One of the most malignant forms of tumor is melanoma on the face. One of the most malignant forms of tumor is melanoma on the face. However, it is 10 times less common than skin cancer. Every year the incidence of this disease increases. Thus, out of 100 thousand people, approximately 6 people fall ill. Moreover, the disease is observed mainly in women. If we talk about the age of patients, the standard is 30-40 years.
Symptoms of the disease
In appearance, lip cancer resembles a small formation or compacted area. It protrudes above the surface of the lip and is clearly visible even in the photo. Ulceration appears in the central part of the melanoma.
Basically, the formation is located at some distance from the midline, on the red border of the lower lip. The consistency of melanoma is dense, inflammation grows and changes shape (you can see this in the photo). In some cases, the tumor takes the form of a fissure or papilloma. Bleeding may occur and scales may be present. Initially, melanoma may resemble an ulcer. At the same time, it penetrates deeply into the tissues, and a transition to nearby tissues is observed. Metastases develop quickly.
In appearance, lip cancer resembles a small formation or compacted area
Classification
In most cases, a tumor on the lip is squamous cell carcinoma. He can be:
The keratinizing variety practically does not metastasize. Growth is superficial and the flow is slow. Non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma has infiltrative growth. In this case, metastases may appear and ulcerations may occur. You can see what both varieties look like in the photo. Sometimes neuroendocrine carcinomas and carcinomas of the minor salivary glands occur.
Metastasis, as a rule, goes to the lymph nodes of the cervical region.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lip
Clinical forms
Lip cancer can have the following forms.
- Endophytic cancer may be ulcerative-infiltrative or ulcerative. The course is malignant. The ulcer goes deep, its edges turn outward, and infiltration of the dermis occurs. There is no pain.
- Exophytic forms: verrucous and papillary. The warty form is formed against the background of productive dyskeratosis. In this case, there are many growths on the lip. Papillary cancer can develop from papilloma. It grows, acquiring a round shape. Next, a scab appears, and infiltration is noted at the base of the neoplasm. Then the papilloma falls off, and the infiltration becomes stronger.
Endophytic squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip
Why does she appear
The development is mainly due to Durey's melanosis, the presence of acquired or congenital moles. Depending on the location, different types can be distinguished:
- intradermal;
- epidermo-dermal;
- mixed.
You can see what they look like in the photo.
Factors influencing the appearance of melanoma include:
- restructuring of the body;
- injuries;
- hormonal disbalance;
- ultraviolet irradiation.
In 40% of cases, the tumor is caused by trauma. In southern regions and countries, the risk of occurrence is due to exposure to the sun. In some cases, changes in hormonal levels can contribute to the regression of melanoma and inhibition of its development.
Particular attention should be paid to borderline nevi, which have a dry, smooth surface without hair. The size of such a formation often does not exceed one centimeter. The tumor is painless, soft, and rises above the skin. Mixed forms are quite rare, dermal ones too.
In 40% of cases, the tumor is caused by trauma
Another cause of inflammation is lip diseases, namely cheilitis. They arise due to trauma to the area by various irritating factors:
- sudden changes in humidity and temperature;
- eating very cold or hot food;
- chewing tobacco or betel nut;
- strong coffee;
- exposure to direct sunlight;
- strong alcoholic drinks;
- viral infections;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Smoking has been proven to play a big role.
At-risk groups
Lip cancer is a malignant tumor arising from the epithelium of the red border of the lips. Look at the photo to see what it looks like. In 70% of cases, patients are men. Typically, cancer occurs on the lower lip.
Precancerous processes – various diseases of the lips: papillomas, chronic cracks, various inflammatory processes. Since the tumor on the lip is a neoplasm of external localization, it is not difficult to diagnose. About 85% of melanomas are detected already at stages 1 and 2.
Typically, cancer occurs on the lower lip
Treatment of lip melanoma
Previously, surgery was considered dangerous. Now this method is used to remove any nevi that do not extend beyond the healthy tissue. This process guarantees a complete recovery.
Forecasts
The prognosis depends on how well the treatment was chosen and on the stage. The five-year survival rate for the first stage is 90%. At subsequent stages it decreases to 70%.
How to recognize melanoma (video)
Disease prevention
You can protect yourself from lip melanoma by following these rules:
- the skin of the lips must be protected from the sun;
- you should stop smoking;
- precancerous processes must be treated in a timely manner;
- When working in hazardous industries, annual medical examination of employees is recommended.
The prognosis for melanoma on the lip depends on the stage of the disease and the timeliness of treatment
Melanoma located on the face is considered one of the most dangerous forms. However, it occurs quite rarely. In appearance, the neoplasm resembles a compaction. Ulcerations and ulcers may sometimes occur. As a rule, metastases go to the lymph nodes of the neck. The main cause of the disease is constant trauma to the lips. The risk group is men aged 30 to 40 years. Treatment is surgery. The prognosis depends on the stage of the disease and the timeliness of treatment. If the tumor is detected at an early stage, melanoma can be successfully treated.

Melanoma is considered one of the most insidious human malignant tumors, the morbidity and mortality from which is steadily increasing from year to year.
They talk about it on TV, write in magazines and on the Internet. The interest of ordinary people is due to the fact that the tumor is increasingly being detected in residents of various countries, and the number of deaths is still high, even despite intensive treatment.
In terms of prevalence, melanoma lags significantly behind epithelial skin tumors (squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, etc.), according to various sources, accounting for 1.5 to 3% of cases, but it is much more dangerous. Over the 50 years of the last century, the incidence increased by 600%. This figure is enough to seriously fear the disease and look for the causes and methods of treating it.
What it is?
Melanoma is a type of cancer that affects melanocytes—pigment cells located in human skin. The disease has a high risk of rapid metastasis, which leads to the development of severe complications and, in severe cases, death of the patient. Every year, about 50 thousand new cases of melanoma are registered in the United States.
Melanoma is more susceptible to white-skinned older people (55-70 years old), but young people over 30 are also at risk of its occurrence. In almost all cases, the tumor is preceded by changes in the form of age spots, moles, dermatitis and other precancerous conditions. Melanoma is often detected at the metastatic stage, but even timely diagnosis often leaves no chance for a favorable outcome due to the extreme malignancy of the neoplasm.
The first link in the timely diagnosis of the disease is the patients themselves, since melanomas usually occur on open, visible areas of the skin. This is important because early detection and diagnosis of melanoma ensures rapid cure with minimal surgery.
Epidemiology
According to WHO, in 2000, more than 200,000 cases of melanoma were diagnosed worldwide and 65,000 melanoma-related deaths occurred.
In the period from 1998 to 2008, the increase in the incidence of melanoma in the Russian Federation was 38.17%, and the standardized incidence rate increased from 4.04 to 5.46 per 100 thousand population. In 2008, the number of new cases of skin melanoma in the Russian Federation amounted to 7,744 people. The mortality rate from melanoma in the Russian Federation in 2008 was 3159 people, and the standardized mortality rate was 2.23 people per 100 thousand population. The average age of melanoma patients diagnosed for the first time in their lives in 2008 in the Russian Federation was 58.7 years. The highest incidence was observed at the age of 75-84 years.
In 2005, the United States recorded 59,580 new cases of melanoma and 7,700 deaths due to this tumor. The SEER (The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) program notes that the incidence of melanoma increased 600% from 1950 to 2000.
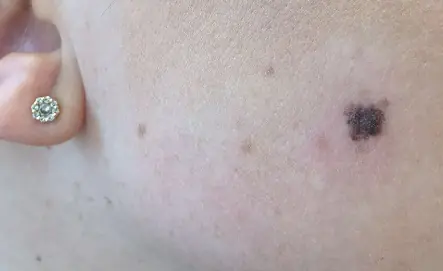
Causes of melanoma development
The reason for the formation of melanoma in the initial stage is the degeneration of melanocytes into malignant cells.
The main theory that explains this process is molecular genetics. Defects appear in the DNA molecule of the pigment cell. Further, under the influence of provoking factors, a gene mutation occurs, associated with a change in the number of genes, disruption of the integrity of chromosomes or their rearrangement. The changed cells acquire the ability to divide unlimitedly, as a result of which the tumor increases in size and metastasizes. These disorders can occur under the influence of unfavorable factors of internal and external properties or a combination of them.
Causes and risk factors:
- Prolonged exposure to the sun. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, including solariums, can cause the development of melanoma. Excessive sun exposure in childhood significantly increases the risk of disease. Residents of regions with increased solar activity (Florida, Hawaii and Australia) are more susceptible to developing skin cancer. Burns caused by prolonged exposure to the sun more than double the risk of developing melanoma. A visit to the solarium increases this indicator by 75%. The WHO Cancer Research Agency classifies tanning equipment as an "increased risk factor for skin cancer" and classifies tanning equipment as carcinogenic.
- Moles. There are two types of moles: normal and atypical. The presence of atypical (asymmetrical, raised above the skin) moles increases the risk of developing melanoma. Also, regardless of the type of moles, the more there are, the higher the risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor;
- Skin type. People with more delicate skin (characterized by light hair and eye color) are at increased risk.
- Anamnesis. If you have previously had melanoma or another type of skin cancer and are cured, your risk of developing the disease again increases significantly.
- Weakened immunity. The negative impact of various factors on the immune system, including chemotherapy, organ transplantation, HIV/AIDS and other immunodeficiency conditions, increases the likelihood of developing melanoma.
Heredity plays an important role in the development of cancer, including melanoma. Approximately one in ten patients with melanoma has a close relative who has or has had the disease. A strong family history includes melanoma in parents, siblings, and children. In this case, the risk of melanoma increases by 50%.
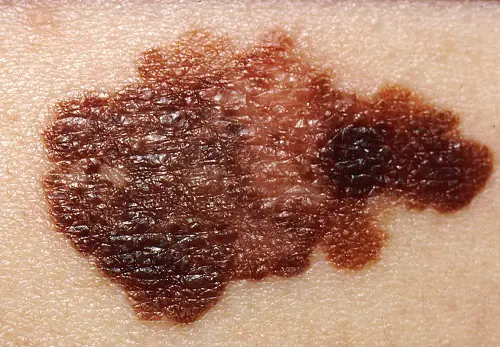
Classification
Clinical forms of the disease:
- Superficially spreading, or superficial. It is observed in 70% of patients, more often in women. This melanoma is characterized by a long period of benign growth. It grows into deeper layers after a long time and has a favorable prognosis.
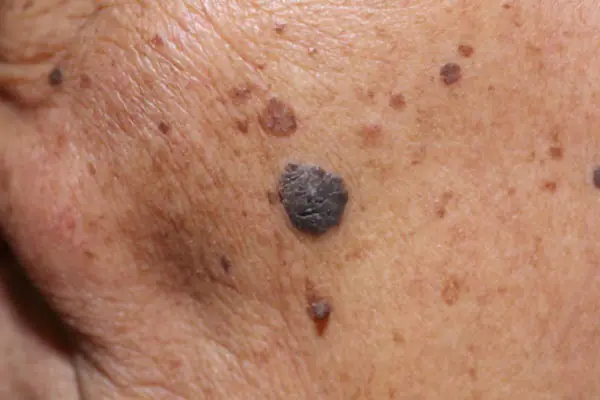
- Nodular (nodular). Invasive variant of the tumor. It quickly grows deep into the skin and looks like a convex round bump. The pigmentation of such a formation is usually black, less often than other dark shades, or is not changed at all. Often, nodular melanoma is detected in elderly people on the limbs and trunk.
- Acrolentiginous. It develops on the surface of the skin and later grows deeper. A distinctive feature is the localization of symptoms - the tumor occurs on the palms, soles or under the nails. This melanoma appears more often in blacks and Asians.
- Lentiginous, or malignant lentigo. The neoplasm in appearance resembles a large flat birthmark. Nests of melanocytes form in the epithelial layer, from where they penetrate inside. It is more common in elderly women over 70 years of age on the face, neck and back of the limbs.
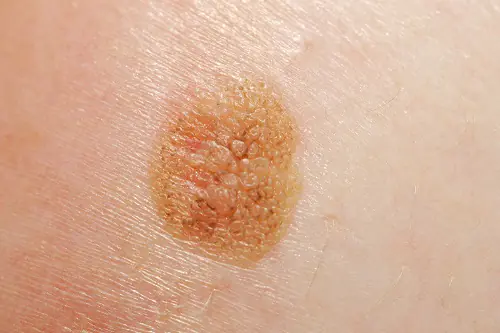
- Pigmentless (achromatic). It occurs quite rarely, in 5% of cases. Changed pigment cells lose the ability to synthesize pigment, so these formations are pink or flesh-colored. A non-pigmented tumor is considered as one of the varieties of the nodular form or is considered a manifestation of metastases on the skin.
Symptoms of melanoma in the initial stage
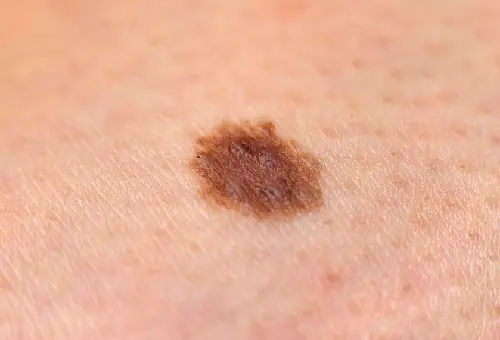
At the initial stage, melanoma (see photo) is no different from an ordinary mole. The main symptoms of the onset of the disease include the following:
- The mole began to grow and bleed and became darker;
- The mole began to itch.
These are the main symptoms that require immediate consultation with an oncologist. Also, do not postpone your visit if the number of moles suddenly increases sharply.
In the initial stage, the thickness of the formation does not exceed 1 mm. A mole that has just begun to degenerate is practically indistinguishable from an ordinary one. An already developing malignant neoplasm can have any size and shape, be weeping, covered with nodes, and bleed. The tumor has a dense consistency and often rises above the skin. The color can be black, brown, blue, gray. Not often, but there are cases when a melanoma lesion does not change color and remains light, similar to ordinary hypomelanosis.
Melanoma can occur in any area of the body. However, most often in women it is diagnosed on the lower leg, and in men - on the back. In older people, the tumor is more often localized on the face. In half of the cases, the formation develops on healthy skin, and in the remaining cases - on the site of pigmented nevi.
Melanoma on the iris of the eye looks like a dark spot of irregular shape; the subungual formation looks like a strip located under the nail plate on the cuticle.
Superficial forms tend to grow slowly, while nodular forms can go through several stages of development in a few weeks.
When a mole becomes malignant, changes can be observed:
- Increased pigmentation;
- Uneven color (presence of several shades);
- Shiny surface of the formation;
- Redness of the surrounding area;
- Blurred edges of the mole, jagged borders;
- Lack of hair;
- The lesion may exceed 5 mm;
- The appearance of nodular small papillomatous elements in the area of the nevus;
- Itching and burning.
As the formation grows and the stage moves to a more serious stage, a more pronounced clinical picture develops.
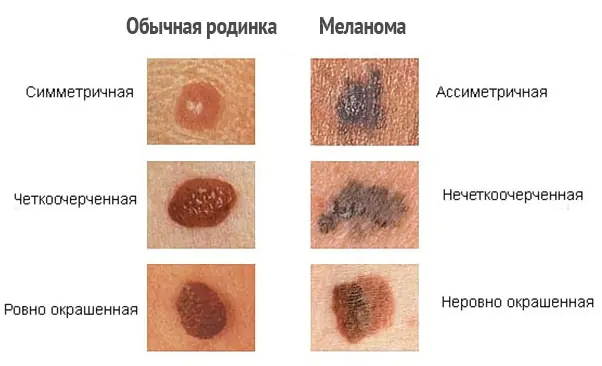
How to distinguish melanoma?
In order to correctly distinguish melanoma and notice the first signs of malignancy, it is necessary to distinguish skin formations, that is, to know the difference between freckles, moles, and nevi. Unfortunately, even many experts confuse these definitions with each other.
| Name | Description |
| Moles | Oval or round formations, dark brown or flesh-colored. The diameter of moles varies from 0.2 to 1 centimeter. As a rule, moles are flat, but sometimes they can rise above the level of the skin. |
| Freckles | Flat, light brown, rounded spots on the skin that darken in the sun and turn pale in winter. |
| Atypical or dysplastic nevi | Larger moles, with uneven edges and uneven coloring. |
| Malignant melanoma | Pigmented and non-pigmented formations on the skin, arising both independently (de novo) and on changed skin (that is, from previous moles). Melanoma develops from the pigment cells (melanocytes) of the skin. Further growing deeper, the tumor acquires the ability to metastasize through the lymphatic and blood vessels to any part of the body. |
Every pigmented formation, be it an old mole or a new nevus, in people over 20–30 years of age should be examined with suspicion of melanoma. In addition to periodic examinations by a dermatologist and oncologist, additional studies should be carried out.
Diagnostics
The quality of melanoma treatment and the prognosis of the disease directly depend on the early diagnosis of the lesion. To determine an oncological diagnosis, an oncologist performs a visual examination of the pathology area. A detailed examination of a malignant neoplasm is carried out using a dermatoscope, which is a special device for viewing pathology in an enlarged form.
In modern oncology clinics, digital dermatoscopes are used, which allow one to view a malignant neoplasm in a three-dimensional image on a monitor screen. An effective additional method for diagnosing melanoma is a blood test for cancer (tumor markers are specific proteins, the concentration of which increases with cancer).
All cancers undergo a biopsy at the final stage of examination. Cytological and histological studies of biological material taken from the primary cancer focus make it possible to establish a final diagnosis indicating the stage and form of oncology.
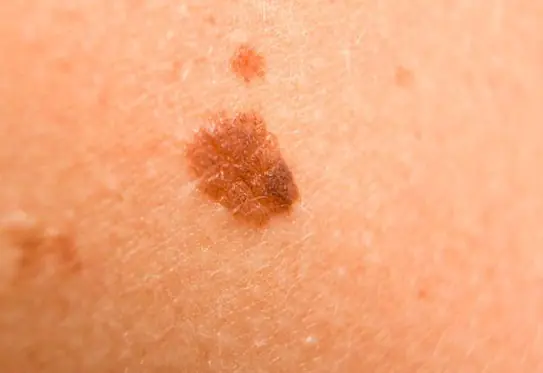
Photo: what melanoma looks like
Below are numerous photos that will help you understand what melanoma looks like in the initial as well as more advanced stages:
How to treat melanoma in the early stages
The main treatment method for early-stage melanoma in 2019 is surgical removal. Both for the primary tumor and for the treatment of relapses, sheath-fascial excision of the tumor is performed. The tumor is removed along with the adjacent area of apparently unchanged skin - depending on the stage, at a distance of 1 cm to 2-3 cm. Together with the tumor, the subcutaneous tissue is removed to the aponeurosis or fascia of the underlying muscle, followed by plastic surgery. Removal of the fascia itself is a controversial issue and is not accepted by some authors. If lymph nodes are affected, their resection is performed.
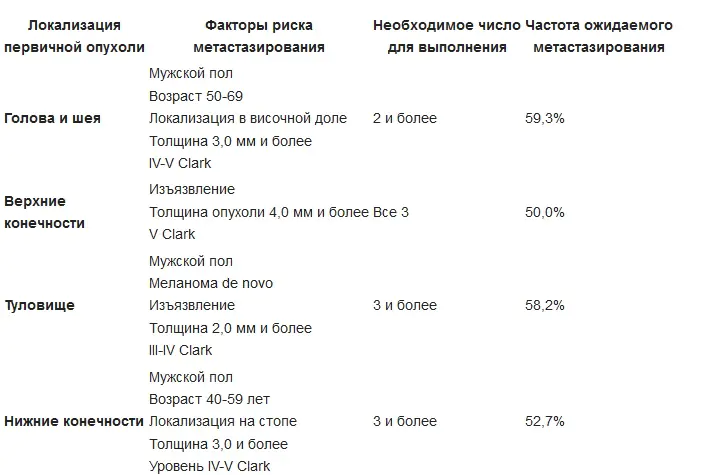
Indications for regional lymphadenectomy for primary cutaneous melanoma:
An option for surgical treatment may be Mohs surgery (Frederick Mohs) - surgical interventions under the control of a microscope, as well as laser sheath excision. Cryodestruction of melanoma is not used due to the fact that the level of invasion into the underlying tissue cannot be accurately determined.
Treatment of melanoma with metastases
The main methods of treating metastatic melanoma are polychemotherapy, immunotherapy and radiation therapy, which are usually used in combination.
Immunotherapy
- Interferon-alpha (IFN-A), interleukin 2 (IL-2) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). A study performed by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) showed that the use of interferon-alpha-2b at maximum tolerated doses provides a significant prolongation of disease-free interval and overall survival compared with no adjuvant therapy.
- Monoclonal antibodies. By prescribing immunotherapy drugs - ipilimumab and nivolumab - to patients with melanoma at stages III and IV, it was possible to achieve tumor reduction in 58% of cases, by more than a third, in the rest - to stop the growth of melanoma for a year. The study results were presented at the 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
- Radiation therapy - total focal dose - 4000...4500 rad. The optimal total dose is 10,000 rad. (Different protocols are different).
- Regional and systemic chemotherapy is used for generalization of the process: dacarbazine (DTIC), carmustine (BCNU), lomustine (CCNU), cisplatin, tamoxifen, cyclophosphamide, etc.
Gene therapy for melanoma is under research, aimed at introducing tumor suppressors p53 gene, p16INK4a, inactivation of the oncogenic signaling pathway - ras, - c-myc, etc.
Research led by Mikhail Nikiforov of the Roswell Park Cancer Institute is in the preclinical stage and shows that the enzyme guanosine monophosphate synthase (GMPS) can trigger the growth of melanoma and could become a target for new drugs against it. The role of GMPS in the development and metastasis of melanoma has now been studied. This enzyme can be blocked using the long-established antibiotic angustmycin A, also known as decoyinine. GMPS levels were found to be elevated in melanoma metastasis samples. Angustimin A is believed to have potential as a targeted therapy for tumors harboring the NRASQ61R or BRAFV600E gene mutation.
A new drug, Keytruda, which was approved by the FDA last year for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer, is undergoing further clinical trials. At this stage, the Sheba State Hospital in Israel is recruiting patients to participate in a clinical trial of the drug in the treatment of melanoma. Foreign patients can also take part in the studies.
Patient monitoring
Patients who have completed radical surgical treatment should be followed up by an oncologist. Observation should be carried out according to the general rules - periodic examinations by a doctor, with control ultrasound examinations.
The rules for clinical observation of patients with melanoma are as follows:
- during preventive examinations, mandatory examination of the skin in the area of the removed tumor;
- mandatory palpation of lymph nodes - cervical, axillary, inguinal-femoral;
- additional ultrasound examination of lymph nodes;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs to exclude metastasis to internal organs;
- If necessary, bone scintigraphy and computed tomography of the brain are performed.
Prevention
Prevention of melanoma involves the use of a cream that protects against ultraviolet radiation and minimal exposure to direct sunlight. It is also necessary to regularly engage in self-examination. In order to answer the question of how long people live with melanoma, it is necessary to understand that it depends on the stage, location, size of the process and the activity of the body’s immune system.
Forecast
With initial and stage II melanoma without relapse, cure is possible; with relapse, the five-year survival rate is approximately 85%, stage III - 50%, stage V - up to 5%.
Melanoma is one of the most common malignant tumor diseases. It appears on the skin, including the face. According to statistics, it occurs in medical practice ten times less often than cancer, but is very dangerous. Every year the number of patients increases.
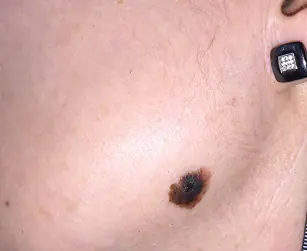
Melanoma occurs on soft tissues, including the lips
The risk group includes women aged 30-40 years. Mucosal melanoma affects soft tissues and causes the spread of metastases to various organs. If the disease is not diagnosed in time and its treatment is not started, death is possible.
Symptoms of the disease
Upon external examination, you may notice a small growth or lump on the skin. As a rule, it protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin and has an ulcer in the center.
In most cases, the lump appears on one side of the lower lip. It has a dense structure and can change size and shape over time, as the tumor can grow. Sometimes melanoma appears as a papilloma or fissure that has a scaly surface. When such a disease occurs, minor bleeding may occur. At the first symptoms, it looks like a small ulcer has appeared on the lip. It gradually penetrates into the tissue structure, affecting the nearby one.
With melanoma, metastases spread quite quickly. Qualified specialists quickly recognize new growths on the skin, but to people without medical education, they appear to be ordinary moles. It is necessary to know the main features of the disease in order to diagnose it in time.
The following features are considered characteristic signs of melanoma:
- asymmetry of formation, in which an irregular or jagged shape is observed;
- color change, which becomes the first signal about a visit to the doctor;
- the size of melanoma can be more than 6 mm; if it becomes larger, then this is a clear sign that the tumor has begun to grow.
The first signs of the disease include an increase in size and color. After some time, ulceration and bleeding may be added to them. In the first stages of development, there may be no symptoms. Already when metastases appear, the patient begins to feel unwell, see worse, feel pain in the bones and rapidly lose weight. In order not to miss the moment when a benign tumor has become malignant, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time if any neoplasms appear on the skin.
A tumor developing on the lip is most often presented in the form of squamous cell carcinoma, which can be of two types: keratinizing and non-keratinizing.
In the presence of a keratinizing form, metastases practically do not spread. The course of the disease is slow and superficial.
In the case of non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma, infiltrative growth is observed, during which ulcerations appear and metastases spread.
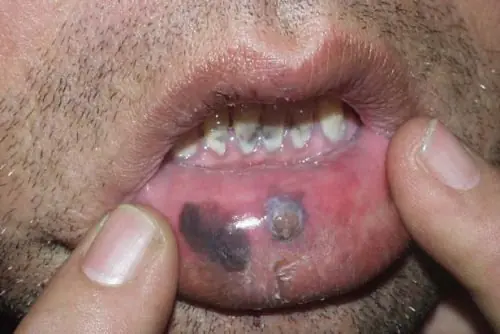
Melanoma on the lip appears as an asymmetrical spot
Classification of the disease
The disease can manifest itself in two forms: exophytic and endophytic.
- Exophytic cancer is presented in the form of warty and papillary type formations. The appearance of warts causes increased keratinization of the skin. In such cases, several growths may appear on the lip. If a papilloma is present on the surface, it can develop into papillary type cancer. It gradually grows and takes the shape of a circle. Having reached a certain stage of development, the appearance of a scab and infiltration at the base of the formation is observed. After that, the papilloma disappears, and the infiltration process intensifies significantly.
- The endophytic form is presented in the form of the appearance of ulcers or ulcerative-infiltrative formations. A malignant course of the disease occurs, followed by penetration of the ulcer into the tissue structure. Infiltration of the epidermis is observed, but there is no pain. Such manifestations are a clear sign that the tumor has long developed into a malignant one, so it is very important not to bring the disease to such symptoms.
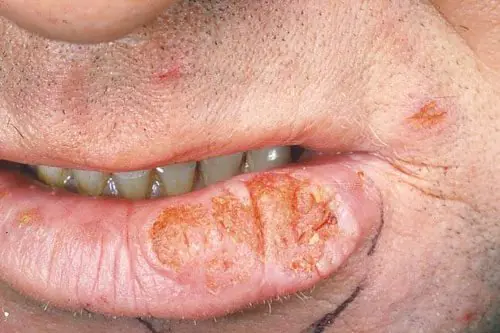
Endophytic melanoma manifests as lip ulceration
Causes of the disease
Melanoma of the lip can be caused by various factors, but the main cause of the disease is Durey's melanoma, as well as acquired and congenital moles that have developed into a malignant tumor. The disease can have different localization. Depending on the location of the disease, melanoma is distinguished:
- epidermo-dermal;
- intradermal;
- mixed.
In the first case, the disease spreads on the surface, in the second - inside the tissue structure, and in the third - there is damage to both external and internal tissue.
The causes of melanoma on the lip may be the following factors:
- disruptions in the functioning of the body;
- previous injuries;
- hormonal imbalance;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays.
According to statistics, in 40% of cases, the disease develops as a result of trauma. In countries located in the south, the disease is caused mainly by increased exposure to sunlight on the skin. In practice, there are also cases when, if the hormonal balance is disturbed, the development of melanoma, on the contrary, regresses.
When examining the skin, it is necessary to pay attention to nevi that have a dry and smooth surface. There is also no hair on such formations. In size, they do not exceed 1 cm.
Another fairly common reason why melanoma develops on the lip is lip disease, cheilitis. The reasons for their appearance may be the following factors:
- changes in temperature and humidity;
- eating hot or cold food;
- systematic chewing of tobacco;
- drinking strong coffee;
- the influence of the sun's rays;
- strong alcoholic drinks;
- infections and viruses;
- lack of hygiene;
- long-term smoking.
The causes of the disease can be different factors, but regardless of their origin, the disease develops rapidly if treatment measures are not taken.

Sun rays activate the process of melanoma formation
Diagnosis of the disease
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis. An experienced specialist identifies a malignant tumor during the initial examination. Next, a series of tests are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. The list of basic diagnostics includes the most effective, as medicine believes today, actions.
- Dermatoscopy. When determining a malignant formation on the lip, a procedure is used that allows you to visually enlarge it and examine it in more detail.
- Biopsy. During this procedure, skin tissue is taken and examined under a microscope. It uses a thin surgical blade to cut off the top layer of skin. Very often, this method is used to determine basal cell carcinoma. There are also other methods for performing this procedure, depending on the type of melanoma on the lip.
- Lymph node biopsy. It is carried out in cases where melanoma has already been diagnosed. It is necessary to detect the spread of cancer.
- Secondary tests. These include: blood tests, computed tomography and positron emission tomography.
Secondary tests are aimed at identifying the extent of cancer development. When donating blood, the lactate dehydrogenase level is examined, an increase in which indicates the spread of metastases.
Computed tomography allows you to examine internal organs and determine the presence of metastases in them. Staging is also used, which allows you to determine the size of the tumor and the extent of its spread.
The choice of method depends on the type of melanoma on the lip.

Using a dermatoscope, the doctor examines the formation
Treatment of the disease
After a thorough diagnosis, comprehensive treatment is prescribed. It consists of various procedures and medications. The list of main treatment methods for melanoma of the lip includes:
- Mosa - micrographic surgery;
- surgical intervention;
- cryosurgery;
- chemotherapy;
- immunotherapy;
- removal of lymph nodes;
- use of monoclonal antibodies;
- use of BRAF inhibitors;
- radiation therapy;
- palliative care;
- use of medications.
The choice of method is based on the stage of the disease, the general condition of the patient and his age.
The main treatment method is surgery, regardless of the stage of melanoma. Most lesions are removed after biopsy analysis. If cancer cells remain after the procedure, an additional operation is performed in which nearby tissue is removed.
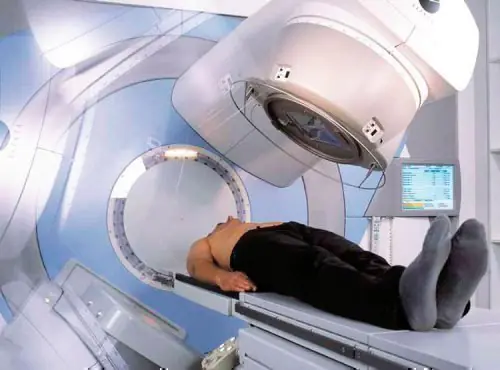
Radiation therapy is one of the methods of treating the disease
More about methods
The Mohs method is also often used for melanoma of the lip - micrographic surgery, which involves the sequential removal of thin layers of skin. After each operation, each layer is examined using a microscope, which allows you to view the presence of cancer.
The use of cryosurgery involves the process of freezing tissue, resulting in its destruction. This method is used extremely rarely.
One of the most common methods of treating melanoma on the lip, which has reached advanced stages of development, is chemotherapy. This is a rather radical measure, but it is also effective. The procedure uses strong chemotherapy drugs. The complex also includes immunotherapy, which is aimed at strengthening the patient’s immunity so that it can cope with cancer cells. It is used after chemotherapy to prevent the appearance of new tumors in the body.
Also, the treatment complex often includes taking BRAF inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies. They allow you to overcome the activity of cancer cells and reduce their development.
The use of radiation therapy, which is aimed at eliminating pain caused by cancer. For melanoma of the lip, it is used extremely rarely.
Palliative therapy is aimed at improving the patient's condition. It helps to cope with pain and prolong life.
Taking medications is aimed at eliminating painful sensations, as well as eliminating the inflammatory process and suppressing cancer cells. Most often, the list of medications includes:
- 5-Fluorouracil;
- Diclofenac;
- Imiquimod;
- alpha interferons;
- vemurafenib;
- monoclonal antibodies.
Taking such medications should be carried out in courses, following all the doctor’s instructions.
Treatment is selected individually, depending on the stage of melanoma. For it to be more effective, it is necessary to diagnose the disease in time and not bring it to a critical state, when it is necessary to apply radical measures. In some cases, even their use becomes useless, since the disease has reached its final stages. Therefore, it is very important to contact a specialist when new growths appear, their color and size change.



