After surgery, a scar remains on the body - an area of connective tissue. Existing methods for getting rid of unsightly marks on the skin are varied. Therefore, the question of how to remove a scar after surgery should be preceded by a brief excursion into the typology of scars. The reasons for differences in the effectiveness of the same products are due to different characteristics of postoperative skin damage.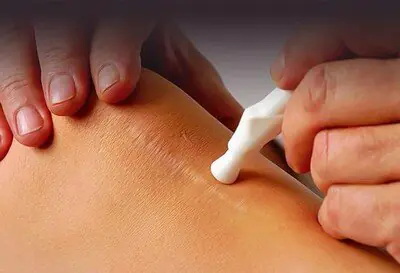
How are different types of scars treated?
Many methods of treating scars are available to specialists in medical and cosmetic clinics. To choose a method for removing scars after surgery, you first need information about the type of damage. It is necessary to diagnose the condition of the patient’s skin and the whole body.
Features of scar correction
| Types of scars | What they look like | How to remove a scar after surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Physiological (normotrophic) | It is located at or slightly below the rest of the skin. | -Sometimes it becomes invisible without treatment. -Silicone film or plate. -Light massage after healing of the incision with oils and creams. -Superficial peeling with fruit acids. |
| Atrophic | Pulled into the skin. | -Start treatment as early as possible. -Chemical peeling. -Use of dermal fillers. -It is not recommended to operate. |
| Hypertrophic | Dense to the touch, rises above the skin. | -Silicone plates. -Ointments with enzymes, hormones. -Microdermabrasion. -Laser resurfacing. -Surgical treatment (surgical excision, plastic surgery). |
| Keloid scar | Significantly rises above other areas of the skin. Causes itching, burning, pain. | -Difficult to correct. -Electrophoresis with hydrocortisone, lidase. -Injections of steroids into the scar area. -Ointments with enzymes, hormones. -Surgical methods can stimulate enlargement and relapses. |
How to remove scars on the stomach?
Minimally invasive surgery has almost eliminated the side effects of surgical interventions in the form of long and wide scars. With a gentle technique, almost no traces of punctures remain. If scars after laparoscopy are properly cared for from the very beginning, the cosmetic effect will be excellent. Much depends on where the punctures are made. Typically, during laparoscopy, the doctor makes 3-4 small holes (about 1 cm or less):
- 1 - below the navel for introducing a mini-video camera into the abdominal cavity.
- 2–4 - in the lower abdomen for introducing microsurgical instruments.
Caring for punctures after laparoscopy is carried out in two stages and includes measures aimed at preventing the formation of scars:
- Applications with a substance that stimulates healing (Curiosin gel).
- Lubrication with a drug that softens scar tissue (Kontraktubeks gel).
Removing a scar on the abdomen after surgery
| Correction methods | What actions are performed | What is the expected effect | How many procedures are recommended? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical excision | Removal, application of cosmetic suture. | Elimination of scar and deformation. | 1 |
| Chemical peels | Treatments with solutions of AHA acids. | Scar surface smoothing, whitening, exfoliation. | 1–8 |
| Microdermabrasion | Treatment of the scar with aluminum oxide powder, grinding the surface. | Elimination of small scars. | 1–10 |
| Laser resurfacing | Administration of glucocorticoids to the keloid. | Reduction of scars. | |
| Physiotherapeutic treatment | Various procedures | Softening scars. | 5–15 |
| Hormone therapy | Administration of glucocorticoids to the keloid. | Reduction of scars. | |
| Silicone pads and other medicines containing silicone | Use simultaneously with drugs for resorption of scars after surgery. | Scars become soft, flat, and elastic. | |
| Application of ointments | Applying to problem areas. | Flattening and normalization of scar color. |
Video about keloid scars after surgery
Cicatrix cream from the Spanish company Catalysis (test results)
The most affordable remedies for scars after surgery - special creams and ointments - promote resorption and healing of scars. Such medications are varied, but their methods of use have much in common. Basically, it is necessary to apply the ointment to postoperative skin lesions 1–2 times a day and continue the course of treatment for at least 8–10 weeks.

Visible results from using the Cicatrix restorative cream from the Spanish company Catalysis appear after 3 weeks (on fresh scars). In 2007–2010, medical centers in Western Europe and Russia assessed the effectiveness of Cicatrix cream in a group of patients with fresh scars. Here are the results of the study published by the Testing Laboratory Center of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Data from the testing laboratory of special dermatological products of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences
The researchers explained the positive results of using Cicatrix cream by the synergistic effect of the interaction of the components:
- Asiatic and madecassonic acids in the Asian centella extract stimulate the activity of fibroblasts and improve microcirculation.
- Pine extract (Pinus sylvestris) has antioxidant properties far superior to vitamins E and C. Prevents collagen destruction.
- A unique lipid complex of ceramides and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid retain moisture.
The restorative drug "Cicatrix" promotes proper wound healing by resorption and reducing the formation of scar tissue. The synthesis of collagen types I and III is activated, which compensates for the lack of the main building material of the skin. Cicatrix cream reduces chronic inflammation in damaged tissues and ensures normal epithelization.

After any surgical intervention, scars remain on the skin. They have their own classification, which involves the use of one or another method of getting rid of scars. Modern cosmetology has effective ways to solve the problem.
Read in this article
Features of various scars
Before choosing a method for getting rid of a stomach scar, you need to understand what it is. In official medicine, the following classification is accepted:
- Physiological. Such a scar is located at the level of the surrounding skin or slightly below. The second name for such scars is normotrophic; they often disappear on their own, but in some cases a complex of gentle cosmetic procedures may be necessary.
- Atrophic. The scar strip appears as if drawn into the skin. Getting rid of the scar will be difficult, but non-surgical. If treatment is started at an early stage of scar formation, then chemical peels will be sufficient.
- Hypertrophic. It rises above the entire surface of the skin and can be removed using aggressive methods - laser resurfacing, plastic surgery, excision, and the use of silicone plates.
- Keloid. In the most severe case, the scar not only rises greatly above the level of the skin, but also gives the person discomfort - itching, pain, a feeling of heaviness and numbness. It is very difficult to correct and will require the use of aggressive methods.
And here is more information about methods of removing scars on the face.
Ointments and creams
Special products offered on the market to get rid of scars are the most popular method of solving the problem. Despite the different names and stated quality characteristics, they are used in the same way: postoperative scars are lubricated 1 - 2 times a day for at least 8 months.
The main advantage of any topical treatment is the small number of contraindications compared to peelings, laser resurfacing and surgical scar removal.
The most effective drugs in this category are:
- Contractubex. Used to get rid of fresh and old scars. Apply 2 times a day. If you are treating an old scar, then when applying in the evening you need to cover the treatment area with a gauze bandage.
Contractubex gel can be used by people of any age, including children. During the treatment period, it is necessary to prevent direct sunlight from coming into contact with the scar. The only contraindication to the use of the gel is individual intolerance, hypersensitivity to its components.
- Zeraderm. This is a silicone gel that can be used immediately after the main wound healing and at the very beginning of scar formation. It also has a healing effect - it relieves a person from itching and pain.
Zeraderm can be used during pregnancy, immediately after childbirth and while breastfeeding.
- Dermatix. A cream that is applied 3 times a day to the scar with light massaging movements. The application layer is 0.5 cm, after 3 - 5 minutes the product is completely absorbed, there is no need to apply a bandage.
If Dermatix cream is started immediately after the scar has formed, the treatment can last only 2 months.
- Kelo-cat. Available in the form of a spray and gel; two pharmacological forms of the drug can be used simultaneously. Kelo-kot forms a protective film on the scar, which serves as an anti-inflammatory agent. This drug can be used by people of any age, it remains effective even if the person is on the beach.
Kelo-kot has practically no contraindications; after it is absorbed, you can apply sunscreen on top and get a tan.
- Mesoderm. A fairly aggressive drug, but it has a more gentle effect on scars than chemical peeling and laser resurfacing. It can be used during pregnancy and lactation, but there are contraindications for the treatment of abdominal scars in childhood.
Mesoderm with long-term use (more than 3 months in a row) can cause side effects - burning, small rashes, tingling at the site of application. It is advisable to refuse further use of the product and contact a cosmetologist or dermatologist to correct the therapeutic regimen.
Scar injections
Only 2 groups of drugs are used to treat scars:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- enzyme agents.
Longidase injections are most often given is an enzyme preparation that helps quickly get rid of hypertrophic scars. Injections are performed once daily, the course is 10 - 15 procedures.
Long-acting corticosteroids are often used. These include Diprospan, Kenalog. Immediately after the administration of these drugs, the scars become softer and less pronounced, itching and pain disappear. The course of therapy is determined individually, the doctor monitors the condition of the scar, but usually 5 injections are performed with an interval of one and a half to two weeks.
Experts recommend a cryodestruction procedure before starting injection therapy. This is the name for the effect of liquid nitrogen on the scar - the collagen fibers of the scar are treated at low temperatures and begin to degenerate. Typically, this is done as follows: apply liquid nitrogen to the scar for 60 seconds, then wait for the treated area to thaw and immediately inject a corticosteroid.
Scar injections are very effective, but can cause unpleasant side effects:
- menstrual irregularities;
- lightening of the skin at the injection site;
- increased body hair growth;
- atrophic processes in the skin.
Watch the video about the treatment of keloid scars with Diprospan:
Grinding
This refers to chemical peeling, which is carried out using products based on organic acids. This procedure should be carried out in a beauty salon or specialized clinic, because it is important to strictly follow the algorithm for its implementation.
Chemical peeling does not always guarantee the removal of a scar, but it will make the scar less noticeable, pale, and almost smooth.
You can carry out the polishing procedure at home using professional cosmetics. They contain only fruit acids, which are gentle on the dermis. This treatment will make the scar less noticeable, but will not remove it.
Disguise with a tattoo
If the scar on the abdomen is whitish or bluish in color and does not protrude too high above the surface of the surrounding skin, then a biotattoo can be made. This is a procedure during which a special coloring pigment is injected into the scar, which makes it evenly colored compared to the entire dermis.
A radical solution to the problem is to perform a full-fledged tattoo directly on the scar.. This is not contraindicated by doctors, it helps to turn a defect in the body into a kind of decoration, and relieves a person of complexes. A full-fledged tattoo visually smoothes the skin texture at the site of the scar and makes it almost invisible to others.
Physiotherapy
To get rid of scars, three types of physiotherapy are used - phonophoresis, laser phoresis and electrophoresis. They are used to deeply inject medications directly into scar tissue. In combination with Logindaza or glucocorticosteroids, it is possible to obtain positive results after just 15 procedures.
Each physiotherapy procedure lasts 2 - 8 minutes and is carried out 2 times a week. Thanks to this, medications remain in the thickness of the scar constantly and have a resolving effect on it.
Separately, radio wave therapy can be performed - a physiotherapy procedure that helps get rid of retracted scars. Each procedure lasts no more than 15 minutes, the therapeutic course is 4 exposures to radio waves at intervals of 2 weeks. This physical procedure is painless, perfectly “tightens” the scar to the level of the surrounding skin and makes it almost invisible.
How to remove a scar on the stomach in the salon and hospital
The most effective method of getting rid of stomach scars is to contact a specialist. Ointments and gels, physiotherapy, chemical peeling will only visually hide the scar and make it less noticeable to others. But if you want to get rid of the problem, then you should resort to more radical methods.
Laser
A laser beam can remove a scar on the abdomen without the use of surgical instruments or general anesthesia. Most often, this method is used to solve problems after cesarean section. The only “inconvenient” nuance is that the gels used for local anesthesia penetrate the woman’s bloodstream, so the procedure is prohibited during breastfeeding.
Corrective laser procedures are carried out in a clinic or salon, but do not imply hospitalization of the patient. In order for the scar to become as invisible as possible, you will need 4 - 6 procedures at intervals of 1 - 2 weeks.
Watch the video about laser scar removal:
Surgical excision
Excellent for old, already healed seams - no other methods will help in this case. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and has many contraindications – from heart and vascular diseases to inflammatory processes in the body.
During the operation, the scar tissue is excised with a surgical instrument, the edges of the skin are again compared and sutured with a cosmetic suture. The postoperative period involves going through all stages:
- daily dressings until primary wound healing;
- the use of anti-scar creams and ointments;
- conducting a course of chemical peeling.
Most often, surgical excision of a scar is used if its edges are uneven, the scar itself is too wide and convex or retracted in relation to the surrounding skin.
And here is more information about scars and their removal after acne.
Abdominal scars can be removed through medical, cosmetic, and surgical methods. In order not to make a mistake in choosing specific procedures, it is worth consulting a specialist. Most often, positive results can be achieved by combining several methods.
As is known, the formation of a scar after damage to the skin during injuries and operations is a biological pattern and is perceived by both surgeons and patients as an inevitable evil. For practice, it is important that the final formation of the scar is completed only 6-12 months after the operation is performed, and at the same time the quality of the scar begins to be assessed by the patient.
Surgical treatment of injuries or life-threatening conditions is one thing; then the surgeon first of all thinks not about the beauty of the future scar, but about uncomplicated wound healing. In this case, as a rule, no complaints are made against the operating specialist, and this is generally fair.
Another thing is aesthetic surgery, when the main goal of the surgeon is to improve the patient’s appearance and minimize scars. By agreeing to the operation, the patient also agrees to the appearance of scars after it. But in this case, their characteristics become the most important indicator of the quality of the doctor’s actions, who, even before the intervention, is obliged to inform the patient in detail about the possible nature of future scars. This information allows the patient to agree or refuse the operation, and after it, if dissatisfied with the characteristics of the scars, to make a claim to the surgeon.
How does wound healing normally occur?
Wound healing is a biological process that lasts about a year and ends with the formation of a mature scar. However, subsequently the tissues that form the scar can change, although to a minimal extent.
Stage 1 of healing – postoperative inflammation and epithelization of the wound (1-10 days after surgery). A distinctive feature of this stage is the connection of the edges of the wound with granulation tissue, and not with a scar. Therefore, when the sutures are removed on days 7-10, the wound can easily open under the tension of the surrounding tissues. To obtain a minimal scar width in the future, this tension must be eliminated or neutralized by applied sutures.
Stage 2 – active fibrillogenesis and the formation of a fragile scar (10-30 days after surgery). Young granulation tissue quickly matures, which is accompanied by a decrease in the number of vessels and cellular elements, on the one hand, and an increase in the number of collagen and elastic fibers, on the other. At the end of this stage, the edges of the wound are already connected by a young, fragile scar, which is relatively easy to stretch and is clearly visible due to the large number of vessels it contains.
Stage 3 – formation of a durable scar (30-90 days after surgery). The number of fibrous structures in the scar increases significantly, and their bundles acquire a certain orientation in accordance with the dominant direction of load on the scar. The number of cellular elements and vessels in the scar tissue is significantly reduced, the scar becomes less bright and less noticeable. During this phase, external forces have a significant influence on the characteristics of the scar. Thus, with longitudinal stretching of the scar, additional formation and clearer orientation of collagen and elastic fibers occur in its tissue, and to a greater extent, the stronger the stretching. If in a patient the processes of fibrillogenesis are initially enhanced and prevail over collagenolysis, hypertrophic and even keloid scars may form, regardless of the direction of stretching.
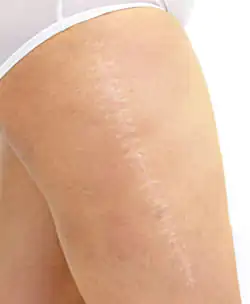
Stage 4 – final transformation of the scar (3-12 months after surgery). It is characterized by increasingly slow maturation of scar tissue with the almost complete disappearance of small blood vessels from it. The scar fades even more. It is important to note that in most cases, it is in the middle of the 4th period (usually after 6 months) that skin scars can be assessed as formed and the possibility of their correction can be determined.
What determines what the scar will be like?
The external characteristics of the scar are influenced primarily by the following factors:
- the location of the wound and, in particular, the degree to which its long axis corresponds to the force lines of the skin (in short, along wrinkles and natural folds the scar will be thinner and less noticeable);
— method of surgical wound closure and the quality of its implementation, including the experience of the surgeon;
— efficiency of drainage (for extensive and complex-shaped wounds).
The patient’s age, immune status, and heredity play a role.
As a rule, scars normally do not cause any physical sensations in their owner. The appearance of signs of tissue irritation in the scar area (tingling, burning) is typical for hypertrophic (protruding above the skin), and especially for keloid (overgrown) scars. But unpleasant subjective sensations acquire practical significance only if they reduce the patient’s quality of life. In such cases, treatment is indicated - scar correction.
Treatment of scars after surgery
In recent years, many attempts have been made to find a way to non-surgically correct scars: from injections of aloe or vitreous to topical treatment of scars with pepsin with hydrochloric acid, thiosinamine, salicylic acid, hydrocortisone and its analogues, or creazote oil. Unfortunately, neither approach showed significant results.
But it still makes sense to use additional methods that improve the quality of scars in the postoperative period. First of all - peace and absence of irritating movements. Under resting conditions, a scar of smaller volume and with more favorable characteristics is formed. It would be advisable to fix the edges of the sutured wound with strips of adhesive plaster, which can well keep this area of skin from stretching for quite a long time (up to 2-4 weeks). This will prevent early expansion of the developing scar. Depending on the specific conditions, the patch strips can be used during the entire period of formation of a durable scar (3-6 months from the date of surgery). They are changed by the patient himself when the patch begins to peel off. In this case, the skin should be washed with soap, wiped dry and sealed with a new strip of plaster. If signs of irritation appear on the skin, stop using the patch until the skin condition is completely normalized.
In order to improve the quality of scars during their formation, special silicone coatings, silicone plates, patches and medicinal gels can be used (for example, Contractubex to prevent the formation of pathological scars).
If signs of hypertrophic or keloid scar formation appear, therapeutic methods such as injection injection of glucocorticosteroids into scar tissue (drug "Kenalog-40").
Unfortunately, the personal experience of every surgeon indicates that it can be difficult, and sometimes impossible, to achieve a significant effect in the correction of scars even through surgery. At this stage of development of medicine, its methods are not able to completely eliminate the scar, or radically influence the general mechanisms of the formation of human scar tissue. The surgeon has the opportunity to exclusively locally influence individual characteristics of the scar, and often with very limited effectiveness. The doctor can only excise the scar and sew it up again, this time in a more qualified manner. For large scars, transplant a skin flap or use dermotension to create excess skin and cover the scar with it.
The doctor makes a decision about scar correction only after assessing the likelihood of treatment effectiveness. A positive decision is made by the surgeon after obtaining the patient’s informed consent, taking into account his psychological status and realistic expectations. An important role in this process is played by detailed informing the patient about the future appearance of the scar with demonstration of similar scars on the monitor screen.

When a surgeon, for one reason or another, cannot offer the patient surgery to improve the quality of the scar, a way out can sometimes be applying a camouflage tattoo to a scar. But this solution is not suitable for everyone, although it is used quite often. And in some cases, tattooing gives excellent results, since the scar is replaced by decoration. But you shouldn't get a tattoo on your cesarean scar if you're going to have another child.
If surgical excision of the scar is not necessary, you can try to smooth the surface of the scar using conservative methods.
Conservative correction of tissue relief disorders in the scar area
A scar is noticeable not only because its tissue differs in appearance from the surrounding skin. Very often, the leading role in the occurrence of an aesthetic defect is played by disturbances in the relief of tissues. It is the unevenness in the damaged area that can make even a small scar more noticeable and thereby significantly worsen the aesthetic characteristics of the appearance. How to make a scar less noticeable?
Disturbances in the microrelief of the scar can be corrected by medicinal, physiotherapeutic methods and biological fillers.
Medicines to make the scar less noticeable
Corticosteroids. Intraruminal steroids remain the mainstay of scar treatment. Corticosteroids reduce scar formation by reducing the synthesis of collagen, glycosaminoglycans, inflammatory mediators, and fibroblast proliferation during wound healing. The most commonly used corticosteroid is triamcinolone acetate at a concentration of 10-40 mg/ml Kenalog, administered into the injured area by needle injection at intervals of 4-6 weeks. The effectiveness of such an introduction as a monomodel and as an addition to the scar excision procedure is very high. Topical corticosteroids are also widely used, which are applied daily directly to the formation. Complications of corticosteroid treatment include atrophy, telangiectasias, and pigmentation disorders.
Immunomodulators. A new method in the treatment of keloid and hypertrophic scars is interferon therapy. Interferon injected into the suture line after excision of a keloid scar can prophylactically prevent relapses. It is recommended to administer 0.5–1.0 million IU every other day for 2–3 weeks, then 0.1–0.5 million IU 1–2 times a week for three months.
Drugs that reduce hyperproliferation of connective tissue cells. A classic remedy for the treatment of scars is hyaluronidase; it breaks down the main component of the interstitial substance of connective tissue - hyaluronic acid, which is a cementing substance of connective tissue, and thus increases tissue and vascular permeability, facilitates the movement of fluids in the interstitial spaces. Hyaluronidase reduces tissue swelling, softens scars and evens out their surface, preventing the formation of scars. Preparations containing hyaluronidase: Lidaza and Ronidase. Lidase solution (1 ml) is injected near the site of the lesion under the skin or under scar tissue. Injections are made daily or every other day; the course of treatment consists of 6–10–15 or more injections. If necessary, repeat courses are carried out at intervals of 1.5–2 months.
Another enzyme-based drug is Longidaz a. "Longidase" is a chemical compound of hyoluronidase with polyoxidonium. The combination of the enzymatic activity of hyaluronidase with the immunomodulatory, antioxidant and moderate anti-inflammatory properties of polyoxidonium provides a wide range of pharmacological properties. It is most effective to use the drug "Longidaza" by ultraphonophoresis or phonophoresis. For ultraphonophoresis, Longidase 3000 IU is diluted in 2–5 ml of gel for ultrasound therapy. The impact is carried out with a small ultrasonic emitter (1 cm 2), with an ultrasound frequency of 1 MHz, intensity 0.2–0.4 W/cm 2, in continuous mode, exposure time 5–7 minutes, course of 10–12 procedures daily or every other 1 day. Using the phonophoresis method (1500 Hz), 3000 IU of Longidase is administered daily (total exposure time 5 minutes, course - 10 procedures). It is also possible to administer the drug inside the scar:
— for small keloid and hypertrophic scars: Longidaza 3000 IU once every 7 days for a total course of 10 injections into the scar;
- for keloids and hypertrophies with a large area of damage: Longidase 3000 IU 1 time in 7 days inside the scar in a course of 8-10 injections, at the same time intramuscular administration of Longidase 3000 IU No. 10.
A well-known drug that inhibits the pathological proliferation of connective tissue cells and at the same time has an anti-inflammatory effect is the Contractubex gel. "Contractubex" is used in surgery and cosmetology in the treatment of postoperative and post-burn scars, including rough scars that impede movement and keloids, as well as stretch marks (striae) after childbirth or after sudden weight loss. Apply to the scar area, 0.5 cm of gel on a scar surface with an area of 20-25 cm² on average 2 times a day.
An enzyme preparation of 9 collagenolytic proteases, Fermenkol cream is a fundamentally new proteolytic preparation. The anti-scar effect of Fermenkol is based on the reduction of excess extracellular matrix in scar tissue.
The effect when using anti-scarring agents is observed approximately 3 weeks after the start of use of the product and the optimal result is usually achieved after 2-3 courses of electrophoresis or phonophoresis, 10-15 sessions or applications for 30-60 days.
Physical and physiotherapeutic procedures to make the scar less noticeable:
Resurfacing will give a positive result for small superficial scars or pinpoint scars due to the consequences of acne. A scar with a smooth surface is much less noticeable than a scar with micro-elevations or depressions.
Laser grinding. The surface treated with a laser beam becomes smoother after epithelialization. Laser resurfacing has all the advantages due to the selectivity and precision of its impact on small areas of the skin (up to 1 sq. mm). The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia, since local administration of even a minimal volume of anesthetic solution can radically change the surface texture of the skin in the scar area. A surgical erbium laser is used. Epithelization of the treated surface occurs within 5-7 days.
Cosmetic procedures, aimed at external correction of the defect (peelings, mesotherapy, dermabrasion) do not give a noticeable result on large scars, but they can make small scars less noticeable.
Silicone plates and bandages. Allows you to smooth the surface of a small scar. Ineffective on hypertrophic scars and keloids.
X-ray therapy (Bucca rays). It is based on the action of ionizing radiation on connective tissue, causing swelling and destruction of collagen fibers and fibroblasts. X-ray therapy is prescribed up to 6 radiation sessions with an interval of 6–8 weeks at a single dose of up to 15,000 R.
Cryosurgery. Cryosurgical agents, such as liquid nitrogen, attack the microvasculature and cause cell death through the formation of intracellular crystals. Typically, 1–3 freeze-thaw cycles of 10–30 seconds are sufficient to achieve the desired effect. It is used only for hypertrophic and keloid scars.
With a formed scar with a duration of up to 12 months, it is possible to carry out treatment with all methods, and with a long-existing scar (more than 12 months), only aggressive methods are effective: injection of corticosteroids into the affected area, excision, radiation therapy, Bucca therapy, laser therapy.
Severe disturbances in the relief of the skin surface in the scar area are clearly visible and are most often caused by the following reasons:
1. Inaccurate comparison of the edges of the wound when applying sutures. Small inaccuracies will smooth out over time. In other cases, surgical correction with precise alignment of the wound edges is necessary.
2. Reducing the fat layer at the level of the scar with its deepening. Options to solve the problem:
- liposuction of the tissues surrounding the scar (fat tissue next to the scar is removed),
— lipofilling in the area of the depression (a layer of adipose tissue is added under the scar),
- introduction of gels and other fillers (the effect is good, the disadvantage is that the gel can migrate and is gradually eliminated from the body),
- plastic with local fabrics.
3. A deep tissue defect at the level of injury, forming a significant depression. Here, depending on the conditions, tissue complexes with a non-axial type of nutrition (on a wide tissue pedicle), as well as island or free flaps can be used.
Moving the scar to a hidden area
The surface of any scar differs from normal skin, and the severity of this problem is most pronounced when the scar is located on open areas of the body. In the vast majority of cases, it is impossible to move the scar to another place, however, there are exceptions to this rule. Thus, during plastic surgery of the anterior abdominal wall, the removal of a significant area of skin along with the scars located on it (for example, after surgery for appendicitis, interventions on the abdominal and pelvic organs) leads to the fact that a new horizontal scar is located in an already relatively hidden area - in the lower abdomen. A prerequisite for performing such operations is the presence of significant excess skin on the abdomen (for example, in women who have given birth).
An important argument in the patient’s consent to surgery is the simultaneous improvement in the shape of the torso.
In general, normotrophic (properly healed) scars generally do not require surgical correction, unlike hypertrophic (protruding) and keloid scars.
Correction of hypertrophic scars

In order to reduce the width of the hypertrophic scar (along with excision), to eliminate functional limitations and reduce unpleasant subjective sensations, it is used z-scar plastic surgery. Due to the fact that the main local cause of hypertrophy of scar tissue is longitudinal stretching of the scar, the main principle of its surgical correction is to change the direction of the scar through plastic surgery with opposing triangular flaps, also known as z-tissue grafting. The scar is excised and triangular flaps are formed along each edge of the wound, after moving which the wound takes on a zigzag shape. When the shape of the wound changes, it lengthens, which sharply reduces the influence of the longitudinal stretch factor. At the same time, a compensatory counter movement of the edges of the wound occurs, which increases their tension in the transverse direction.
Injections of the drug "Kenalog-40" with lidocaine into the tissue of the developing scar have a direct effect on the mechanism of scar formation, reducing the intensity of fibrillogenesis. It is advisable to start administering the drug from the 3rd week after the operation, the effect will be most pronounced. However, even at a later date you can get a good effect. The course of treatment is 3-4 injections, which are repeated at intervals of 5-7 days. Possible complications - when the drug spreads to the tissues adjacent to the scar, atrophy of the subcutaneous fatty tissue and skin may develop with the formation of depressions.
For small hypertrophic scars, conservative treatment is used - the above listed physical and physiotherapeutic methods, medications.
Correction of keloid scars
Due to the fact that the main reason for the formation of keloid scars is the body’s abnormal reaction to injury, expressed in a special course of wound healing processes with the formation of a keloid, attempts to influence a keloid scar only by surgical methods, unfortunately, are ineffective.
If we talk about excision of keloid scar, then it is possible, but only if the surgeon has sufficient knowledge and practical skills.
The most effective treatment method in this case is injection into the scar tissue drug "Kenalog-40", which allows you to significantly reduce the volume of the outer part of the scar (sometimes to normal size). In the postoperative period, an additional course of glucocorticosteroid therapy is advisable in all cases.
Can also be carried out locally X-ray therapy (Bucca rays), which in itself can give positive results in the treatment of keloid scars.
Can also be used in the complex treatment of patients with keloid scars. gel "Kontraktubeks" and balneotherapy.
Of great importance immobilization of keloid scar, including the use of special silicone coatings.
Thus, at present, keloid scars remain one of those diseases for which treatment with known methods is not sufficiently effective.
One can only hope that in the near future medicine will find ways to influence these processes so that they result in the formation of normal tissue.



