As you know, such a branch of medicine as plastic surgery began to develop relatively recently. Nevertheless, to date, many discoveries have been made in it. Today, it is possible to enlarge or reduce almost any organ, change its shape, transplant it, etc.
One of the procedures performed by plastic surgeons is skin grafting. This operation has been practiced for many years, and every year it is improved. There are cases where almost the entire skin was transplanted. Thanks to this procedure, you can not only hide defects, but also completely change your appearance.
What is skin grafting?
Replacing the damaged area with a new skin flap is called dermoplasty. This operation is performed in a surgical department. Indications for it may vary. In most cases, this is damage to the skin and the inability to restore it in any other way. There are several types of dermoplasty. The most common method is to transplant skin from one area of the body to another, which is the site of damage.
Recently, other transplantation methods have been actively developed. In equipped clinics and research institutes, new cells are “grown” under special conditions. Thanks to this, the skin can be “created” rather than taken from another area. This is a huge breakthrough in medicine! Currently, this method has not yet become widespread, however, developments are underway in this area.
In what cases is skin grafting performed?
Skin grafting is a surgical procedure that is necessary to replace a damaged area of tissue, as well as for cosmetic purposes. Currently, a similar procedure is carried out in almost all large clinics. A surgeon of any specialty must be proficient in the technique of skin grafting. However, to ensure that there is no cosmetic defect left after the operation, special preparation is required. Therefore, skin grafting on the face and open areas of the body must be performed by a plastic surgeon.
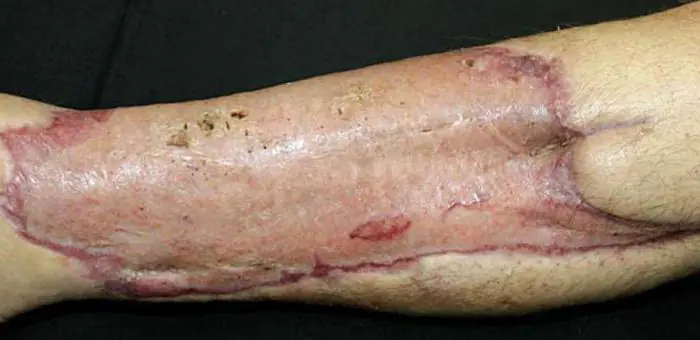
Most often, such surgical intervention is performed only in cases of necessity (for health reasons). Typically, skin grafting is required after radical surgery, massive burns, or traumatic injury. In addition, such surgical intervention may be necessary during plastic procedures. In some cases, people who do not have strict indications for this operation wish to undergo skin transplantation, for example, if they want to hide a scar or tissue pigmentation. Sometimes dermoplasty is performed to change the color of the skin. However, it is worth remembering that, like any surgical intervention, this operation has certain risks. Therefore, in most cases it is performed only when necessary.
Indications for dermoplasty
The main indications for skin grafting are tissue damage. Violation of integrity can be caused by various reasons. The following indications for dermoplasty are distinguished:
- Burns. This refers to significant damage to the skin due to exposure to high temperatures or chemicals. Dermoplasty after burns is especially common among children. This is due to the fact that children are more likely to have accidents at home. As a rule, children who have been scalded by boiling water are admitted to the trauma department. Among the adult population, chemical burns received at work are more common, and less common at home.
- The presence of scar tissue occupying a large area of the skin.
- Traumatic defeat. Skin grafting after injury is not performed immediately. First of all, it is necessary to stabilize the patient's condition. In some cases, dermoplasty is indicated several weeks or months after the formation of the primary scar.
- Long-term non-healing wound surfaces. This group of indications includes bedsores, trophic ulcers in vascular diseases, and diabetes mellitus.
- Plastic surgery on the face and joints.
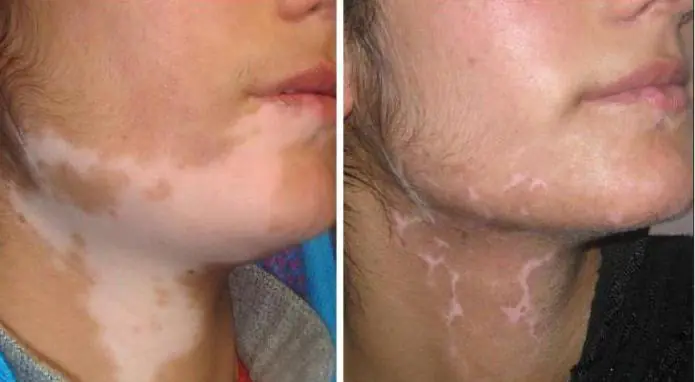
In addition, skin transplantation can be performed for dermatological diseases and congenital defects. Often this operation is performed in the presence of vitiligo - depigmented areas of tissue. Hyperkeratosis and large birthmarks can also be grounds for dermoplasty. In such cases, the indications are considered relative, and the operation is performed at the request of the patient in the absence of severe somatic pathologies.
What methods of skin grafting are there?
There are 3 methods of skin transplantation. The choice of method depends on the size of the defect and its location. Please note that the method of skin transplantation is chosen by the attending physician in accordance with the equipment of the clinic. Depending on where the material for transplantation is taken from, auto- and allodermoplasty are distinguished.
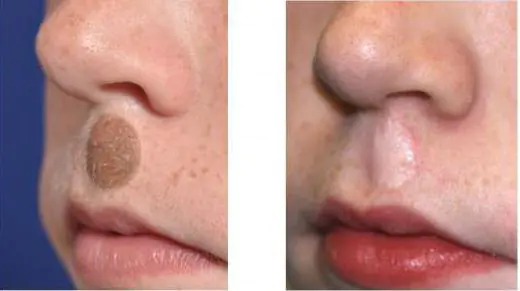
A separate type of transplantation is tissue skin grafting.
- Autodermoplasty is performed when the lesion is less than 30-40% of the body area. This surgical intervention means transplantation of skin from one area to another (affected). That is, the transplant is taken from the same patient. Most often, the area of skin from the gluteal region, back, and side of the chest is used. The depth of the flaps ranges from 0.2 to 0.7 mm.
- Allodermoplasty is performed for massive defects. Often, skin grafting is performed in this way after 3rd and 4th degree burns. Allodermoplasty means the use of a donor skin flap or the use of artificial (synthetic) tissues.
- Cellular dermoplasty. This method is used only in some large clinics. It involves “growing” skin cells in laboratory conditions and using them for transplantation.
Currently, autodermoplasty is considered the preferred method, since the engraftment of one’s own tissues occurs faster, and the risk of developing graft rejection is significantly reduced.
Preparation for skin grafting
Before proceeding with skin graft surgery, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Even if the defect is not very large, it is necessary to assess whether there is a risk from surgery and how high it is in a particular case. Immediately before dermoplasty, laboratory tests are performed. Among them: OBC, OAM, blood biochemistry, coagulogram.
In case of massive injuries, when an allograft is required, more tests must be taken. After all, a skin transplant from another person (or synthetic material) can lead to rejection. The patient is ready for the surgical procedure if the total blood protein does not exceed 60 g/L. It is also important that the hemoglobin level is within normal limits.
Surgical technique
Skin grafting for burns is not performed immediately, but after the wounds have healed and the patient’s condition has stabilized. In this case, dermoplasty is delayed. Depending on where exactly the damage to the skin is localized, how large it is in area and depth, a decision is made on the method of surgical intervention.
First of all, prepare the wound surface. For this purpose, areas of necrosis and pus are removed. Then the defective area is treated with saline solution. After this, the affected tissue is covered with a graft. It should be borne in mind that the skin flap taken for transplantation decreases in size over time. The edges of the healthy tissue and the graft are sutured. Then apply a bandage moistened with antiseptics, healing agents, and dioxidine ointment. This helps to avoid infection of the postoperative wound. A dry bandage is applied over it.
Features of the operation depending on the type of dermoplasty
Depending on the depth and location of the lesion, the surgical technique may differ slightly. For example, if a skin transplant is performed on the face, it is necessary to perform autodermoplasty. In this case, the skin flap should be split. For this purpose, the transplant is taken with a special device - a dermatome. With its help, you can adjust the thickness of the cut of the skin fragment. If facial surgery is required, cellular dermoplasty can be performed.
In case of massive burns or injuries, the skin's own reserves are often insufficient. Therefore, it is necessary to perform allodermoplasty. Skin transplantation on the leg with a large wound surface is carried out using a synthetic material - a special mesh that fixes the graft.
What complications can arise after dermoplasty?
Complications may occur during skin grafting. Most often this is graft rejection. In most cases, it develops due to infection of the sutures. After autodermoplasty, rejection is observed less frequently. Another complication is bleeding from the wound.
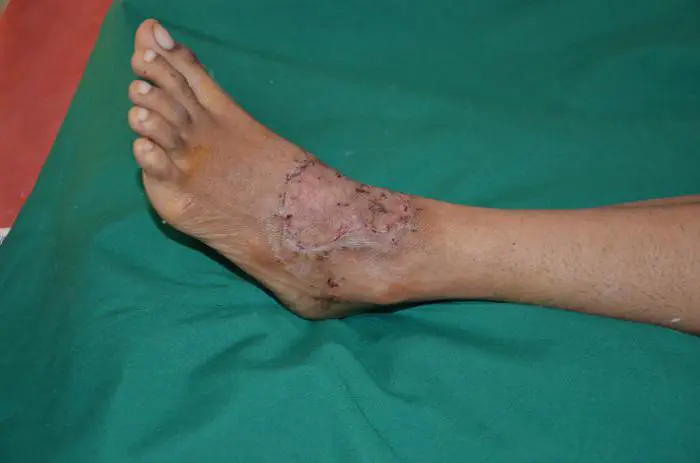
Skin grafting: photos before and after surgery
Skin grafting is performed quite often. Before you decide to have surgery, you should look at the photos before and after surgery. In most cases, qualified doctors predict the outcome and provide the patient with an image that shows what the damaged area will look like when the graft takes root.
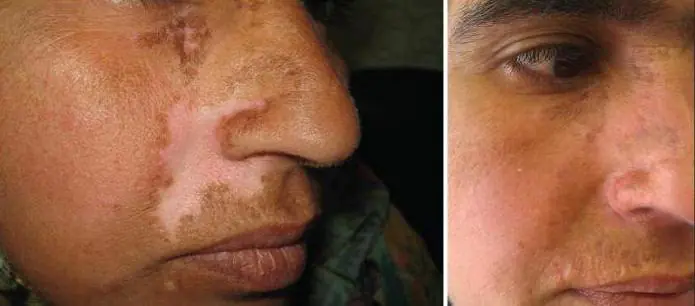
Prevention of complications of surgery
There are several risk factors for developing complications after skin grafting. Among them are the patient’s childhood and old age, the presence of somatic pathologies, and reduced immunity.
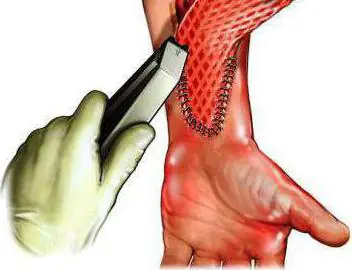
To avoid transplant rejection, it is recommended to use hormonal drugs in the form of ointments. To prevent bleeding and inflammation, the medication “Pyrogenal” and antibiotics are prescribed.
For some categories of patients, skin graft surgery is the only way to continue a normal life. For severe burns and tissue deformations, epidermal transplantation is necessary. The procedure allows not only to eliminate cosmetic defects, but also to get rid of wounds that do not heal for a long time.
Indications for transplantation
Skin grafting after burns in children and adults is the main way to treat severe injuries. If a person loses a significant portion of tissue, it does not just cause cosmetic defects. In some cases, such an injury leads to the death of the patient, since the skin is the main barrier that protects the internal organs from infections.
The skin grafting procedure is indicated in the following cases:
- 3rd and 4th degree burns;
- injuries due to which the patient lost a significant part of the skin;
- the presence of scars and other imperfections that remain after previous injuries or surgical interventions;
- wounds that do not heal for a long time;
- plastic surgery of the face or body.
The appropriateness of skin restoration using surgical methods is determined by the attending physician. If there is a large amount of damaged tissue that cannot recover on its own, a decision is made to perform a transplant.
Pros and cons of skin grafting
Any surgical intervention has certain advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of skin graft surgery include the following factors:
- the patient gets rid of cosmetic imperfections that are ruining his life. This is especially important when it comes to damage that is on the face. After transplantation, victims feel much more confident;
- internal organs are protected from pathogenic microorganisms. The new skin after engraftment performs its barrier functions;
- The patient’s well-being improves, as non-healing wounds that caused pain disappear. Metabolic processes are also regulated, which generally affects the state of the body.
The disadvantages of the procedure primarily include the likelihood of tissue rejection. Regardless of whether skin from donor parts or synthetic material is used, they may not take root.
Another point is that not all people are ready to undergo a transplant. This is not about the fear of going under the surgeon's knife. Many patients are embarrassed by the thought of receiving donor skin. In this case, consultations with a psychologist help.
What materials are used for transplantation?
During surgery, several types of transplantation material can be used:
- healthy tissues of the victim himself. This type is used most often;
- layers of donor skin. They are used if the patient’s own skin is not enough;
- animal tissues;
- artificial material.
In addition, there is a classification of materials depending on how damaged the burned area is. If the burn has affected the upper layers, then grafts up to 3 mm thick are required. For a medium-type wound, the thickness is no more than 7 mm. The most complex cases require grafts with a thickness of more than 1 cm. The choice of material is based on a medical opinion, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Operation methods
If there are serious skin lesions, surgery should be performed as quickly as possible. Only in this case can complications be avoided and the victim’s condition improved. The doctor prescribes a transplant after 1 month if the damage is not very serious, and after 2 to 3 months if the injuries are significant.
To speed up the healing process, dying tissue is removed, but this must be done with caution so as not to worsen the patient's condition. Manipulations are carried out when about 2 to 3 weeks have passed since the burn. Dead areas are removed gradually when the dressings are changed.
When carrying out the intervention, work is carried out by 2 groups of medical workers at once. The first takes tissue for transplantation, the second prepares the patient for surgery. Use one of several types of procedures:
- a thin layer of skin is transplanted, which promotes rapid survival and reduces the risk of rejection;
- Thick section transfer is usually applied to prominent areas (face, neck). Scars in this case are less noticeable;
- In addition to skin transplantation, cartilage or fatty tissue is also restored.
How is the operation performed?
Any such intervention begins with the selection of healthy areas. Depending on the location where it is taken, the area is processed and the required layer is cut out. If tissue is taken from a living donor, anesthesia is used. The areas usually used are the hips, buttocks, back, and chest. The area is cut out using a special tool.
At this point, a second group of doctors prepares the patient for surgery. The affected area is further treated and dried. In this case, there should be no inflammatory processes. Then the transplantation itself begins.
A piece of healthy skin is placed over the damaged area. If the damaged area is small, it is fixed using special glue or staples. Serious injuries require surgical sutures. After this, doctors secure the area with a tight bandage. The entire manipulation takes no more than an hour, so it is considered a fairly simple procedure.
On the first day after transplantation, the patient's condition is closely monitored. Bandages are changed regularly and the surface is treated with disinfectant solutions. During and after the procedure, the victim may experience unpleasant symptoms such as bleeding or infection of the surface. In addition, skin sensitivity decreases and there may be a risk of rejection.
The likelihood of complications is most often encountered by people with poor immunity and certain chronic diseases. Age is also a risk factor. Interventions should be used with caution in young children and the elderly.
Recovery period
Whether the tissue has taken root will become clear within a week after transplantation. During this entire period, the bandage is not removed, it is simply changed regularly. If pus and inflammatory processes appear, this indicates that the body is rejecting the material. Even if it takes root, rehabilitation after skin grafting will be required for several months. The most severe cases require rehabilitation therapy for six months.
During this entire period, the patient will need to follow the doctor's instructions. First of all, several groups of drugs are prescribed to relieve various symptoms that arise during the rehabilitation period. Glucocorticosteroids are prescribed, as well as agents to eliminate inflammatory processes and tissue regeneration.
During the recovery period, the victim needs to use physical therapy. It is necessary to remember the possibility of deformation of joints and tendons during scar formation. Therefore, it is important to start rehabilitation as early as possible. The part of the body on which the transplant was performed must move frequently and a lot. The restorative course of procedures will be selected by the attending physician.
Physical therapy, electrophoresis, and magnetic therapy are used. During physical therapy, special medications are used to soften scars and relieve inflammation. In some cases, additional surgery may be required to correct remaining cosmetic imperfections.
For many patients, skin graft surgery after a burn is the only way to continue a normal life. Despite all the difficulties associated with its implementation, the benefits of transplantation are much greater. It improves the quality of life of burn victims and restores their ability to enjoy life.
Skin grafting is a technique used in traumatology and plastic surgery. Most often, skin obtained from other places on the body of a sick person is used. Temporarily, you can use synthetic material or obtained from donors - humans or animals.
Healing skin wounds
Wounds that occur on the skin heal in several stages. Immediately after the injury the process begins hemostasis (dynamics of bleeding development). They take part in it platelets, which are transformed within the wound into aggregates, and protein - fibrin. Together they cover the wound and form a clot. Thus, they prevent fluid loss and infection of the injury site.
Inflammation develops at the site of injury. It reaches redness, swelling and increased local temperature, the patient feels pain. The function of the organ is impaired.
At subsequent stages of healing, gradual granulation of the tissue occurs, filling from the edges of the wound with epithelial cells and healing. If the wound is deep (includes the dermis), in its place a scar is formedwhich can tighten the skin, limiting mobility and causing contractures.
Indications for skin transplantation
Indications for skin grafting are situations in which there is danger wound infection or scar tissue formation that impairs organ function. A transplant is also necessary if the wound area is large and can lead to fluid and electrolyte imbalance, hypovolemic shock or extensive infection.
Special cases are, for example, facial wounds (torn, chewed), which threaten deformation and the appearance of serious cosmetic defects.
Another group of such injuries are burns (resulting from, for example, a fire, a chemical or a hot liquid), which pose a serious threat to health and life.
Skin grafting after burns
Burns covering 25-30% of the body surface are considered an immediate threat to life, regardless of their depth. Since there is a sharp disturbance in the water-electrolyte balance. Extensive swelling appears, and a large amount of fluid is lost through the surface of the wounds. Together with the fluid, plasma proteins are lost, the deficiency of which increases the symptoms.
The result of this can be shock with a sharp decrease in blood pressure, cerebrovascular accident and even death of the patient. Extensive wounds are also gateways for microorganisms, which can penetrate the blood, causing sepsis.
Protection from burns with conventional dressings results in the healing process taking a very long time and leaving scars. Therefore, deep wounds (spanning the full thickness of the skin or deeper) are considered an absolute indication for skin grafting.
Skin grafting - obtaining material
The source of material for transplantation is skin from healthy areas. This is most often the thighs, buttocks, and the area under the shoulder blades. The goal is to obtain a single piece of skin of a certain thickness and structure. The skin is taken immediately before transplantation.
In the case of flaps of intermediate thickness, which contain the epidermal layer and part of the thickness of the dermis, this procedure is performed using a device called dermatome. Full thickness flaps are cut by hand. Their advantage is that they take root without the tendency to tighten and form scars, and provide complete correction of a deep defect.
Flaps of intermediate thickness can be cut to form a mesh. Then healing in the “holes” of the mesh occurs, as in the case of other wounds - through gradual granulation and epidermation. This type of treatment increases the risk of skin tightening and scarring, but may be necessary if a large surface area of the body is damaged.
Where can skin grafting be applied?
The resulting material can be placed almost anywhere on the body, in particular:
- on the face
- on the scalp and neck
- on limbs, especially on curved surfaces
As a result, it is possible to avoid the formation of cosmetic defects, contractures, and limited mobility of the limbs or neck. On other surfaces of the body, taking into account the fact that transplantation is in many ways superior to wound dressing, the procedure speeds up healing and improves the final effect.
Skin grafting - healing stages
Partial-thickness skin grafting involves accurately transferring the resulting flap onto a well-cleaned and prepared wound surface and securing it under pressure. To prevent the flap from moving along the surface of the wound, it is often fix. The full thickness petal is secured using skin sutures.
Initially, the petal receives nutrients only from surface liquids. Within a few days it is “fertilized” substrate with fibrin, and then granulation tissues. Next, the blood vessels grow into the flap and begin to provide it with nutrients.
Over the next few months after transplantation, nerve endings are formed, which makes it possible to restore sensitivity at the transplant site.
Complications of skin grafting
The main complications of skin transplantation are:
- infections at the site of flap harvest or implantation
- flap necrosis
- hematoma
- the formation of a fluid bubble under the flap, which delays the growth of the graft and the final healing of the wound.



