What is myocarditis and why does it occur? Symptoms of the disease. Diagnosis, treatment of the disease depending on the etiology and form. Prevention of myocarditis.
- What is myocarditis
- Why is it developing?
- Main features
- Diagnostics
- How to treat myocarditis
- Prevention
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium), as a result of which its functioning is aggravated. Pathology can lead to sclerotic changes in cells and even death. The statistics are frightening: 9-25% of all cases of sudden death are from damage to heart tissue. The prognosis for the recovery of patients is significantly higher if the disease is detected in the early stages and full treatment of myocarditis is carried out in accordance with medical recommendations.
What is myocarditis?
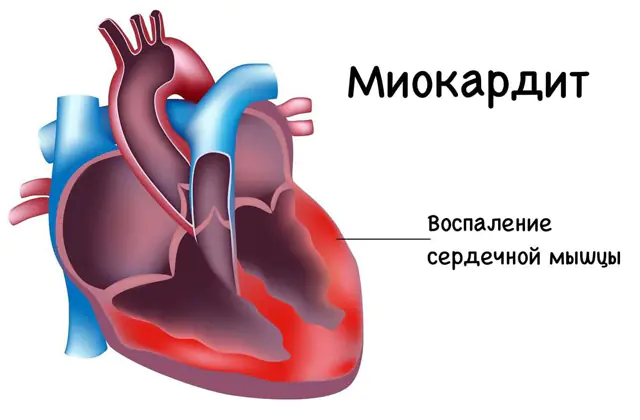
The heart consists of specific muscle fibers, the tissue formed from which is called the myocardium, as well as endothelial and connective tissue. At the same time, the relative sizes of the heart muscle are several times larger than those of the outer and inner layers. Inflammatory damage to these muscle fibers is called myocarditis.
Pathology is quite difficult to account for. According to various sources, in young people who died of unknown causes, autopsies showed signs of heart disease in 2-42% of cases. In HIV-infected patients, this figure is significantly higher - 50% of cases. However, the statistics do not take into account situations where myocarditis caused complications, and the death could not be directly associated with cardiac problems.
In 16% of adults and 46% of children, inflammation of the heart muscle leads to non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy with subsequent development of sudden cardiac death. Men get sick much more often than women, but the disease in the stronger half of humanity is much milder. Myocarditis in children is dangerous due to complications due to late diagnosis, but it is easier to treat in the early stages than in adults.
The classification of the disease is quite extensive. Based on the nature of tissue damage, diffuse and focal forms of myocarditis are distinguished. In the first case, all the muscle tissue of the heart suffers, which is why the symptoms of the pathology are brighter and the course is more acute. The pathology is diagnosed primarily in young people under 40. The focal form is those cases when individual areas of the heart muscle become inflamed. This disease is more treatable, and the likelihood of complete restoration of heart function is much higher.
In domestic medicine, they also use a classification of the disease depending on the provoking factors, the rate of progression and other indicators.
Important! The diagnosis of “myocarditis” is made exclusively during a comprehensive examination and identification of not only the signs of the disease, but also the causes that caused it.Why does myocarditis develop?
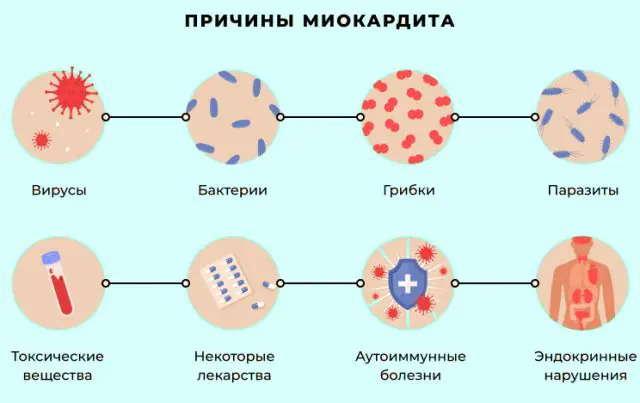
The photo shows the causes of myocarditis
Depending on the causes of myocarditis, several types of the disease are distinguished. The infectious type is caused by viruses (adenovirus, rubella, HIV), bacteria (diphtheria, streptococci, staphylococcus), parasites (toxoplasmosis, the presence of trypanosomes in the body), fungi (cryptococcus, Candida fungus and others).
Non-infectious myocarditis, in turn, is divided into several subtypes:
- rheumaticas a consequence of the development of connective tissue rheumatism (in this case, cardiac dysfunction is also a symptom of the provoking disease);
- allergic- caused by an active reaction of the body to external stimuli, which can be both medications and transplanted organs;
- idiopathic— the etiology of the pathology has not been fully identified, but the symptoms of this subtype are pronounced, and the likelihood of death is much higher.
This classification does not include diseases caused by injuries and exposure to excessive doses of radiation, since they are difficult to classify as classic subtypes of non-infectious pathology. Depending on what causes myocarditis, treatment recommendations may differ slightly. It is extremely important that the pathology is detected as early as possible.
Main signs of myocarditis
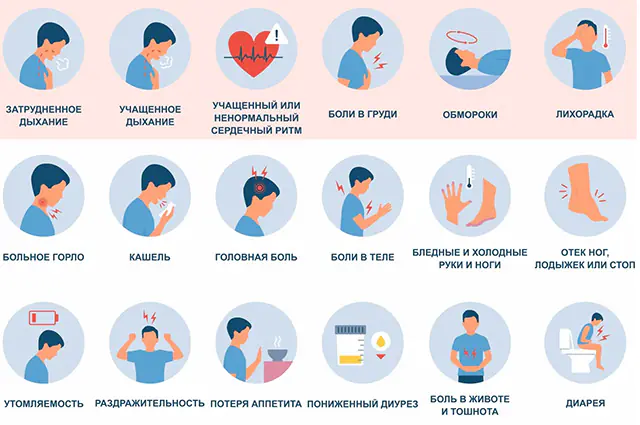
The photo shows the symptoms of myocarditis in adults
The general clinical picture of myocarditis in adults is characterized by the appearance of shortness of breath, heart pain, constant fatigue and a depressive or apathetic state. With systematic measurements of the heart rate, it becomes clear that the heart rhythm is unstable.
Based on the development of symptoms of the disease, several forms of inflammation of the heart muscle are distinguished:
- Lightning fast. Myocarditis develops extremely quickly, the symptoms are pronounced, and have a clearly visible relationship with the viral pathology that caused the inflammation. If the disorder is not properly treated, the likelihood of complications increases - heart failure, hypotension. A distinctive symptom of the disorder is a decrease in the contractility of the heart.
- Acute. It does not develop as rapidly as fulminant myocarditis, but it is also dangerous due to complications; myocarditis of this form can lead to heart failure. A distinctive sign of the disease is the expansion of the cavities of the heart.
- Chronic. Leads to stretching of the heart cavities, the upper level of blood pressure becomes permanently elevated.
Manifestations of myocarditis also depend on the factors provoking the pathology: in infectious diseases, the clinical picture is supplemented by signs of infectious pathology; in the allergic form, joints hurt, the temperature rises, and in idiopathic pathology, a significant increase in heart size may be detected.
Disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle are typical not only for older age groups, but also for children and adolescents. At the same time, the signs of myocarditis from an early age until the end of puberty are somewhat different in comparison with the adult clinical picture. This is due to the physiological specifics of the development of the cardiovascular system.
The child will be sent for examination to diagnose myocarditis if he has the following symptoms:
- does not gain weight in accordance with recommended standards;
- pulse quickens;
- breathing is frequent;
- legs and arms are constantly cold;
- many days of physical lethargy against a background of emotional anxiety.
From 2 years of age, the signs of myocarditis become more pronounced. The child develops swelling in the arms, legs, and eyelids. The baby may complain of chest pain and constant fatigue, and a chest cough appears. In general, the manifestations of myocarditis are quite heterogeneous and nonspecific, so parents should, at the first complaints, take the child to an experienced pediatrician, who, if necessary, will send him for further examination.
Note! With a mild form of the disease, the symptoms are hidden, which significantly complicates the diagnosis.Diagnosis of myocarditis
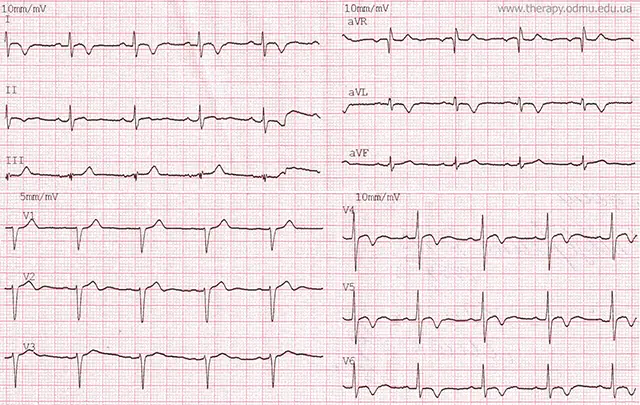
The photo shows an ECG of a patient with viral (H3N2 influenza virus) myocarditis. Inversion of "T" in V4-V6. Nonspecific disturbances of intraventricular conduction, clearly visible in III. Remember that troponins may be elevated in a patient with myocarditis (so myocarditis may be confused with NSTEMI and normal coronary arteries may be found on angiography).
The standard in diagnosing myocarditis is the method of endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) - invasive sampling of heart muscle tissue. The study allows us to determine the current condition of the heart and the causes of myocarditis, if confirmed. However, the sampling process is quite complicated, so it is carried out only in extreme cases: acute cardiac pain, the left ventricle of the heart increases in size, suspicion of cardiac cell degeneration and other signs, including going beyond a number of laboratory test indicators. If EMB is performed by an experienced practitioner, the likelihood of complications is minimal (up to 0.8%).
To confirm the presence of myocarditis, it is recommended that the patient also undergo:
- physical examination - measurement of pulse, pressure, auscultation and others;
- radiography to assess the size of the heart and identify congestive processes in the lungs;
- electrocardiography to assess the effectiveness of the system by a cardiologist;
- general blood and urine tests to assess health status;
- blood test for markers of cardiac pathologies;
- viral diagnosis (if a viral form of the disease is suspected).
Myocarditis in adults and children is diagnosed based on the results of a comprehensive examination. It is mandatory to establish the root cause of the disease and what complications have begun to develop. All data is used to formulate a therapeutic program.
How to treat myocarditis?
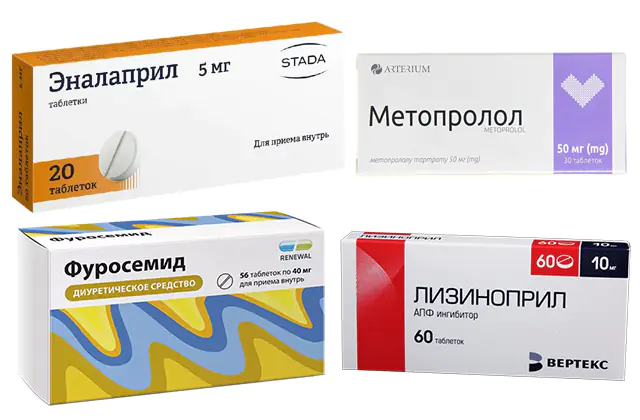
Medicines for the treatment of cardiac myocarditis
Treatment for myocarditis depends on the type and form of the disease, the patient's age, general health and other related factors. In mild forms, aggressive treatment is not required; it is enough to limit the patient’s physical activity. But if the disease is severe, hospitalization or providing complete rest to the patient at home may be necessary. Cardiac function will need to be maintained with medication until tissue recovery from inflammation is complete.
The patient is selected with medications for myocarditis, the diseases that caused it, as well as for the prevention of complications.
The treatment regimen is prescribed strictly individually; how to treat myocarditis is recommended exclusively by the doctor:
- antibiotics in cases of bacterial nature of the disease;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- medications to stabilize heart rhythm;
- antithrombosis drugs.
To maintain cardiac function, the following are prescribed:
- Enalapril- a drug to lower blood pressure, delaying the conversion of the angiotensin-converting system. Packaging will cost only 5 hryvnia, 47 rubles. If there are contraindications to Enalapril, analogues of the drug may be recommended - Lisinopril, Ramipril.
- Metoprololor its analogues - Corvitol, Bisoprolol. The drugs belong to the group of beta blockers; the medications are effective for heart failure. A package of Metoprolol costs 11 hryvnia in Ukraine, and 59 rubles in Russia.
- Furosemide or other diuretics. The drugs reduce the load on the cardiovascular system. 50 tablets of Furosemide cost 8 hryvnia, 34 rubles.
In severe forms of the disease, medications will not cure myocarditis; hardware support or heart transplantation will be required.
Among the hardware procedures actively used are:
- artificial injection of blood into the aorta to normalize blood circulation, but at the same time there is a decrease in pressure on the heart;
- artificial saturation of the body with oxygen or removal of waste products;
- forced pumping of blood into the systemic circulation.
Hardware treatment will require lengthy rehabilitation, including adherence to a diet, special physical activity, giving up bad habits and excessive fluid consumption.
Important! Refusal to treat myocarditis will lead to the development of complications - heart failure, stroke, arrhythmia, sudden death.Prevention of myocarditis
The pathology is nonspecific, so a separate method for preventing the disease has not been developed. Preventive measures are aimed at protecting against the causes of myocarditis. To do this you need:
- Undergo routine vaccination and revaccination, and during periods of exacerbation of ARVI, avoid crowds of people;
- Keep your hands clean - personal hygiene is a reliable means of preventing infections, viruses, and bacteria;
- In the summer season, use repellents, since ticks are carriers of a number of dangerous diseases;
- If a person has problems with the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, visit a doctor for a preventative health assessment.
If all preventive measures are followed, the likelihood of normal heart functioning is much higher.
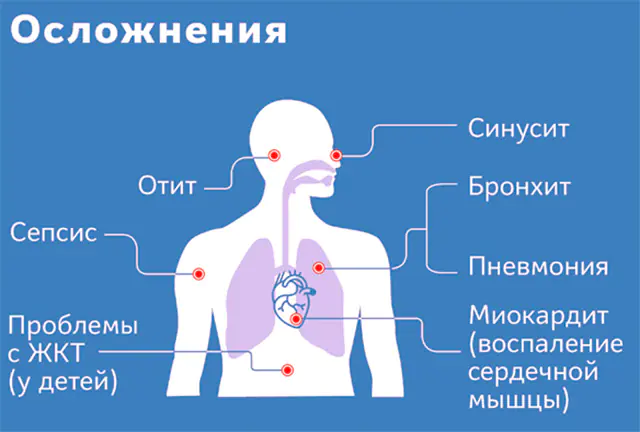
The photo shows possible complications of myocarditis
Myocarditis is a pathology that strikes directly at the heart. Complications from inflammation of the heart tissue can even lead to the death of the patient. The worst prognosis for treatment is in newborns, since due to age-related physiology, early diagnosis of the disease is complicated. But in adults, timely therapy will completely normalize the activity of the heart. It should not be forgotten that it is always easier to take preventive measures than to treat myocarditis. And although narrowly targeted preventive measures have not yet been developed, general prevention of health conditions will improve well-being and reduce the risks of a number of pathologies, including inflammation of the heart muscle.
What is myocarditis and how to treat it - watch the video:



