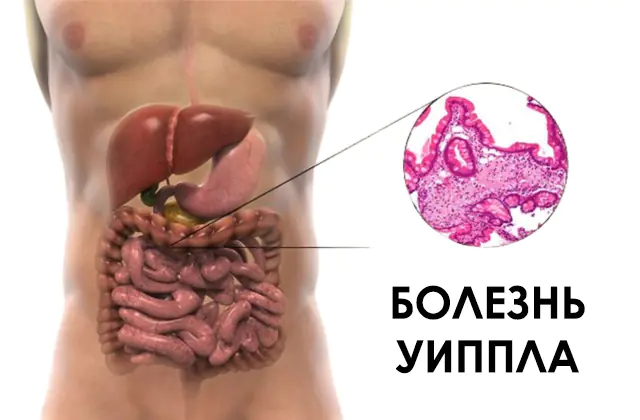
What is Whipple's disease and what causes it? Symptoms, diagnostic measures. Treatment and methods of prevention.
The content of the article:- Causes of Whipple's disease
- Main symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
Whipple's disease is a rare infectious pathology that affects the lymphatic system of the small intestine and the synovial membranes of the joints. Pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in the mucous membrane of the small intestine in excess quantities, which leads to impaired absorption of nutrients. Treatment for Whipple's disease is long-term and involves the use of antibiotics and corticosteroids.
Causes of Whipple's disease
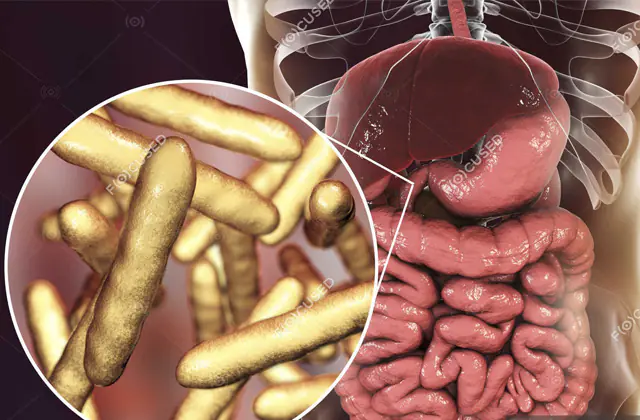
3D model of Tropherim microorganisms - the causative agent of Whipple's disease
Whipple's disease is a pathological process that was discovered by pathologist J. Whipple at the beginning of the twentieth century. During the autopsy, the doctor discovered that there were multiple lipid accumulations on the walls of the small intestine. The pathogenesis of Whipple's disease is based on a violation of the process of synthesis and breakdown of lipids. The disease is infectious in origin and occurs in 1 out of several million patients. Men over 45 years of age are at risk.
The causes of Whipple's disease are associated with exposure to gram-positive pathogenic microorganisms (tropherime), which have a three-layer cell wall. The pathogen was identified in the early 90s thanks to PCR diagnostics. First, Whipple's tropherim affects the mucous membranes of the small intestine, after which, along with the bloodstream, they penetrate the brain, heart, liver, joints, and organs of vision.
Pathogenic microorganisms can be detected in the tissues of the mucous membrane if the pathological process is active. Tropherimes are also present in saliva, even during remission. Patients with Whipple's disease have impaired humoral and cellular immunity, and there are signs of adrenal dysfunction.
The route of infection for Whipple's tropherima is fecal-oral, especially in childhood. Cases have been recorded in which whole families fell ill, but the reliability of the information that the disease is transmitted from patient to patient has never been confirmed.
According to the stages of development of the pathological process, the disease is characterized by extraintestinal manifestations, impaired absorption of nutrients in the small intestine, and multiple organ manifestations.
Whipple's disease is a chronic pathology with long-term remissions and relapses. If there is no preventive therapy, complications appear during the period of repeated exacerbation of the pathological process. Dangerous disturbances in the functioning of the body, including death, are observed. Coordination of movement is impaired, and the likelihood of developing dementia increases. If the spinal cord and cerebral cortex are affected, the development of seizures, tremors, and deterioration in psycho-emotional and physical well-being are observed.
The prognosis is relatively favorable with timely detection and treatment of the disease. Patients note a significant improvement in their well-being just a few weeks after starting therapy. However, it is possible to achieve full regression only with the help of long-term, persistent treatment and compliance with all the recommendations of the attending physician. At the first symptoms of improvement, you should not interrupt the treatment regimen, so as not to provoke a re-exacerbation of the disease.
Main symptoms of Whipple's disease

Whipple's disease is multifactorial, that is, it affects many organ systems, including the central nervous and cardiovascular, and lungs.
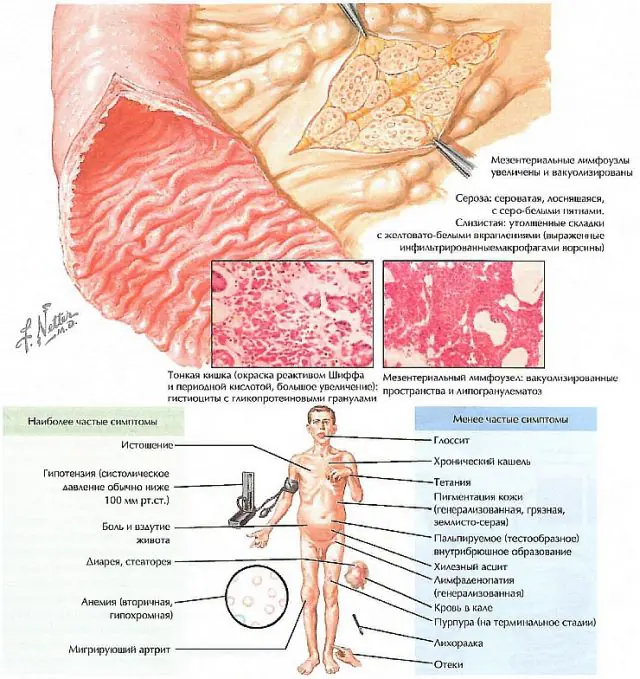
Symptoms of Whipple's disease include diarrhea, fever, and joint pain. The disease also has symptoms similar to malabsorption: diarrhea, flatulence, foul gas, thirst, increased drowsiness, lethargy, apathy, muscle weakness. Feces are not formed, have a pasty or liquid consistency, and an unpleasant odor. The frequency of bowel movements is up to 5-7 times a day.
Depending on the stage of development of the pathological process, characteristic complaints arise:
- The extraintestinal stage is accompanied by fever and polyarthritis.
- Intestinal - diarrhea, protein deficiency, weight loss, hypovitaminosis, impaired absorption of fats and nutrients.
- Systemic manifestations develop in the form of neuralgia, pancarditis and other disorders of the central nervous, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems.
With symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, patients complain of decreased blood pressure, hyperpigmentation of the skin, anorexia, disturbances in sodium concentration, a sharp drop in blood sugar levels, which causes tremors, increased aggressiveness, weakness, and darkening of the eyes.
If Whipple's disease affects the skin, symptoms of erythema are observed; organs of vision - uveitis, keratitis, retinitis; cardiovascular system - pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis.
If the causative agent of the disease reaches the central nervous system, it significantly reduces hearing and vision, and damage to the nerve endings localized in the skull is observed.
Diagnosis of Whipple's disease
Whipple's disease is diagnosed by a gastroenterologist. He asks the patient about emerging symptoms and medical history. Prescribes a biopsy of enlarged lymph nodes and the mucous membrane of the small intestine, a coprogram (stool examination), radiography of the esophagus, ultrasound diagnostics, MRI and CT of the peritoneal organs. A histological examination of the obtained samples is carried out.
Features of diagnosing Whipple's disease:
- Laboratory blood tests can reveal anemia, reduced protein concentration, impaired albumin production, and micronutrient deficiency.
- Radiation diagnostics using contrast agents can reveal how thick the mucous membrane is, how dilated the intestine is, and whether there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes.
- Endoscopic diagnosis determines whether there is edema and how thick and stretched the folds of the duodenum are. Preference is given to enteroscopy and fibroduodenoscopy.
- Thanks to histology, undigested pathogenic microorganisms are identified, which are accurately identified by PCR diagnostics.
Whipple's disease must be differentiated from the following pathological conditions: celiac disease (gluten intolerance), connective tissue diseases, infective endocarditis, Crohn's disease.
Treatment options for Whipple's disease
For Whipple's disease, long-term (at least 1 year) drug therapy under the supervision of the attending physician is indicated. The diet involves increasing the amount of protein in the diet to 150 g and reducing fat to 30 g per day. The patient must receive sufficient nutrients for the normal functioning of the body. To correct metabolic disorders, enteral nutrition mixtures are used, as well as albumin and amino acids. To confirm the effectiveness of therapy, an assessment of the patient's well-being, as well as the results of histological studies and biopsy, is required. The most favorable option for successful treatment for patients is to achieve a pronounced, stable remission.
Medications for Whipple's disease
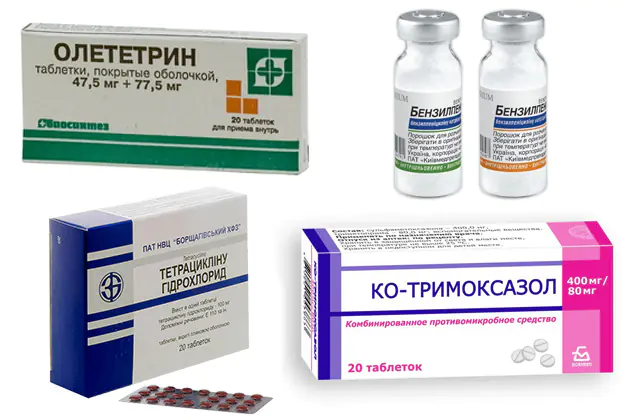
Drug therapy for Whipple's disease involves the use of antibacterial drugs:
- Tetracycline hydrochloride. At the first stage, antibacterial drugs are used that penetrate well through the blood-brain barrier. The drug is taken for 3-4 months. After achieving and maintaining remission, they switch to the following regimen of using the medication: every 48-72 hours for 7-9 months. With good results, you can take tablets every 4 days. The cost of the drug is 50 rubles. (20 UAH). Analogue - Oletetrin.
- Co-trimoxazole. Also used in complex therapy of Whipple's disease. This is a complex antimicrobial medicine that blocks bacterial cell division. Available in the form of tablets for internal use. The drug is taken 2 tablets twice a day. It is necessary to ensure that the interval between the use of tablets does not exceed 12 hours. Price - 30 rub. (12 UAH). Analogues: Baktekod, Bi-Septin, Groseptol, Duo-Septol.
- Benzylpenicillin. If cerebral lesions are detected, the use of drugs containing benzylpenicillin is indicated. Their parenteral administration is indicated for 14 days, followed by a transition to Co-trimoxazole. The drug is used for 12-24 months, until negative PCR diagnostic results are achieved. Cost - 23 rubles. (9 UAH). Analogues: Bicillin-5, Procaine Penicillin.
As an addition to the basic antibacterial treatment of Whipple's disease, the following is used:
- Prednisolone. A drug with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. The dosage of tablets is calculated depending on the body weight and age of the patient. Do not use for ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum, kidney dysfunction. Cost - 100 rubles. (40 UAH). Analogue - Methylprednisolone.
- Bifiform. A drug for the correction of microflora disorders caused by the use of antibiotics. It is recommended to use simultaneously with antibiotics prescribed by the doctor. The drug helps eliminate manifestations of dysbiosis in the form of bloating, stool disorders and intestinal motility. The product is taken 1-2 capsules once a day. Price — 440 rub. (170 UAH). Analogues: Probiz, Bifidumbacterin.
- Penzital. An enzyme preparation based on pancreatin, which is produced in the form of tablets for internal use. Helps with conditions that are accompanied by pancreatic insufficiency. Copes with flatulence, diarrhea, dyspepsia. Cost - 155 rubles. (60 UAH). Analogs: Digestal, Wobenzym, Zentale, Creon.
- Regidron. A drug for the correction of water and electrolyte disorders based on sodium chloride, sodium citrate, potassium chloride. A bag of powder must be dissolved in 1000 ml of water and used within 24 hours. Duration of therapy is up to 72 hours, unless the doctor recommends a different dosage regimen. Cost - 620 rubles. (240 UAH). The drug has no exact structural analogues.
- Multi-tabs Intensive. Multivitamin complex to replenish deficiencies based on fat-soluble vitamins and minerals. Used for hypo- and vitamin deficiencies, and for mineral deficiency. It has a beneficial effect on the immune system, improves physical and psycho-emotional state. Tablets are taken 1 pc. 1 time per day during meals. Cost - 440 rubles. (170 UAH). Analogue - Complivit.
Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a gastroenterologist. Regular diagnostics are required to monitor the dynamics of treatment and adjust drug doses or change the treatment regimen. Self-medication is unacceptable, as it can cause irreversible complications.
Folk remedies for Whipple's disease

Traditional medicine is not able to completely cure the disease and is used to alleviate the clinical picture along with medications and diet correction.
Effective folk recipes for the treatment of Whipple's disease:
- Chamomile is mixed with yarrow and calendula flowers, pour 600 ml of boiling water and leave on low heat for 20 minutes. The resulting drink is cooled, filtered and taken 1/3 glass twice a day before meals.
- Pour boiling water over the tansy and leave for 30 minutes. Take instead of tea 1-2 times a day. Honey can be used as a sweetener.
- A herbal mixture based on burnet, alder cones, bird cherry berries, fennel fruits, mint, St. John's wort, chamomile is poured with hot water and boiled in a water bath for 20 minutes. Leave for 40 minutes, filter, take 30 ml three times a day before meals.
- Mint is mixed with rose hips, chamomile, yarrow, poured with hot water, and boiled for 15 minutes. Take 1/3 cup 2-3 times a day for 10 days. Then you can take a break and repeat the course of treatment again.
- Mix 3 tablespoons of lungwort with the same amount of flax seeds, cinquefoil rhizomes and rose hips. Pour into a thermos, pour boiling water, leave for at least 6 hours, it is better to leave the drink overnight. Take 1 glass 60 minutes after meals for 20 days.
- To provide a pronounced antibacterial effect, they use the following herbal mixture: wormwood is mixed with yarrow, wild rosemary, tansy, and plantain. The active ingredients are boiled in a water bath for 20 minutes, left for half an hour, filtered and taken 1/4 cup twice a day after meals. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- A mixture based on sage, calendula, celandine and eucalyptus exhibits bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties. The dried raw materials must be mixed in equal proportions and used to prepare infusions and decoctions. Take 100 ml 1 time per day before going to bed.
If, while using recipes for traditional treatment of Whipple's disease, the patient's well-being worsens and new symptoms appear, this must be immediately reported to the attending physician.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well, give up bad habits, maintain a drinking regime, and give preference to moderate physical activity: walking in the fresh air (at least 10,000 steps per day), yoga, swimming. It is important to undergo regular preventive examinations with a gastroenterologist. Patients with a history of Whipple's disease are advised to undergo clinical examination in the gastroenterology department every 2-4 months and consult with an infectious disease specialist every six months.
What is Whipple's disease - watch the video:



