Causes of radiculopathy. Symptoms of cervical, thoracic, lumbar type of disease, diagnostic methods. Methods of conservative and surgical treatment, preventive measures.
The content of the article:- Reasons for appearance
- Symptoms of radiculopathy
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment methods
- Medicines
- Healing procedures
- Surgical intervention
- Prevention
Radiculopathy is a pathological condition of the spine, which is characterized by compression of the nerve roots. Other names for the disease are radiculitis and radicular syndrome. The disease is often diagnosed in people over 50 years of age whose profession involves physical stress on the spinal column.
Causes of radiculopathy
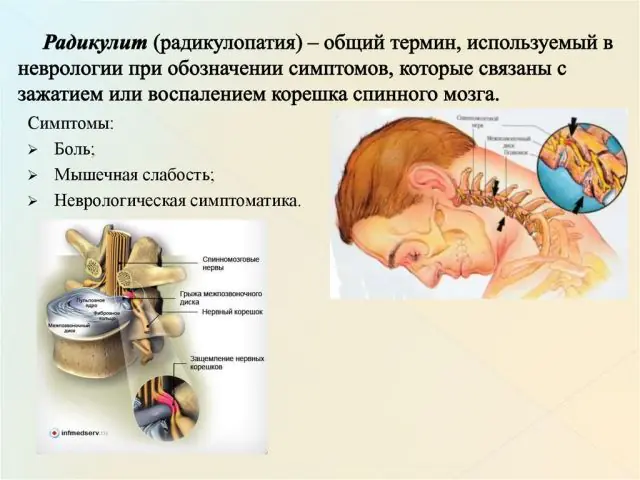
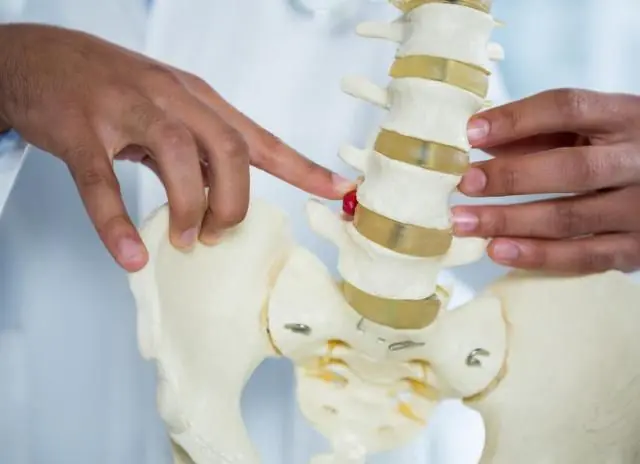
Diagram of radiculopathy
In the initial stages of radiculopathy, a person does not feel pain. Over a long period of time, his spine slowly undergoes degenerative changes. The first blow is taken by the cartilage. Under the influence of external or internal factors, they become dehydrated, deformed, and lose elasticity. An intervertebral hernia gradually forms, which compresses the nerve root.
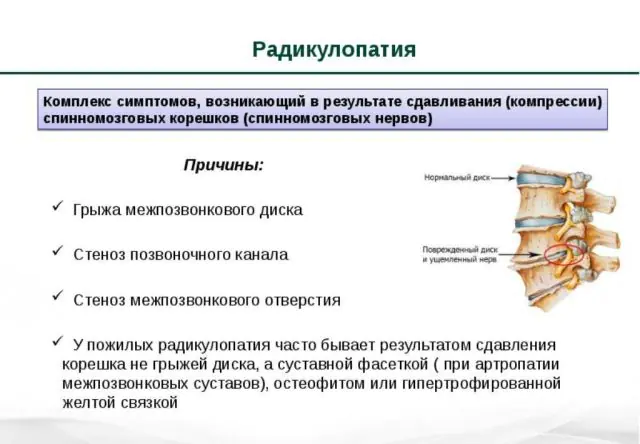
Another common cause of radiculopathy is the appearance of osteophytes. This is the name for bone growths that form due to failures in metabolic processes involving calcium. They encircle the tissues of the joints and spinal discs, limiting their mobility. The disease can be recognized by a characteristic crunching sound accompanied by pain.
Other causes of spinal radiculopathy:
- genetic predisposition;
- overweight and tall;
- consequences of surgery on the spinal column;
- stoop, incorrect posture;
- heavy physical activity;
- metabolic failure due to severe dietary restrictions;
- bad habits that impair blood circulation in bone tissue (smoking, drinking alcohol, drugs).
Radiculopathy develops as complications of the following diseases:
- Osteomyelitis. The disease is characterized by infectious inflammation of the spinal cord and all bone elements. The acute form of the disease is characterized by vivid symptoms and severe pain, and therefore undergoes immediate treatment. Chronic osteomyelitis has vague, inexpressive symptoms, which is why patients allow complications to develop.
- Scoliosis. Spinal curvature disrupts the structure and function of the musculoskeletal system. The spinal discs are in an incorrect, unnatural position. They rub against each other, causing inflammatory processes in the cartilage. Without constant qualified treatment, the disease is often complicated by radiculopathy and other pathologies.
- Diabetes. The disease is characterized by metabolic disorders. Because of this, minerals accumulate in the tissues, forming lumps and growths. In addition, diabetics are often obese because insulin promotes the accumulation of fat in tissues. As a result, the musculoskeletal system undergoes irreversible degenerative-dystrophic changes.
Overeating, bad habits, and an inactive lifestyle accelerate the development of the disease and lead to dangerous complications.
Main symptoms of radiculopathy
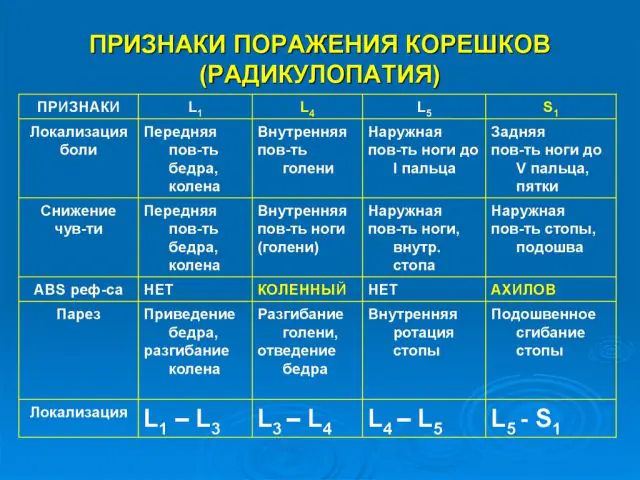
The nature of the symptoms of radiculopathy depends on the location of the spinal lesion. Common symptoms include back pain, tingling of the muscles of the limbs, and the adoption of a forced body position while resting.
Radiculopathy of the cervical spine is manifested by pain in the back of the head. It intensifies in the morning, due to which a person often blames an uncomfortable body position during sleep and is unaware of his diagnosis.
Cervical radiculopathy can be suspected based on the following symptoms:
- pain when sneezing and coughing;
- frequent dizziness;
- feeling of weakness in the arms;
- cold skin of the face and hands;
- peeling of the skin.
In the later stages, the patient places his head in an unnatural position and constantly massages his neck to relieve pain.
Thoracic radiculopathy is considered a rare disease, since the spine in this place has the least flexibility. The causes of this type of radicular syndrome are hypothermia, mechanical damage, and compression by a tumor.
Symptoms of thoracic radiculopathy include pain:
- between the shoulder blades;
- in the chest area;
- in the shoulder joint;
- in the armpit;
- on the middle finger of the hand.
With thoracic radiculopathy, the pain intensifies during a deep breath, bending over, or wearing tight clothing. Due to the fact that the nerve roots are connected to the digestive organs, during the acute phase spasms appear in the stomach, esophagus, and pancreas.
Lumbar radiculopathy is the most common type of radicular syndrome. It is characterized by acute unbearable pain in the lower back. During an attack, a person is literally immobilized, unable to straighten up, inhale and exhale.
In addition to the pain symptom, the following signs appear with lumbar radiculopathy:
- decreased physical activity;
- difficulty lifting weights;
- numbness of the lower extremities;
- intestinal disorders;
- sexual dysfunction.
Lumbar radiculopathy is divided into sciatica (pain radiates to the leg), lumbodynia (pain is concentrated in the lower back), lumbar sciatica (pain spreads to the entire lower part of the human musculoskeletal system).
Methods for diagnosing radiculopathy
If radicular syndrome is suspected, the patient is referred for consultation to a neurologist. The specialist examines the medical history and asks about the patient’s work and lifestyle. He learns about the characteristics of pain symptoms and the accompanying signs of radiculopathy.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient to the following diagnostic procedures:
- X-ray. This type of examination allows you to see the location of all intervertebral discs and notice the exact location of the degenerative-destructive process. To carry it out, the patient takes off clothes and jewelry and stands or lies down in front of the X-ray machine. At the doctor’s signal, he freezes and holds his breath. The shooting process lasts a few seconds, after which the person gets dressed and waits for the specialist to take the picture.
- MRI. After determining the location of the spinal lesion, the doctor directs the patient to undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the affected area. The study shows the condition of soft tissues, including nerve fibers. To do this, the patient lies down on a couch that slides inside the MRI machine. It revolves around a person and takes a series of layer-by-layer photographs. The results are recorded on disk and given to the patient.
- Electromyography. To determine the degree of muscle damage, the patient undergoes a bioelectrical study procedure. To do this, he is placed on a couch, and surface or needle sensors are attached to his skin. After turning on the device, the person is asked to relax, tense up, and take a deep breath. The device records the nature of the response impulses, and the specialist deciphers the result and gives recommendations for treatment.
- Lumbar puncture. The study reveals the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in the cerebrospinal fluid. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The patient is positioned on his side in the fetal position. The doctor inserts a thin needle under the covering of the spinal cord. He draws in some liquid and takes it to the lab for analysis. The patient should be at rest for several hours after the puncture, after which he can go home.
At a follow-up consultation, the neurologist examines the test results, makes a final diagnosis, and explains how to treat radiculopathy.
Treatment options for radiculopathy
Treatment of the disease depends on its stage. At the initial stages, the doctor prescribes conservative therapy. It includes taking medications, courses of physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises.
Medicines for the treatment of radiculopathy
Mydocalm for the treatment of radiculopathy
The acute form of radiculopathy is characterized by attacks of severe pain. To improve your well-being, the doctor prescribes a set of medications. This list includes:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs can suppress the production of special enzymes - cyclooxygenases, which trigger the body's response to pain, fever, and inflammation. The price of Diclofenac is 120 rubles in Russia (51 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 40 mg. Analogues - Ibuprofen, Indomethacin.
- Painkillers. Medicines do not eliminate the cause of the pain, but they help a person take a break from unpleasant symptoms, get to the hospital or home, and fall asleep at night. The tablets are taken on a full stomach, washed down with a large volume of clean water. The price of Baralgin is from 430 rubles in Russia (170 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 5 ampoules. Analogues - Analgin, Ketorol.
- Muscle relaxants. Medicines block impulses in skeletal muscles. As a result, the tone decreases, relaxation occurs, until the patient is completely immobilized. The products have a mild analgesic effect. The price of Mydocalm is from 420 rubles in Russia (156 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 30 tablets. Analogues - Metacin, Prorezin.
- Chondroprotectors. The medicine restores cartilage tissue, activates the production of intra-articular fluid, and has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. The drugs are produced in the form of tablets and ointments. The price of Chondroitin is 560 rubles in Russia (236 hryvnia in Ukraine) for 60 capsules. Analogues - Artra, Dona.
Treatment procedures for radiculopathy
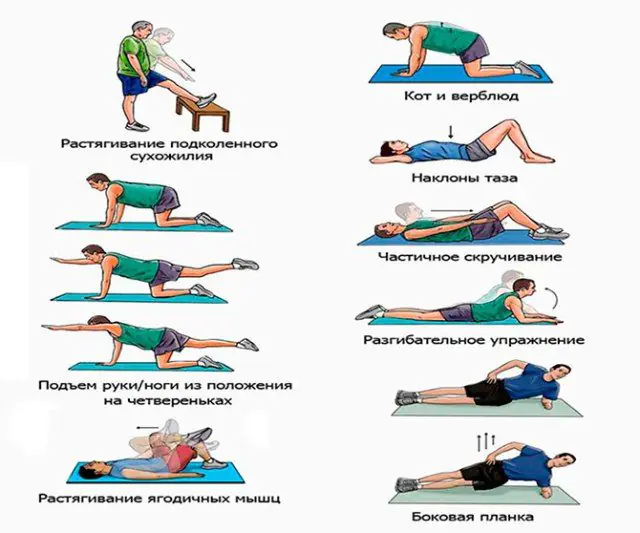
In addition to drug therapy, the doctor prescribes massage courses. During the session, the specialist warms up the muscles with light patting movements, and then rubs, kneads the skin, and hits it with the edge of the palm. As a result, spasms are relieved, blood circulation and lymphatic drainage are improved.
Therapeutic gymnastics prevents further displacement of the spinal disc, strengthens the back muscles and overall human health. The complex compiled by the doctor includes bending and arching the back, turning the torso to the sides, and pulling the knees to the chest.
It is useful for patients with radiculopathy to swim, take a leisurely walk, or hang on a horizontal bar.
To restore spinal mobility, the doctor prescribes a course of physical therapy. The most effective procedures include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, shock wave therapy, and ultraviolet irradiation. The result can be seen after 10-12 sessions.
Surgery for radiculopathy
Discectomy surgery for radiculopathy
The operation is prescribed for patients with persistent acute pain, numbness of the limbs, problems with urination, and sexual dysfunction associated with radiculopathy.
There are several methods of surgical intervention.
- Laminectomy - removal of part of the bone. As a result, the space in the area of the pinched root expands. The person feels a weakening or elimination of symptoms.
- Chemonucleolysis — dissolution of intervertebral hernia by slowly introducing a special solution. Indications for its implementation are protrusion of the spine (without the development of complications).
- Discectomy — partial or complete removal of the vertebral disc. Depending on the patient’s condition, the operation is performed open and endoscopically.
Surgical procedures for radiculopathy are considered complex and are performed under general anesthesia. Before performing them, the doctor makes sure that there are no contraindications: pregnancy, bleeding disorders, acute period of a chronic disease.
Prevention of radiculopathy

Radicular syndrome cannot be completely cured. However, the patient can achieve a state of stable remission. To do this, he must change heavy physical work, reduce sports activities, and temporarily give up active recreation.
If you have radiculopathy, monitor your daily caloric intake. If you become overweight, switch to a safe diet based on the consumption of easily digestible foods: lean fish, poultry, fermented milk drinks, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Buy an orthopedic mattress of medium hardness. Make sure that during sleep the spine is in a comfortable position, does not pinch the nerve endings, and does not arch. Do not carry backpacks or bags on one shoulder.
Give up weightlifting, mountain climbing, and all types of wrestling. Instead, if you have radiculopathy, do yoga, walk, or swim in the pool. Spend your holidays in specialized sanatoriums in environmentally friendly places.
What is radiculopathy - watch the video:



