery
Surgery followed by tumor removal is the main method of treating melanoma, especially at the initial stage of the disease.
There are the following surgical methods for tumor removal:
- Simple excision – this method is suitable for flat melanomas and involves minimally invasive intervention. Along with the damaged areas, healthy tissue around is also removed to prevent relapse;
- Wide tissue excision – performed after a biopsy, the results of which showed the presence of a tumor process;
- Amputation – used if melanoma is localized on the finger;
- Lymph dissection – removal of lymph nodes located in close proximity to the tumor.
- Surgery for metastatic melanoma – does not cure the patient of the tumor, but improves his quality of life by removing the symptoms caused by metastasis in any organ.
Supportive treatments
Definitely indicated for melanoma diet, which involves proper nutrition to reduce the effects of chemotherapy.
For melanoma, you must follow these rules:
- Reduce your fat intake and focus on proteins and carbohydrates;
- Food should be cooked exclusively by steaming or in the oven;
- It is strictly forbidden for a patient with melanoma to go on various diets for weight loss;
- It is necessary to eat small portions every two to three hours;
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Increase the amount of foods in your diet that contain vitamins E and A and folic acid;
- Increase consumption of foods with antioxidants (broccoli, carrots, pumpkin).
It is prohibited to eat:
- Pork and beef;
- Butter;
- Fast food;
- Baking;
- Ice cream;
- Chocolate;
- Seeds;
- Pine nuts.
The following products will have a beneficial effect on the condition of a patient with melanoma:
- Green tea;
- Fish;
- Vegetables, both raw and boiled (especially pumpkin, radish, tomatoes);
- Fruits or freshly squeezed juices;
- Poultry meat;
- Seafood.
Prevention
People who are predisposed to developing melanoma need to follow some rules that will reduce the risk of the disease:
- Reducing sun exposure is the main prevention against melanoma;
- It is necessary to protect exposed skin from direct rays of the sun (wear sweaters with sleeves, hats or caps and pants);
- The use of sunscreen is recommended;
- Knowledge about the first signs and symptoms of melanoma is necessary so that if one of them is detected, immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment;
- It is necessary to examine the skin for the presence of new formations or changes in old ones, so as not to miss the transformation of a mole into melanoma;
How long will the patient live after diagnosis?
The prognosis for this cancer depends on several factors, one of which is tumor metastasis.
If melanoma has metastasized, the patient’s lifespan depends on the number of affected organs:
- one – seven months;
- two – up to four months;
- more than two organs – less than two months.
One of the factors influencing the patient's life expectancy is the location of the tumor process. The prognosis is more favorable when melanoma is located on the forearm and lower leg, less so on the scalp, hand, foot and mucous membranes.
Melanoma recurs very often. Scientists have found that the malignant process can start again even ten years after complete recovery.
However, when stage I melanoma is detected and this formation is removed in a timely manner, the prognosis is more than favorable (97% of patients survive).
What are the recommendations after treatment for melanoma?
For patients who have survived skin cancer, there is a list of mandatory rules that must be followed in order to avoid or promptly detect recurrence of the disease.
First of all, every month the patient should independently or with the help of relatives examine their skin for the presence of suspicious formations and the first alarming symptoms of relapse.
The patient must adhere to a schedule of visiting a specialist for consultation and examinations (as indicated).
Patients with cured first stage of the disease are recommended to visit the doctor once every three months for the next few years. With the second, third and fourth stages - once every month for four years.
It is also very important to avoid sunlight and stop visiting solariums if the patient used these services before illness.
Such patients must qualitatively change their lifestyle. Exercise, adequate sleep, and proper and balanced nutrition are encouraged. Quitting bad habits (drinking alcohol, nicotine) is an important measure in preventing relapse.
Playing sports does not involve intense physical activity. This could be walking, aerobics, fitness.
This disease is extremely stressful for the psyche. And even if the disease was overcome, unpleasant memories can still haunt the mind of such a person. Therefore, it is important to use stress prevention methods (meditation, relaxation). It is recommended to visit a psychotherapist if the patient cannot independently cope with the negative emotional background of the disease.
The participation of family and loved ones in rehabilitation after treatment for melanoma is also important. Regular communication, support, and spending time together will only have a beneficial effect on the psychological state of the patient.
Video on the topic
Skin melanoma is one of the most malignant human tumors, often with an unpredictable course. You can now find a huge number of “articles” on the topic of melanoma on the Internet. The vast majority of them do not have an author, a huge number are written by people without medical education. Reading such materials can lead an unprepared person to neurosis.

Very often on the Internet I answer questions related to one or another sign of melanoma. Most often people find one of the symptoms and give themselves a fatal diagnosis. The main thing I want to say in this article is that one single sign of melanoma, in itself, is not a reason for panic and suspicion regarding this disease.
16 signs of melanoma
Now it is necessary to give all the signs by which an inexperienced person might suspect melanoma.
The list, which is given in the book of one of the leading experts in this field, Valentin Vadimovich Anisimov, “Skin Melanoma (Part 2),” seems to me the most complete:
- horizontal growth of nevus
- vertical growth of nevus above surrounding tissues
- the appearance of asymmetry or irregularity of the outlines (scalloping) of the edges of the nevus, i.e., a change in its shape.
- complete or partial (uneven) change in the color of the nevus, the appearance of areas of so-called associated depigmentation.
- the appearance of a feeling of itching and burning in the area of the nevus.
- ulceration of the epidermis over the nevus.
- wetting of the surface of the pigmented nevus.
- bleeding from its surface.
- hair loss on the surface of the nevus.
- inflammation in the area of the nevus and in the tissues surrounding it.
- peeling of the surface of the nevus with the formation of dry “crusts”.
- the appearance of small pinpoint nodules on the surface of the nevus.
- the appearance of daughter pigmented or pinkish formations (satellites) in the skin around the nevus. 14) change in the consistency of the nevus, determined by palpation, i.e. its softening or loosening.
- the appearance of a shiny glossy surface of the nevus.
- disappearance of the skin pattern on the surface of the nevus.
Now that we have listed the 16 signs of melanoma, I will try to show how this list works.
I think that if this is not the first time you are reading about melanoma on the Internet, you have already found one of the symptoms in yourself.
Fortunately, in most cases, there must be several of them, or the rate of change must be high. Now we will analyze them all in detail:
Sign 1 "horizontal growth of nevus"
In almost every person, almost all moles increase at least a little during life. Does everyone have melanoma? I think no.
At the same time, if a mole has grown by several millimeters in a few months, you need to urgently show it to an oncologist.
Signs 2 and 12 - “vertical growth of the nevus above the surrounding tissues”, “appearance of small pinpoint nodules on the surface of the nevus”
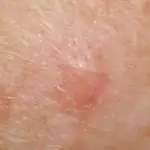
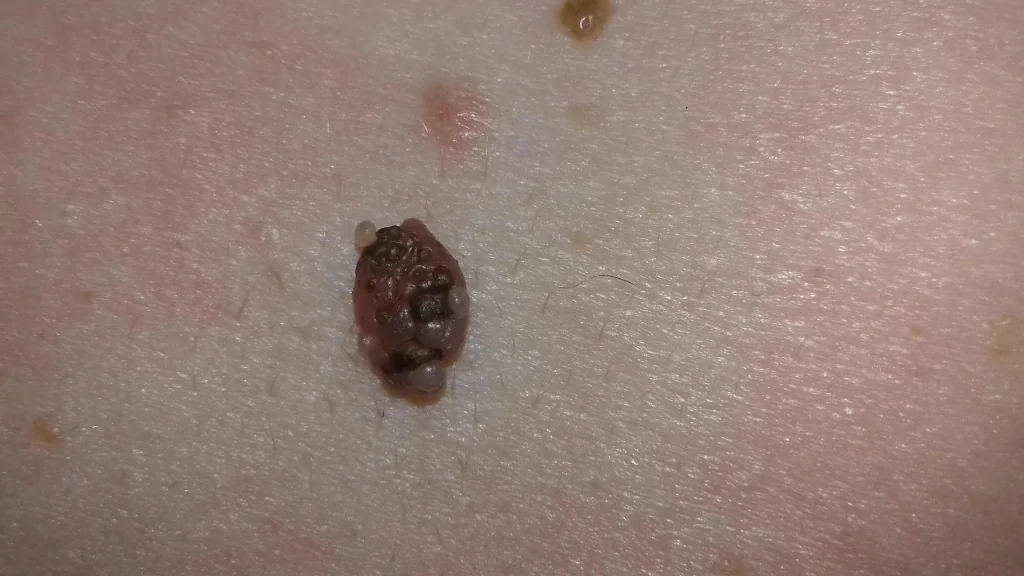
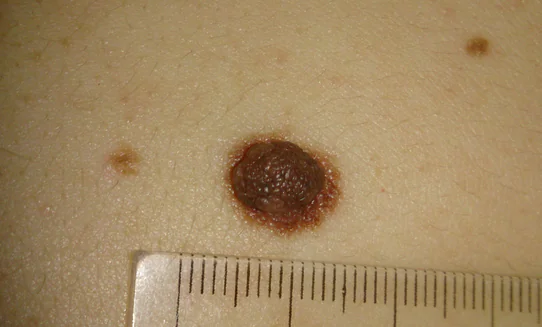
Very often, people in panic ask me: “My mole is growing in height and growths are appearing on it! I’m dying.” If everything looks like the picture below, you need to urgently see an oncologist - it’s most likely melanoma.
At the same time, there is a separate type of skin formations - papillomatous nevi. They are also sometimes called warty. Often small papillomatous nodules appear on their surface, which a person without experience can easily attribute to symptom No. 2 or No. 12. The photo below is a typical example of a completely benign mole with nodules that have appeared on the surface:
I talk in more detail about the growth and enlargement of moles in this article.
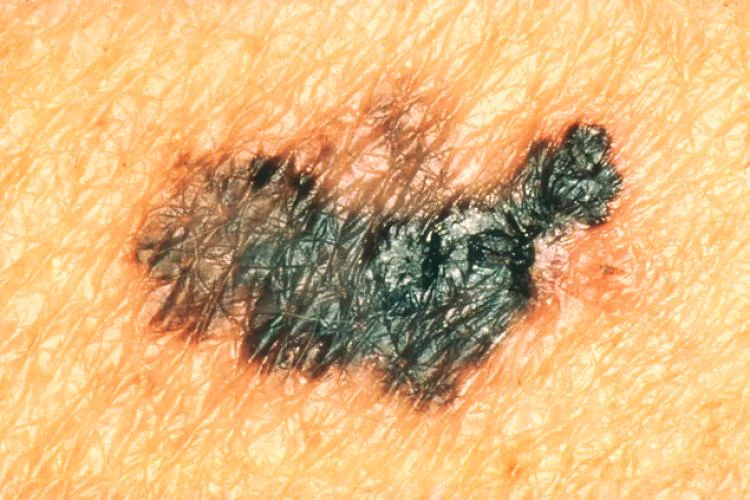
Sign 3 - “the appearance of asymmetry or irregularity in the outline of the nevus.”
If the nevus has become asymmetrical along two axes, its entire edge has become scalloped or began to remind coastline on the geographical map - it’s time to go to the oncologist.
However, if you look closely at any mole on the body with a magnifying glass, even with low power, you will not find perfect circles or straight lines. In no nevus is the pigment distributed 100% evenly.
You can read more about moles with uneven edges here
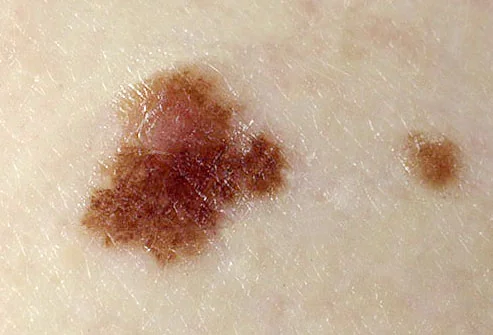
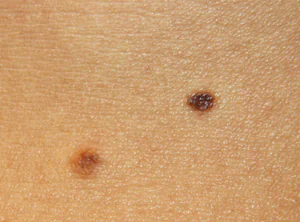
Sign 4 “uneven change in color of the nevus (mole), the appearance of areas of so-called associated depigmentation”
Melanoma is characterized by uneven distribution of pigment. If it is melanoma, the depigmentation (lighter area) will be as irregular in shape as the mole itself:
A benign nevus (mole) can also normally have an uneven distribution of pigment, but it will not be as pronounced:
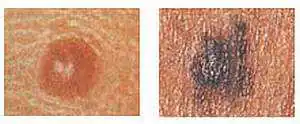
Depigmentation may surround the mole. This most often occurs in halo-nevi:
I discuss moles with uneven coloring in more detail in a separate article.
Sign 5 - “the appearance of itching and burning in the area of the nevus”
Yes, itching and burning can indeed be signs of melanoma. However, any part of the body can itch, including a completely benign mole. In the absence of other signs, all fears are groundless.

You can read more about this sign in this article.
Signs 6 and 7 - “ulceration of the epidermis over the nevus”, “wetting on the surface of the nevus”
In my experience, ulceration appears mainly in melanomas in late stages, when there is no longer any doubt about the diagnosis. This symptom is more relevant, in my opinion, for basal cell skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma). This disease is much less formidable; people die from it extremely rarely.
For a benign mole, an ulcerated surface and weeping are also possible - immediately after trauma:
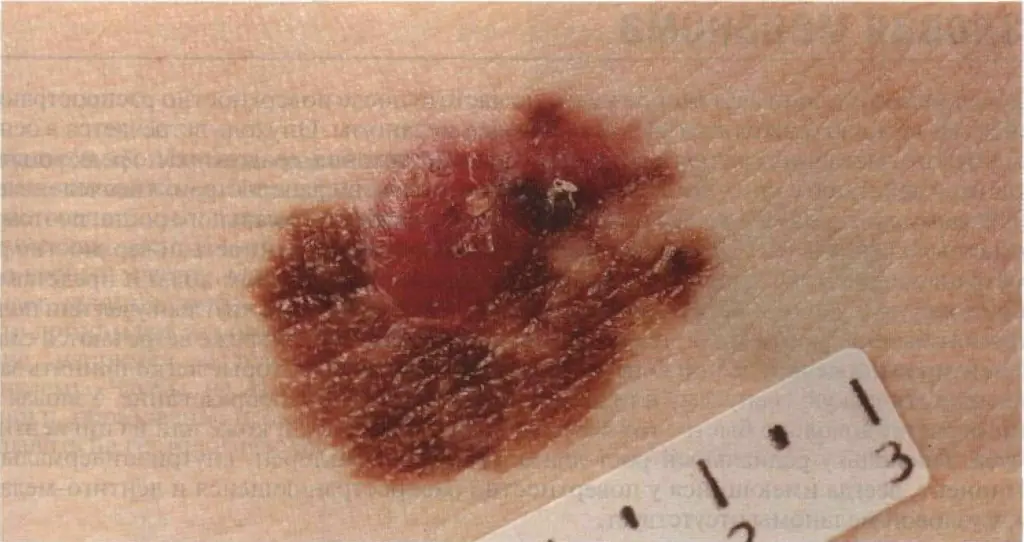
Sign 8 - “bleeding from the surface of the nevus.”
Yes, indeed one of the common features of melanoma is spontaneous bleeding without previous trauma to the mole. Even this one sign will make any oncologist seriously doubt the benignity of the mole.
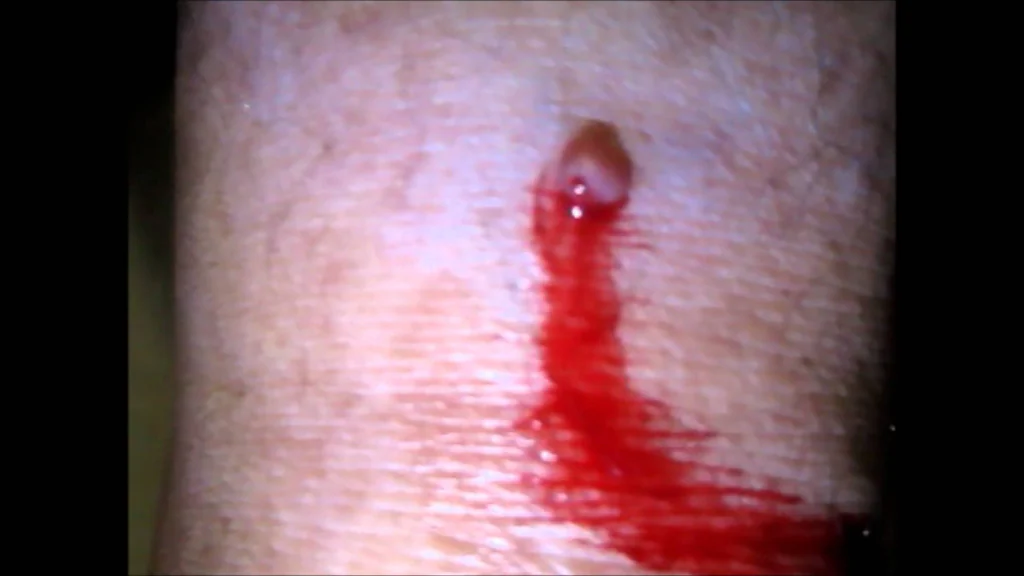
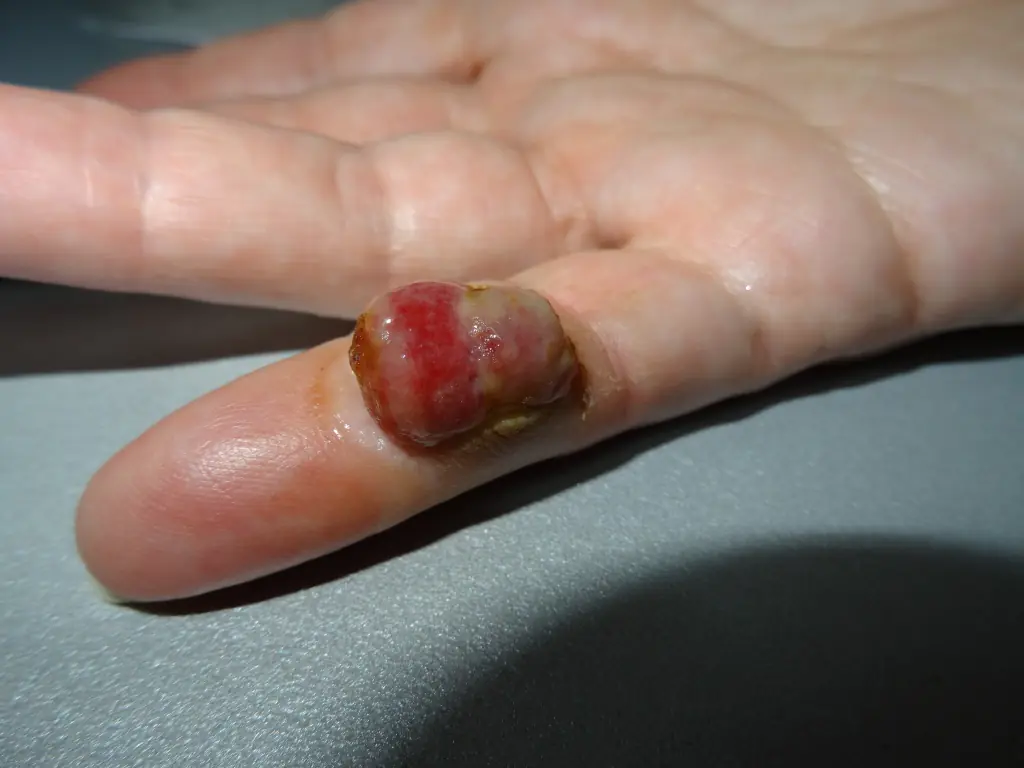
However, in my practice several times I came across a rather rare type of skin tumor - pyogenic granuloma. These formations appear very quickly, bleed, however, they are 100% benign:
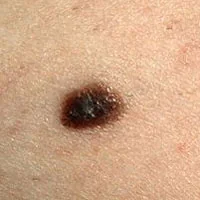
Sign 9 - “hair loss on the surface of the nevus.”
This sign may indicate that the mole has become malignant. If the mole is 5 mm or more and several hairs have disappeared from its surface at the same time and they do not appear. Moreover, if the same mole began to grow and doubled in size in 2 months, these are already 2 alarming signals at the same time and such a mole should be shown to an oncologist without delay.
In addition, I should note that in my practice once I encountered a melanoma, the surface of which was covered with hair.
At the same time, there are a huge number of moles, the surface of which is not covered with hair and at the same time they are completely benign. People also often panic if one hair grew from a mole and it suddenly fell out. Please do not despair - it should appear no later than in 2-3 weeks.
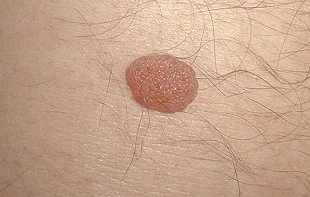
I wrote this article about hair on moles.
Sign 10 - “inflammation in the area of the nevus and surrounding tissues”
Redness and swelling of the tissue around the mole may be a consequence of melanoma cells growing into the surrounding skin.
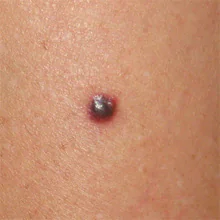
However, it must be remembered that in case of inflammation of the sebaceous gland, which is located under or next to the mole, “pimples” may form. If such a focus of inflammation is located next to a mole, you will see symptoms of inflammation - redness and soreness. How to distinguish a “pimple” from a sign of melanoma? It’s very simple - wait 1-2 weeks and it should go away on its own.
Inflammation of a mole is a common occurrence. I analyze it in this article
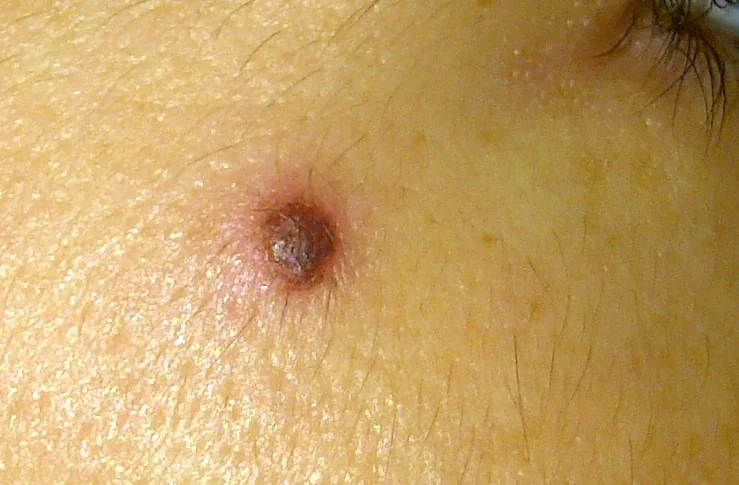
Sign 11 - “peeling on the surface of the nevus with the formation of dry crusts”
Yes, the surface of melanoma (or basal cell carcinoma) may be covered with crusts that form due to weeping or bleeding. And this is a truly alarming sign.
At the same time, there is another type of neoplasm - keratopapillomas (keratomas). Crusts regularly appear on the surface of such formations, which then fall off.
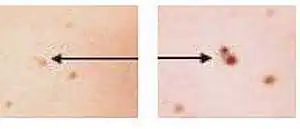
Sign 13 “the appearance of daughter pigmented or pinkish formations (satellites) in the skin around the nevus”
In later stages, melanoma can give intradermal metastases, which appear as black formations around the primary tumor focus.
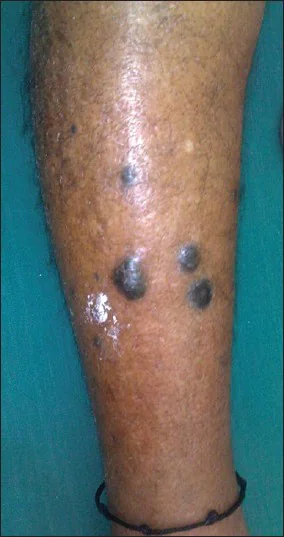
At the same time, very often people mistake for this symptom the usual appearance of a new mole next to an existing one. In the vast majority of cases there is nothing wrong with this:
Sign 14 - “change in the consistency of the nevus, determined by palpation, i.e. its softening or loosening”
Unfortunately, I cannot comment on this sign. All melanomas encountered in my practice were quite dense and none of the patients noted softening.
Sign 15 - “the appearance of a shiny glossy surface of the nevus”
Melanoma cells refract and reflect light rays in a special way. The consequence of this may be the appearance of a glossy surface on the mole.

At the same time, there is a separate type of skin tumors - blue nevi. These moles very often have a glossy surface and are completely benign:
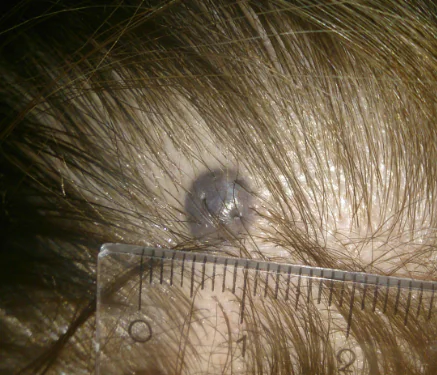
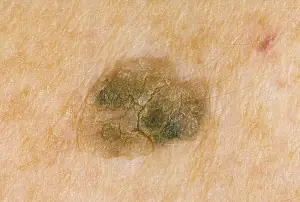
Sign 16 - “disappearance of the skin pattern on the surface of the nevus”
Most often, there is no skin pattern on the surface of melanoma. This is due to the fact that tumor cells lose their normal functions and engage in only one thing - constant division. As a result, after the mole degenerates, the skin pattern disappears.
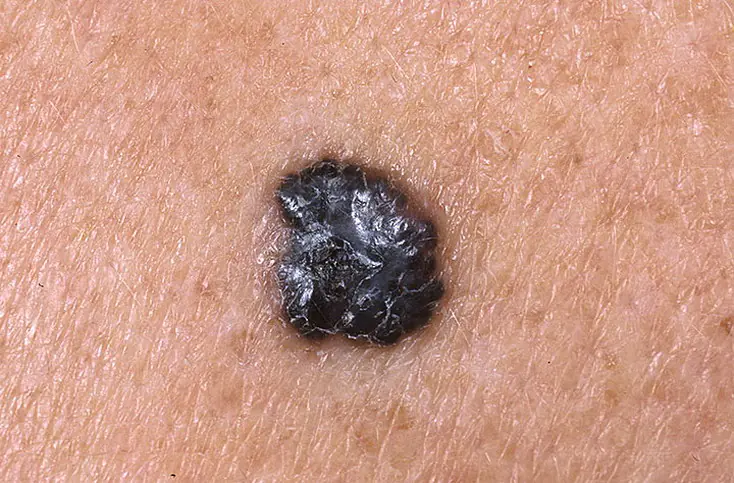
At the same time, there are a huge number of benign moles on the surface of which there is no skin pattern:
I don’t see any point in further detailed analysis of all the signs. All of them can be interpreted in two ways - both in favor of melanoma and in favor of benign changes. Only the presence of two signs at once or the rapid onset of changes can indicate a malignant mole.
I think that I was able to clearly show you that each of these signs separately cannot clearly indicate melanoma.
Briefly about the main thing:
Don’t panic if, after reading horror stories on the Internet, you find yourself with a sign of melanoma! Most likely everything is fine.
The presence of only one of the 16 symptoms is very unlikely to indicate a malignant mole. Each of them individually can occur in benign neoplasms.
If a symptom develops over several months, you should definitely see an oncologist.
The likelihood of melanoma is very high if there is more than one sign - in this case, be sure to see an oncologist. You should also come to this doctor if you have even the slightest doubt that your mole is benign.
If you still have questions, the following will help you:



