
Causes and symptoms of scleroderma. Stages of the disease, diagnosis. Basic methods of treating scleroderma with medications and folk remedies. Doctors' recommendations.
The content of the article:- Causes
- Main symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
Scleroderma (from “sclerosis” - “hardening”, “dermis” - “skin”) is an inflammatory disease characterized by hardening of the skin and blood vessels with the formation of constricting scars in them. In addition, the disease can affect several internal organ systems (almost the entire body).
Causes of scleroderma
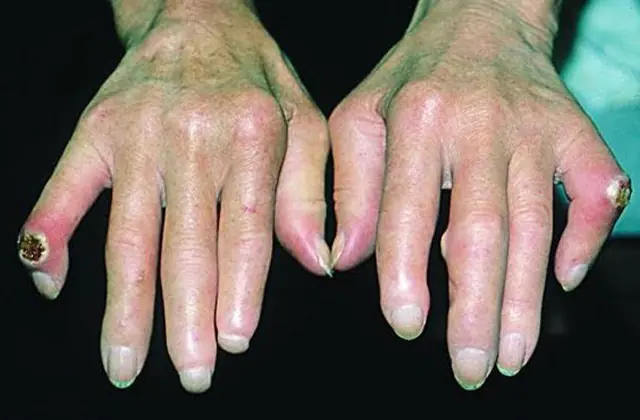
The photo shows systemic scleroderma
It is still unknown exactly what causes scleroderma, but the disease belongs to the group of autoimmune pathologies. The basis of all disorders is the incorrect reaction of the body's immune cells.
With scleroderma, there is a decrease in the level of T-suppressors - this is a class of lymphocytes that prevent the attack of their own cells. When there are few of them, the body begins to destroy everything, not distinguishing “its own” from “theirs.” This happens due to the production of antibodies (immune particles) directed at connective tissue cells. Connective tissue is fibers made of strong proteins (collagen, fibrin) that make up the frame of any organ and its outer shell. The favorite site of the inflammatory reaction in scleroderma is the lining of small blood vessels.
There is an assumption that autoimmune disorders trigger viral diseases, that is, viruses irritate the immune system, which secretes antibodies against them. After the pathogen is destroyed, antibodies in the body are preserved and begin to act not against the virus, which no longer exists, but against the cells in which it previously lived (viruses can only exist in cells).
Scleroderma is also considered a hereditary disease. It is not the disease itself that is transmitted, but a certain type of immune system response.
Important! Scleroderma can be triggered by cold, trauma, vibration, chemicals, allergies, nervous disorders and hormonal imbalances.Main symptoms of scleroderma
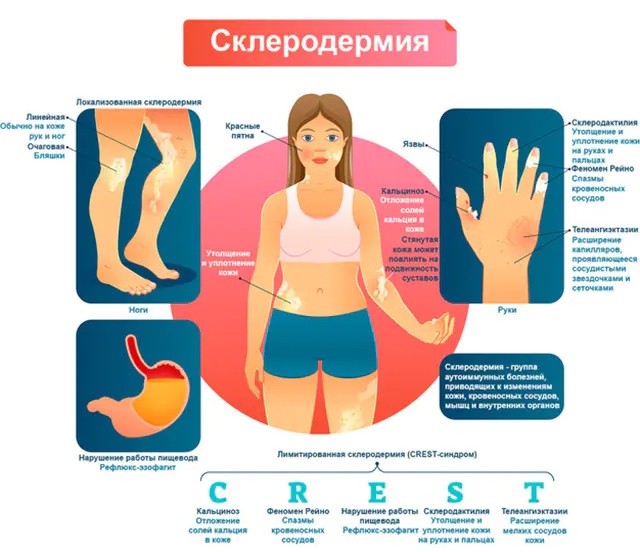
The photo shows the symptoms of scleroderma
The disease has external and internal symptoms. If only the skin is affected, then it is focal scleroderma, and if additional symptoms of damage to internal organs occur, it is systemic scleroderma. The disease occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission (absence of obvious symptoms).
When the disease develops:
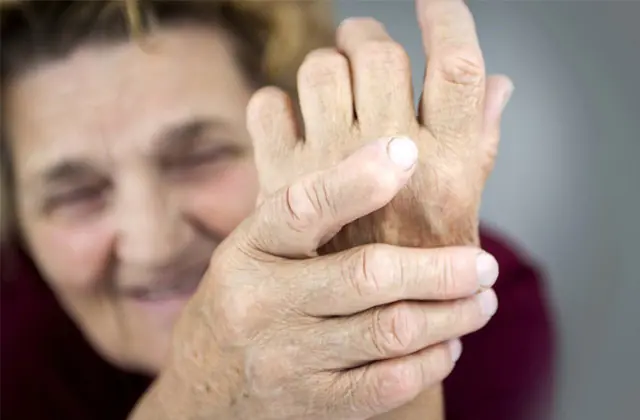
- Skin symptoms. Dense swelling appears on the face and hands, the mobility of the fingers is impaired, they become shorter, the nails become deformed, and ulcers appear. Baldness is also typical. Skin symptoms on the hands are symmetrical. There is pain when touched. Areas with pigment spots and lesions appear on the skin of the face where the skin is whiter than its normal tone. Dilated capillaries are visible on the face, chest, lips.
- Damage to mucous membranes. It manifests itself as watery eyes and redness of the eyes, chronic runny nose, painful sores in the mouth, cough and sore throat.
- Raynaud's syndrome. This syndrome develops when exposed to cold. The blood vessels in the skin of the fingers react - they sharply narrow. As a result, the fingers become cold, pale, even with a bluish tint, pain, numbness, and “goosebumps” occur. Such sensations with scleroderma occur on the feet, face, lips and even the tip of the tongue. After the end of the attack, all phenomena disappear.
- Arthritis. The articular membrane is also connective tissue, so violent inflammation occurs in it, which manifests itself as pain in several joints at once, especially small ones, and thickening of the periarticular soft tissues. Flexion and extension in the affected joints are impaired, but, unlike other forms of arthritis, the joint itself is not destroyed. The small bones of the fingers and toes are also affected. The bone tissue is partially destroyed, so the fingers become shorter and deformed.
- Myositis. Scleroderma causes damage to the tissue that is included in the muscle fibers (intermediate tissue), resulting in pain, muscle weakness and a feeling of stiffness. Soft tissues tend not only to harden, but also to calcify. This occurs due to the accumulation of calcium in the finger area. Foci of lime accumulation appear through the skin in the form of white lumps.
- Digestive disorders. Digestion is already disrupted at the level of the esophagus, which is manifested by difficulty swallowing, heartburn, and ulcers can form in the mucous membrane. Constipation and bloating are also common.
- Pulmonary symptoms. Scleroderma is manifested by frequent pneumonia, shortness of breath, cough, and attacks of suffocation.
- Heart symptoms. The disease causes heart failure, inflammation of the heart muscle and heart defects. All this is manifested by cardiac arrhythmia, shortness of breath, palpitations, general weakness, and inability to perform daily physical activity.
- Kidney damage. Signs of kidney failure are detected during a urine test. Sometimes the only signs of scleroderma are high blood pressure and swelling.
- Neuropathy. The nerves of the upper and lower extremities are mainly affected, which is manifested by pain in the arms and legs along the nerves, and sensitivity is impaired.
- Hormonal imbalance. Insufficiency of thyroid hormones, sex hormones, and diabetes mellitus often develop due to insulin deficiency.
- Change your appearance. Characterized by general exhaustion and weight loss. Due to prolonged swelling, the face loses facial expressions, skin folds are smoothed out, wrinkles disappear. Overall, the face resembles a frozen mask. Due to the tension of the skin, the nose becomes pointed, reminiscent of a bird's beak.
The disease “scleroderma” goes through several stages, which correspond to the severity of the pathology:
- Initial. The patient experiences joint pain, Raynaud's syndrome, palpitations, frequent respiratory tract infections, and a constant feeling of cold.
- Generalized. All known symptoms of the disease appear.
- Terminal. It is characterized by profound changes in organs, with the development of their failure. The patient is exhausted.
Diagnosis of scleroderma
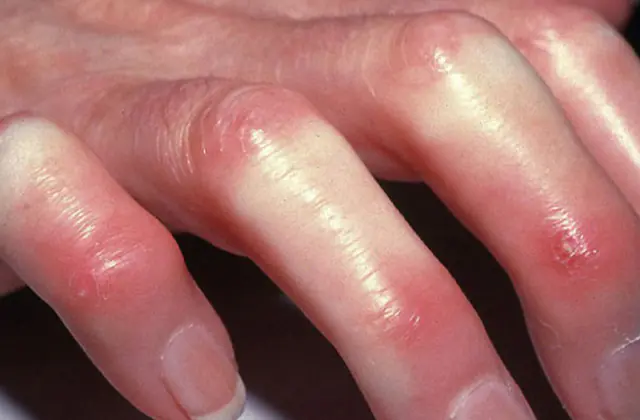
There are criteria by which you can find out that a person has scleroderma. Diagnostics is based on examination data, analyzes and instrumental research methods. Laboratory tests are also needed to determine the activity of the inflammatory process.
Methods for diagnosing scleroderma:
- General blood analysis- detects anemia (deficiency of red blood cells and hemoglobin), high level of leukocytes and increased ESR;
- General urine analysis- detects protein in the urine (a sign of kidney damage) and a special substance hydroxyproline, which is formed during the destruction of connective tissue;
- Blood chemistry— detects signs of inflammatory activity (high levels of CRP, seromucoid, fibrin), increased protein levels;
- Immunological blood test- characterized by the detection of antibodies to cell DNA (antinuclear antibodies) and scleroderma antibodies, as well as the presence of rheumatoid factor, low levels of T-lymphocytes;
- X-ray examination of bones, lungs, gastrointestinal tract— reveals structural changes due to the destruction of connective tissue;
- Electrocardiography- detects symptoms of heart muscle destruction, arrhythmia;
- Capillaroscopy- examination of small capillaries reveals a tendency of blood vessels to narrow (Raynaud's syndrome).
Diagnostic criteria for scleroderma include:
- Large criteria- symmetrical compaction and thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes. The lump may spread to the face, neck and torso.
- Small criteria- hardening of the fingers, changes in the finger pads (scars, retractions), bilateral replacement of lung tissue with scar tissue on x-ray (pneumosclerosis).
If 1 major and 2 minor criteria are present, then the diagnosis of scleroderma is considered reliable.
Methods for treating scleroderma
Treatment of the disease is effective at the initial stage, the person can fully recover. On the second, doctors manage to alleviate the symptoms. If it is already terminal scleroderma, treatment has no effect. The goals of therapy are to stop the thickening process, improve blood circulation and suppress autoimmune reactions. For this purpose, the appropriate groups of drugs are used - anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, vasodilators, immunosuppressants.
Medicines for the treatment of scleroderma
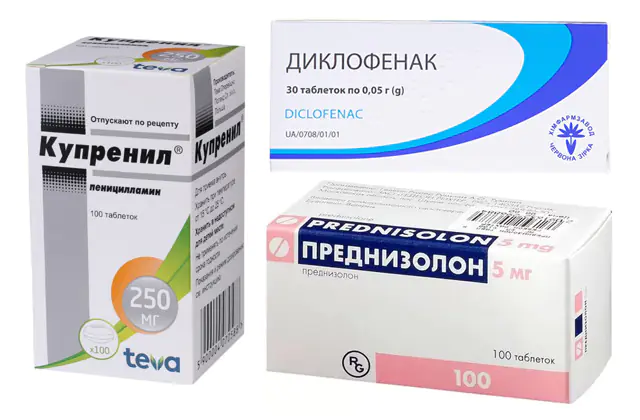
D-penicillamine is the main drug that inhibits the growth of scar tissue. This therapy is called antifibrotic. Taken in tablet form, long-term use is required. An analogue of the drug is Cuprenil. The price for a pack of 100 tablets is about 1,300 rubles (530 hryvnia)
To treat inflammation in scleroderma, drugs that suppress autoimmune reactions are used. These include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (non-hormonal), hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (corticosteroids) and immunosuppressants.
The main anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of scleroderma are:
- Prednisolone. Tablets cost from 190 rubles (37 hryvnia) for 5 pieces, ampoules - from 50 rubles (28 hryvnia). Analogue - Methylprednisolone.
- Diclofenac. The price for tablets is from 14 rubles (6 hryvnia). Analogues - Nurofen, Ketonal.
- Meloxicam. The price of tablets is 50 rubles for 20 pieces (20 hryvnia). Analogs of the drug - Aroxicam, Zelox, Melox.
- Methotrexate. Tablets cost 80-200 rubles (30-80 hryvnia). Analogs include Metotab and Methoject.
- Cyclophosphamide. The tablets cost 600-700 rubles (240-280 hryvnia). Analogues of the drug - Cyclophosphamide, Cytoxan.
- Mofetil. 50 tablets cost from 5,300 rubles (2,200 hryvnia). Analogues - Supresta, Maysept.
- Cyclosporine. The price ranges from 300 to 1200 rubles (120-500 hryvnia). Analogues - Tacrolimus, Sandimmune, Prograf.
To prevent circulatory disorders and deformation of the fingers, drugs are used that dilate blood vessels and also prevent their spasm, which is especially important for Raynaud's syndrome.
Vasodilator drugs approved for use in scleroderma include:
- Amlodipine. The price is 50-130 rubles per pack of 30 tablets (20-53 hryvnia). Analogs include Norvasc, Normodipin.
- Diltiazem. Price - from 85 to 270 rubles (35-110 hryvnia). Analogues - Cardil, Diacordin.
- Dipyridamole. Price - from 400 to 700 rubles (165-290 hryvnia). Analogs include Kurantil.
Folk remedies against scleroderma
If scleroderma has been diagnosed, folk remedies can help reduce the severity of the inflammatory process and alleviate skin symptoms. However, they only complement the main drug treatment of the disease, enhancing the effect of the drugs. Treating the disease with herbs alone is ineffective and dangerous.
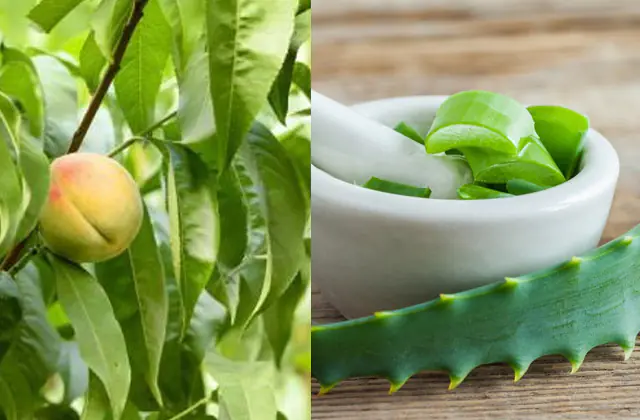

To treat scleroderma you can use:
- peach leaves. 1 spoon of dried leaves is crushed to a powder, poured with a glass of boiling water. Leave with the lid closed for 20 minutes, then filter, add a spoonful of honey, stir and drink (daily dose - 1 glass).
- Aloe. Aloe juice helps with skin symptoms, especially if there are sores. The leaves of the plant need to be ground to make a paste, then lubricate the affected area with it and cover with a gauze bandage.
- Herbal collection. You need to collect clover, chamomile, plantain leaves, immortelle, mint, raspberries, and lingonberries. All this is taken in equal portions (the herbs need to be chopped). Then 2 tablespoons of the collection are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water. After this, the broth should be kept in a thermos for about 10 hours, and then strained. Drink 50 ml of decoction for 3 months.
Video stages and symptoms of systemic scleroderma:



