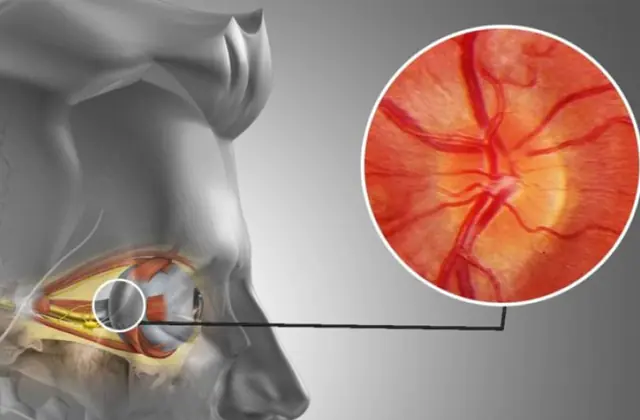
Description and causes of optic neuritis. Main symptoms and diagnosis. Treatment methods for optic neuritis.
The content of the article:- What is optic neuritis
- Reasons for development
- Main symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
Optic neuritis is an ophthalmological pathology that is accompanied by inflammatory processes in the optic nerves. Often observed in patients with multiple sclerosis, infectious diseases that negatively affect the central nervous system. The inflammatory process can affect both the optic nerve sheath and its trunk.
What is optic neuritis?
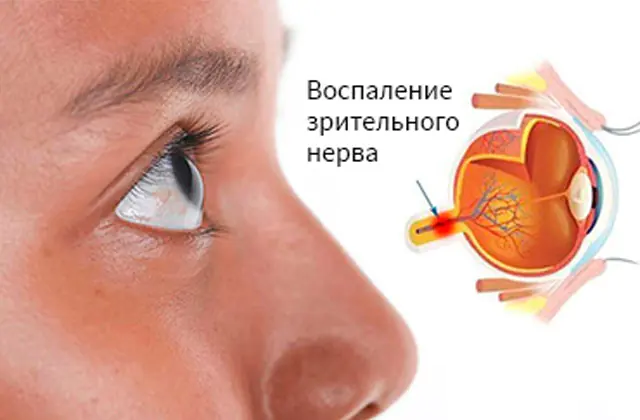
Optic neuritis is a severe ophthalmological disease that leads to rapid loss of vision (most often reversible). It develops in people with a history of multiple sclerosis, bacterial and viral infections that affect the central nervous system. The risk group includes patients aged 25 to 45 years, mostly female, as well as people with genetic mutations.
The disease begins acutely: in the period from 2 to 48 hours, a sharp decrease in visual acuity is observed. Neuritis can affect one or both eyes at once. In more than 20% of cases, the disease is recurrent in nature.
With mononeuritis, one nerve is affected, with polyneuritis - 2 or more. Depending on the location of the pathological process, neuritis is:
- ascending— the intraocular parts (discs) of the optic nerves become inflamed;
- downward- any segments of nerves are affected.
The prognosis depends on the severity of the pathological process. With mild optic neuritis, vision is restored in more than 70% of patients after 30-50 days. In this case, color perception and contrast sensitivity may be impaired. Severe disease leads to atrophy of the optic nerves. The progression of the pathological process is fraught with irreversible impairment of visual acuity.
Causes of development of optic neuritis

The causes of optic neuritis are associated with exposure to:
- foci of chronic infections, that is, dental diseases, sinusitis, otitis, inflammatory processes of the reproductive system;
- systemic diseases of the body - autoimmune encephalitis, lupus erythematosus;
- infectious pathologies of viral origin - acute respiratory viral infection, herpes, measles, mononucleosis;
- intoxications: methyl alcohol and its derivatives, medications from the group of antibiotics, as well as drugs with an ototoxic effect (streptomycin, gentamicin);
- bacterial infections - tuberculosis, syphilis, meningitis;
- diseases of the central nervous system - multiple sclerosis, acute encephalomyelitis;
- pregnancy pathologies;
- inflammatory diseases of the organs of vision - keratitis, iridocyclitis, chorioretinitis, endophthalmitis.
Descending neuritis of the optic nerve is most often caused by poisoning and diseases of the central nervous system, ascending - by inflammatory processes affecting the membranes of the eyes.
Main symptoms of optic neuritis
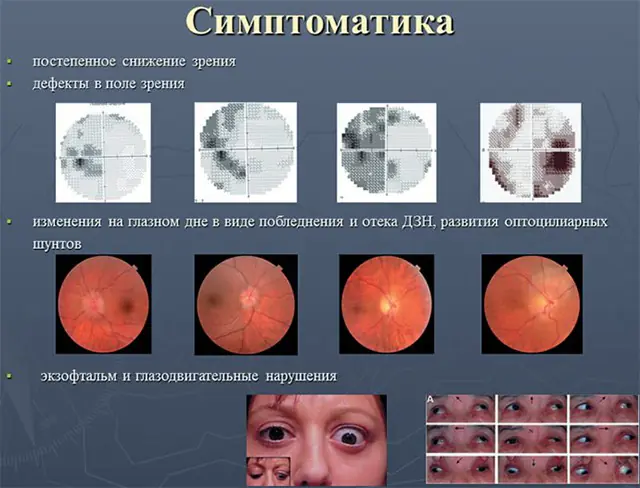
With neuritis, vision may remain within normal limits, but complaints arise about the formation of spots in the field of vision.
Optic neuritis is accompanied by the development of the following general symptoms:
- pain in the eye sockets and brow ridges, which intensifies with motor activity of the eyes;
- pupillary defects;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity;
- central, arcuate or paracentral visual field defects;
- impaired perception of color and light.
With ascending neuritis, during the first 24-72 hours, the development of hyperemia, blurred boundaries, and edema is observed. The vessels dilate and hemorrhages form. The duration of the acute period of the disease is up to 40 days. Afterwards, hyperemia and swelling of the discs are eliminated, hemorrhage is reduced, and the shape of the disc is restored and becomes clearer.
Severe disease is rare and is accompanied by disc atrophy. As the pathological process worsens, the symptoms of optic neuritis are supplemented by a sharp increase in body temperature.
With descending neuritis, the clinical picture is different. There are several possible inflammatory changes that affect nerve endings:
- With axial inflammation, central vision dysfunction occurs and the patient cannot undergo functional tests.
- When the nerve sheaths are damaged and the inflammatory process spreads deep into the nerve trunks, exudate accumulates under the sheaths. This leads to the development of intense pain in the eyeballs, which increases with motor activity of the eyes.
- The most severe option is the development of the transversal type, in which damage to all tissues of the optic nerves is observed. The patient may lose vision almost completely.
The danger of the descending form of optic neuritis is that, despite the clinical picture, making an accurate diagnosis can be difficult. Functional changes are visible no earlier than 1 month after the onset of the inflammatory process: ophthalmoscopy does not reveal changes in the optic nerve head. Only an experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of optic neuritis

To make an accurate diagnosis, an in-person examination by doctors of several specialties is required: ophthalmologist, ophthalmologist. Ophthalmologists take into account the patient's complaints and check visual acuity. With mild neuritis, it is important to differentiate the disease from pseudoneuritis and congestive disc. This is especially important for patients with minor changes in visual acuity and a blurred overall clinical picture. Additional fundus angiography is required to confirm the diagnosis. This is a diagnostic procedure by which the structure of the retina and focal lesions in it are determined.
MRI with contrast agents is recommended for patients who complain of blurred vision and the development of pain in the area of the eyeballs during physical activity.
The neurologist conducts the following studies:
- Echo-encephalography- ultrasound diagnostics of the brain, with the help of which intracranial pressure indicators and the presence of space-occupying tumors are assessed. This diagnostic method precedes MRI and CT of the brain.
- Lumbar puncture— a puncture needle is inserted into the lumbar spine to examine the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
In severe cases of the pathological process, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and consultation with an infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist, or immunologist are recommended.
Treatment options for optic neuritis
The patient is urgently hospitalized. The main goals of treatment for optic neuritis are to suppress infection and inflammation, prevent dehydration, and normalize metabolic processes in the central nervous system. The decision on how to treat optic neuritis is made by the doctor, taking into account the clinical picture and associated disorders. Management is carried out by neurologists. Concomitant consultation with doctors of related specialties may be required: otolaryngologists, ophthalmologists, dentists, phthisiatricians, infectious disease specialists.
Medications for optic neuritis
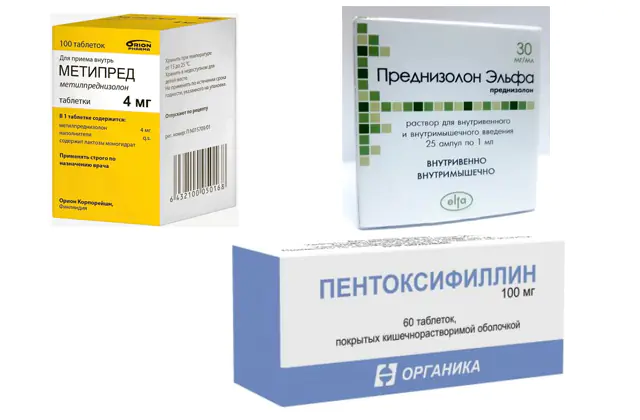
Medicines are selected depending on the cause that provoked optic neuritis. If multiple sclerosis is suspected, the following medications are recommended:
- Methylprednisolone. Intravenous infusion of 500-1000 mg over 72 hours. A drug from the group of corticosteroids that affects all phases of the inflammatory process. The dosage is selected strictly individually for each patient. The medicine has an extensive list of side effects and is not recommended for long-term use. Cost - 190 rubles. (75 UAH) Analogues: Metipred, Medrol.
- Prednisolone. They switch to using it over the next 10 days. This is a medicine with anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, corticosteroid effects. Used for eye diseases (acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes). Contraindicated in patients with systemic fungal infections. Price - 110 rub. (40 UAH). There are no exact structural analogues.
Preparations based on Methylprednisolone and Prednisolone are also used locally in the form of drops. The combination of local therapy for optic nerve neuritis and systemic exposure enhances the anti-inflammatory effect. Medicines help delay the onset of the disease for at least 24 months.
Note! The use of Prednisolone in the form of tablets for internal use does not lead to normalization of the functioning of the visual organs and can aggravate the course of neuritis, as well as provoke its relapse.If optic nerve atrophy is observed, drugs that normalize blood microcirculation are used: Pentoxifylline. This is a medicine that increases blood circulation and increases the volume of blood flowing and reduces its viscosity. Eliminates disorders of peripheral and cerebral circulation. The cost of the drug is from 45 rubles. (18 UAH) Analogs: Vazonit, Trental.
Folk remedies against optic neuritis

Folk remedies are used as a complement to basic treatment recommended by a doctor. Optic neuritis is a complex disease that requires an integrated approach; elements of herbal medicine are used to relieve symptoms.
Effective folk recipes for optic neuritis:
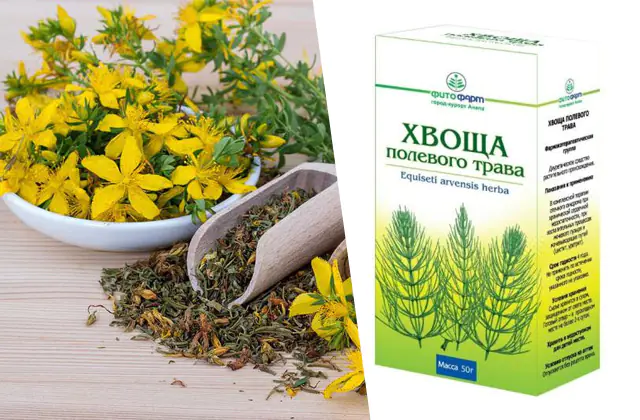
- Patients are advised to take St. John's wort juice. It is squeezed from the above-ground part of the plant and taken 1 teaspoon twice a day for a month.
- It is useful to use an infusion of horsetail herb. Dried crushed herb is poured with boiling water and left for 2-3 hours. The resulting drink is taken during the day, 1/3 cup for 14 days, after which they take a break. The course of treatment can be repeated with prior agreement with your doctor.
- For neuritis, complex herbal preparations are most effective. Common heather is mixed with sweet clover, calendula and linden flowers, oats, blueberries and plantain. The dried raw materials are mixed, ground in a coffee grinder and poured with boiling water (400 ml). Infuse in a warm place for 2-4 hours, filter and take 0.5 cup three times a day after meals.
- Barberry is mixed with heather, blackberry, lavender, dandelion, plantain and yarrow. The resulting collection is crushed to a powdery state, boiled in a water bath, infused and filtered. Take 1/4 cup 4-5 times a day for a month.
- For cases of optic nerve neuritis, use a healing decoction based on birch, heather shoots, and linden flowers. All components are mixed in equal proportions, refractory oil (coconut, cocoa) is added, and boiled in a water bath for 15 minutes. At the end, a decoction based on flaxseed is added. All components are mixed, placed in a glass jar and stored on the refrigerator door. Apply to the affected areas of the eyes three times a day. The course of treatment is 2 months. In case of individual intolerance to plant components, the composition of the ointment can be changed after consulting with a therapist.
- To reduce the symptoms of inflammation and irritation, lotions based on strong tea leaves are applied to the eyeballs.
There is no specific prevention of neuritis. Patients are advised to exclude traumatic lesions of the eyeballs, promptly treat acute and chronic infectious diseases, regularly sanitize teeth and potential foci of infection - tonsils. At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Video about optic neuritis:



