Causes and types of pleurisy. Symptoms, diagnostic methods, procedural and drug treatment. Possible complications and prognosis for pulmonary pleurisy.
The content of the article:- What is pleurisy
- Main reasons
- Developmental symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Features of treatment
- Treatment methods
- Medicines
- Therapeutic procedures
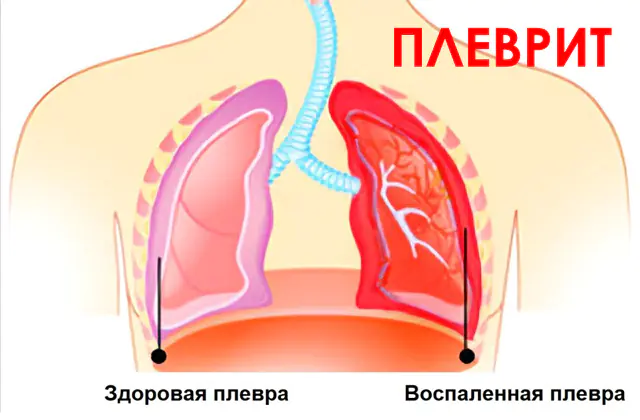
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the serous membranes lining the surface of the lungs and chest. Usually a secondary condition resulting from injury or infection. It responds well to treatment. If left unattended, it can lead to serious complications.
What is pleurisy?
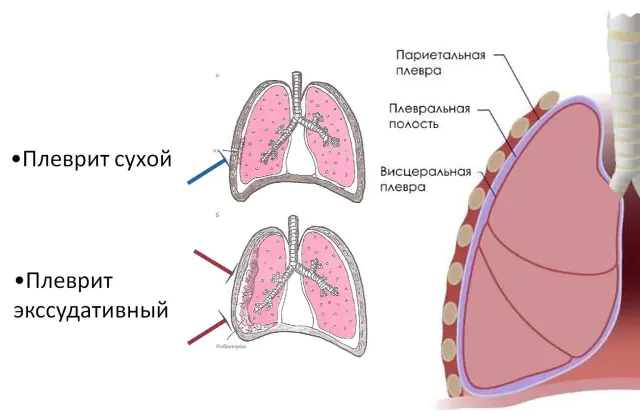
The human chest cavity is lined with a connective tissue membrane consisting of two layers - the pleura. One of the layers of pleura covers the surface of the lungs and is called visceral. The other, parietal, is adjacent directly to the chest. The space between them, called the pleural cavity, is filled with fluid - this mechanism reduces the friction of the membranes during breathing. Pulmonary pleurisy is inflammation of the pleura with the appearance of pathological discharge or protein deposits in the pleural cavity.
There are two fundamentally different types of pleurisy:
- Dry- with a small amount of pathological secretions (exudate), completely absorbed by the pleura. Protein plaque, which subsequently remains on the pleura, together with edema, interferes with the free sliding of the pulmonary membranes, which disrupts the normal mobility of the lung.
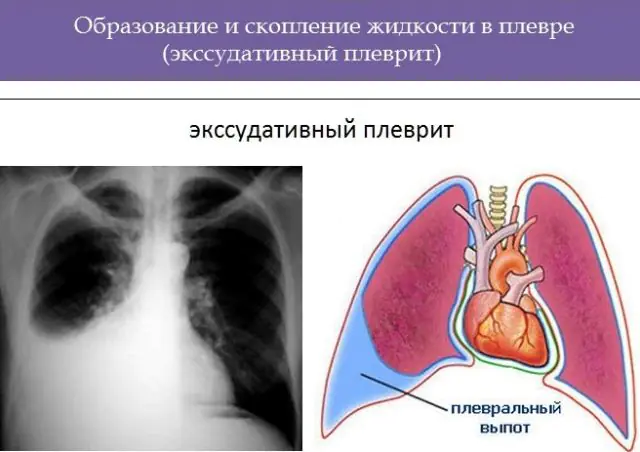
- Exudative- with abundant formation of secretions in the pleural cavity. Depending on the presence of a pathological agent, they are divided into aseptic and infectious. The main infectious agents of pleurisy are streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus and pneumococcus.
Exudative pleurisy, in turn, has subtypes depending on the characteristics of the resulting pathological fluid, the location of the foci of its accumulation, as well as the nature of the flow:
- depending on the nature of the exudate- purulent, hemorrhagic, eosinophilic, chylous or pseudochylous, serous or serous-fibrinous;
- by location of exudate foci- diffuse, encysted;
- according to the course of the disease- chronic, acute, subacute.
Treatment of pleurisy is always aimed at eliminating the primary cause of inflammation.
It is important! Dry pleurisy is usually considered a secondary condition to another serious illness or injury. Exudative pleurisy can develop both as a secondary condition and as a separate disease caused by an infectious pathogen. This type of disease is called primary.Main causes of pleurisy
There are several causes for the most common forms of inflammation. By the characteristic symptoms of pleurisy, which differ for the dry and exudative forms, one can judge the primary pathology, and, conversely, in some serious diseases one can speak of a high probability of developing one or another form of pleurisy.
Dry pleurisy often occurs with pulmonary tuberculosis, as well as with other lesions of the respiratory (pneumonia, abscess or lung cancer) and digestive (pancreatitis, cholecystitis) systems.
Exudative pleurisy can develop from a dry form, be a sign of an infectious lesion, a tumor or diffuse disease (rheumatism, arthritis), internal trauma to the chest, or pulmonary embolism.
As a rule, with a dry form of inflammation, the primary disease is known even before the onset of the disease. The causes of pleurisy in exudative form are determined by the results of laboratory analysis of pathological fluid.
Symptoms of the development of pleurisy
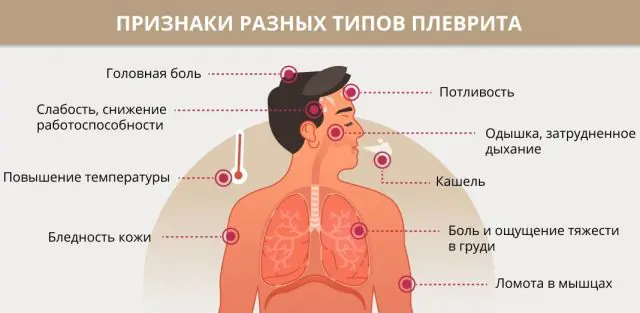
The symptoms of the development and course of pleurisy in adults and children are the same, while they differ for the dry and exudative forms.
The following symptoms are characteristic of dry pleurisy:
- the patient feels an intermittent dull pain in the affected half of the chest;
- the pain intensifies when inhaling and coughing, but decreases when squeezing - the person will try to lie on his side or hold on to it with his hands;
- the pain also intensifies when bending in the opposite direction from the affected side;
- depending on the affected area of the pleura, the pain may radiate to the shoulder or abdomen;
- possible pain when swallowing, obsessive hiccups;
- dry cough and shortness of breath appear;
- general malaise occurs - weakness, increased body temperature;
- during breathing, including at a considerable distance from the patient, a specific noise from pleural friction is heard;
- Nausea and stomach upset may occur.
In the future, the disease may transform into an exudative form or relapse. Recovery may also occur, usually within 1 to 3 weeks.
Exudative forms of pleurisy have a less pronounced course:
- pain is noticeably felt at the onset of the disease, with the accumulation of exudate in the chest cavity, the pain syndrome decreases;
- attacks of dry cough appear that do not bring relief;
- shortness of breath gradually appears, a feeling of heaviness in the chest, the patient’s breathing becomes less deep and more frequent;
- general malaise appears with an increase in body temperature to 39°C, pallor, cyanosis of the mucous membranes;
- in advanced forms, displacement of the mediastinal organs may be observed, heart rhythm is disturbed, and blood pressure decreases.
Methods for diagnosing pleurisy
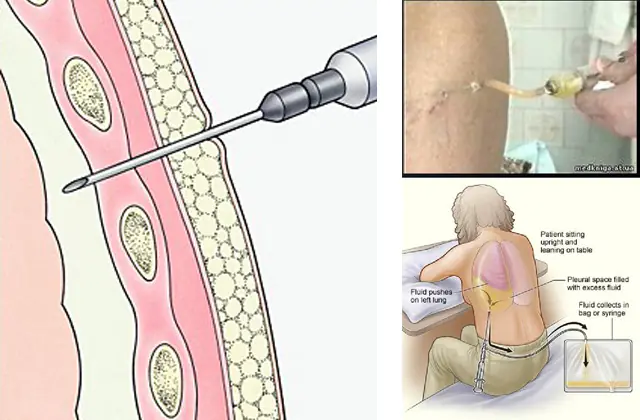
The diagnosis of pleurisy uses physical examination, radiography and ultrasound, as well as laboratory analysis of blood and pathological fluids. In severe cases, a biopsy (tissue sample) of the pleura may be performed.
Examination of the patient allows one to identify characteristic external signs of pleurisy, as well as differentiate between the dry and exudative forms of the disease. The doctor pays attention to the patient’s posture, mobility and changes in the volume of the chest, and extraneous noises during breathing.
An x-ray allows you to determine the presence of excess fluid in the pleural cavity, its approximate volume and possible displacement of organs. Ultrasound diagnostics is used to accurately determine the amount of excess fluid, and also as a clarifying method if encysted pleurisy is suspected.
Analysis of pathological fluid is mandatory in case of exudative form of pleurisy. The material is taken by pleural puncture (thoracentesis) - pumping out fluid using a special puncture needle. In the future, based on the appearance and morphological composition of the taken material, differential diagnosis of a specific type of exudative form of pleurisy is carried out.
With tuberculous pleurisy, Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be found in the pleural fluid and sputum of the patient.
Biochemical and some other types of blood tests can be used as an additional diagnostic tool. In any case, a blood test is required if traces of blood are found in the puncture material: the ratio of red blood cells to other blood components (hematocrit) may indicate a possible hidden injury, tumor or pulmonary embolism. Diagnosis of thromboembolism is carried out by scintigraphy - the injection of a drug with an isotope substance, based on the behavior of which in the bloodstream, conclusions are drawn about the possibility of a blood clot.
A pleural biopsy is performed if it is impossible to obtain the necessary material using other methods.
Features of treatment of pleurisy
Care for patients with pleurisy that has developed against the background of tuberculosis is carried out in a tuberculosis clinic, and bed rest is not always necessary. Combination chemotherapy is also used in the treatment of tumor pleurisy.
Features of pleurisy therapy:
- The first step is differentiation between the secondary and primary forms of pleurisy. In the secondary form, a set of therapeutic measures is prescribed aimed at getting rid of the disease or injury that provoked the disease.
- Bed rest is indicated; in case of dry pleurisy, a tight bandage is applied to the chest.
- If necessary, the cough is relieved with antitussives, and the pain syndrome is relieved with painkillers.
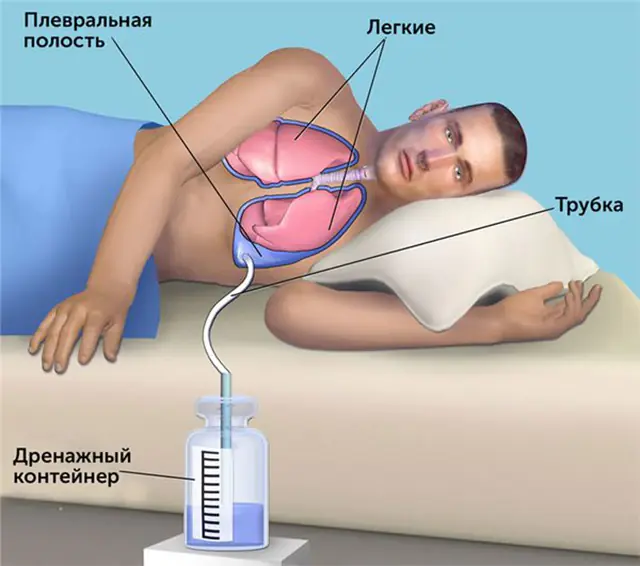
- Exudative pleurisy requires regular drainage - pumping out pathological fluids from the pleural cavity. This becomes especially important in case of pleural empyema.
- For infectious or purulent pleurisy, antibiotics are prescribed, taking into account personal tolerance and sensitivity.
- At the same time, maintenance therapy is carried out - blood transfusion, plasma, breathing exercises, protein diet.
- To stimulate the resorption of exudate, corticosteroids and diuretics may be prescribed.
Methods for treating pleurisy
Therapy of the disease involves an integrated approach aimed at eliminating the symptoms and causes of inflammation and preventing possible complications of pleurisy.
Medicines for pleurisy
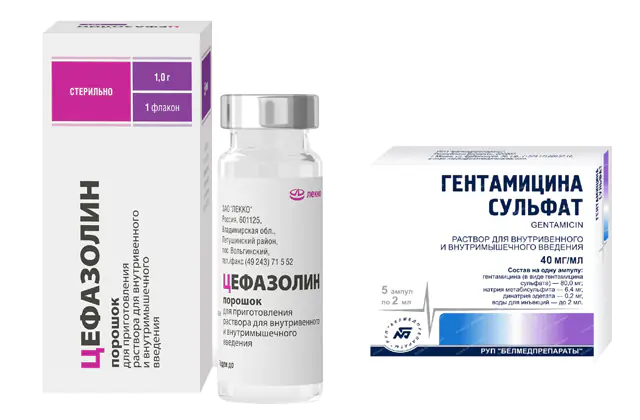
All drugs used in the treatment of pleurisy can be divided into the following categories:
- Antibiotics- a combination of Cefazolin and Gentamicin or Cefotaxime with Clindamycin. Antibiotics are administered intrapleurally and intravenously. Each drug is prescribed depending on the specific pathogen, but in any case, one one-time set of two drugs will cost about 600 rubles. (240 UAH).
- Antituberculosis drugs- Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol (analogues - Inbutol, Combutol). The drugs suppress the synthesis of RNA of the causative agent of tuberculosis. The cost of each is 40-60 UAH. per pack (or about 130 rubles).
- Corticosteroids- Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone. The cost of the injection solution will be 400 rubles. (100-180 UAH).
- Painkillers- Ibuprofen (analogue - Ibuprom). Suppresses the synthesis of inflammatory mediators and has an antipyretic effect. A package of such painkillers will cost 100-200 rubles. (40-80 UAH).
- Antitussives— Codterpin IC (Codesan IC). Has a sedative effect. One blister will cost 150 rubles. (55-60 UAH).
In each individual case, the drug therapy plan must be drawn up individually, taking into account the patient’s personal intolerances. If you have pleurisy, you should never self-medicate.
Therapeutic procedures for pleurisy
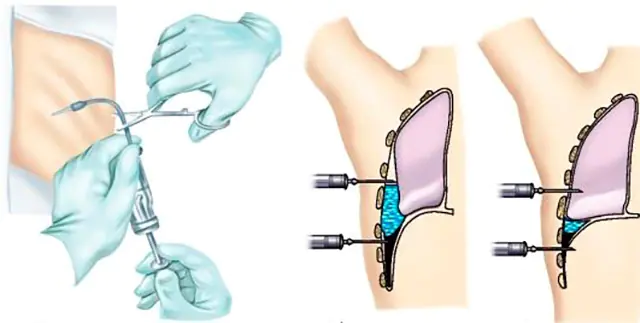
The photo shows a diagram of thoracentesis for pleurisy
The main therapeutic procedure for pleurisy is thoracentesis (pleural puncture). It is performed both to collect pathological material for diagnosis and to alleviate the condition of patients with exudative forms of pleurisy.
The procedure is performed using local anesthesia. After anesthesia, a needle is inserted into the region of the VII-VIII intercostal space from behind, and the fluid is removed using a syringe. If the procedure was carried out to remove purulent contents, it is possible to use drainage followed by the administration of antibiotics.
If suppuration still continues 30-40 days after the start of the procedures, an operation is performed - pleurectomy, that is, complete removal of the diseased area of the pleura with possible removal (resection) of the affected area of the lung.
Note! Often a complication of other serious diseases and requiring surgical procedures for both diagnosis and treatment, pleurisy cannot be cured using any folk remedies. Any delay without qualified medical care risks serious complications, including chronic shortness of breath, arrhythmia and pathological adhesions in the pleura. In addition, pleurisy itself can serve as a sign of an as yet undiagnosed disease, which will certainly make itself felt later.Any pleurisy is dangerous, at least as dangerous as the primary causative agent of the disease that provoked the inflammation. Prevention of illness means, first of all, prevention of diseases of the respiratory system. It is also worth paying attention to the condition of the liver and gallbladder. Never leave pneumonia to chance and use the TB vaccine. And, of course, if pleurisy has already been detected, the recommendations of your attending physician must be followed with special care. The prognosis with timely treatment is always favorable - only advanced cases left unattended can pose a serious threat to life and health.
How to treat pleurisy - watch the video:



