Cheese poisoning is one of the most dangerous and severe pathological conditions of the human digestive system and the entire body as a whole. This is explained by the fact that cheese is rich in milk protein, contains a large amount of vitamins, beneficial microelements, acting as a breeding ground for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. Most often, indigestion is caused by poisoning with blue cheese, since bacteria that produce toxins can actively multiply in such cheese.
The content of the articleCauses of cheese poisoning
Is it possible to get poisoned by cheese? Of course, cheese, like any other product made from milk, can spoil and cause intoxication of varying degrees of severity. In order for the poisoning effect to occur, the following causal factors must be present, under the influence of which cheese becomes dangerous to human life:
- incorrect storage conditions in retail outlets (for each type of product in this category, the manufacturer determines its own temperature regime in which it must remain for a certain period of time and not lose quality, but if the cheese is stored in a warm place, without sufficient ventilation, then in this case pathogenic bacteria begin to develop there);
- non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards by workers at the enterprise where the goods are welded or by sellers directly in the store;
- the use of low-quality or infected milk (cattle are prone to diseases dangerous to humans such as listeriosis and brucellosis, and raw milk is used to make cheese, so poisoning can be caused by infectious agents of these diseases);
- the presence of bacterial microorganisms such as E. coli and salmonella in the warehouses and refrigerators of the manufacturer or store where products are sold.
Can you get poisoned from blue cheese? Unfortunately, intoxication of the body by varieties of cheese with noble mold is a fairly common phenomenon. Together with cultures of beneficial bacteria, a fungus can successfully develop and camouflage itself, the spores of which produce a toxic substance that can cause gastrointestinal upset, as well as a large number of accompanying signs of poisoning.
Symptoms of cheese poisoning
Signs of cheese poisoning appear in the first 1-2 hours after a person has consumed the infected product. The severity of the clinical picture may depend on how much poor-quality food was eaten. Symptoms of cheese poisoning are as follows:
- physical weakness, drowsiness, decrease in blood pressure to a level of 90 per 60 units of tonometer readings;
- complete disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, which causes watery diarrhea, nausea, vomiting of curd contents;
- dizziness, pain in the temporal region of the head;
- pain in the central part of the abdomen, which is of the nature of spasms and spreads throughout the abdominal cavity;
- increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees Celsius;
- a slowdown in the outflow of urine, and when going to the toilet, urine of a rich brown hue is observed, which indicates the removal of toxins through the kidneys;
- strong feeling of thirst;
- heart rhythm disturbances (possible signs of tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia).
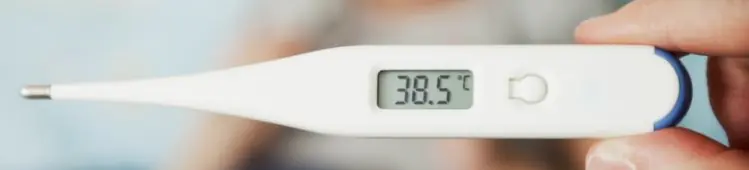
Camembert cheese poisoning has a similar clinical picture. It is important to remember that if the milk from which the products are made was contaminated with listeriosis or brucellosis, then in addition to the indicated symptoms, sweating, aching pain in the joints, and fatigue are added.
First aid for poisoning
Is it possible to eat cheese after poisoning? In the future, of course, you can consume dairy products from this group, but immediately at the moment of peak intoxication you must stop eating any food. You are only allowed to drink water and sweet tea. In the first minutes after the manifestation of pathological symptoms of poisoning, you need to call an ambulance, and before its arrival, carry out the following actions:
- Place the patient in a horizontal position on his side. The hand located on the lower side should be placed under the head so that in case of vomiting, all the masses secreted from the stomach flow freely outside the oral cavity.
- Rinse the stomach. The person is given to drink as much warm water as possible, and then a gag reflex is provoked by placing fingers in the larynx area. Along with gastric juice, undigested remains of low-quality cheese and pathogenic microorganisms that cause the poisoning effect are thrown out.
- Application of sorbents. To prevent toxins produced by infectious microorganisms from spreading through the blood, the poisoned person is given drugs that absorb some of the toxic substances. These are medications such as Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Smecta, Atoxil.
If there is a high fever and headache, a person is given 1 tablet of Paracetamol. Upon arrival of the emergency doctors, it is necessary to tell in as much detail as possible about all the therapeutic actions that were carried out on the patient. Then comes the hospitalization stage. After poisoning, cheese is temporarily excluded from the diet so as not to overload the weakened digestive system. The patient is on a special diet.
When poisoned, cheese can cause a persistent feeling of disgust in the patient and an increased gag reflex. A similar condition is observed for several months after recovery. This suggests that the intoxication of the body was actually caused by pathogenic bacteria consumed together with a fermented milk product.
Drug treatment for cheese poisoning
What to do if you are poisoned by cheese? In most cases, people poisoned by this product do not seek medical help at the hospital. Although such behavior can be safely called irresponsible, because an infection that develops in the gastrointestinal tract can cause not only short-term upset of the digestive system, but also cause a large number of complications, disruption of the kidneys, liver, and central nervous system.
After hospitalization of a patient with signs of food poisoning in the infectious diseases or toxicology department, the following therapeutic manipulations are carried out in relation to him, aimed at removing toxic substances from the body and restoring metabolic processes:
- (the patient is given an enema with an antiseptic solution, the effect of which ensures the gentle removal of bacterial microorganisms along with feces, which guarantees an improvement in the patient’s general well-being within 5-10 minutes after the procedure);
- intravenous drip with physical solution, glucose, Piracetam (prescribed to maintain the vitality of the body, as well as restore the water-salt balance, which was disturbed due to a large amount of bowel movements with liquid diarrhea);
- sorbent preparations that are taken orally in the form of tablets or a pre-prepared suspension (Atoxil, Activated Carbon, Enterosgel, Smecta, White Coal);
- vitamin-mineral complexes, if the patient’s body is severely depleted by food poisoning.
If severe strains of infectious microorganisms are detected, the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy in the form of medications such as Metronidazole, Biseptol, Trichopolum. Depending on the clinical picture revealed by the examination results, the attending physician may prescribe other types of drugs to the patient.
Restoration of the body
Poisoning with expired cheese is considered the most severe infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the fact that after the product’s shelf life has expired, the natural decomposition of milk protein begins, releasing a large amount of dangerous toxins. In combination with an associated infection, the danger of expired cheese increases several times. Spoiled blue cheese is even more dangerous, since along with noble bacterial cultures you can eat spores of pathogenic fungi, which can be very difficult to get rid of.
After suffering from food poisoning with cheese, it is recommended to follow the following rules for restoring the body so that the gastrointestinal tract organs begin to function as usual as soon as possible:
- do not overeat, the last meal should be at 18-00 hours;

saturate your diet with cereal porridges, salads from fresh vegetables;- Avoid lactic acid products for the first 2 weeks;
- drink as much liquid as possible (mineral water is allowed, but without gases);
- do not eat meat products (possible if the body is weakened);
- rest more, avoid sports and heavy physical activity;
- give up alcohol, tobacco products, and drugs.
In combination with prescribed medications, following these simple rules will allow you to quickly restore metabolic processes in the body and forget about the negative consequences of eating spoiled cheese.
Prevention of poisoning
In order not to suffer from food poisoning and not become a patient in the infectious diseases department, it is recommended to pay special attention to preventive measures, which include the following aspects:
- How can you tell if cheese has gone bad? First of all, smell the product. It should have a natural milky smell. There should be no sharp or specific odors.
- Ask the seller to cut a small slice of cheese. If, after eating a product, bitterness and an unpleasant aftertaste form in your mouth, then it is better to refuse to purchase such a product.
- Do not buy suluguni cheese, mozzarella, braid at spontaneous markets, since products of this type are the easiest to counterfeit and quite often they are made in artisanal conditions without observing sanitary and hygienic standards.
- Pay attention to the quality of the product and its production time. It’s better to overpay a little, but buy a product from a manufacturer whose brand is known in the market and whose company actually produces high-quality natural cheese.
- Do not add cheese to pasta and other dishes if you do not intend to eat them within the first 3-4 hours from the end of cooking. There is a high probability of such food souring and, accordingly, the onset of poisoning. If you are poisoned by pasta, read useful information here.
At the first signs of intoxication in the body, it is recommended to immediately go to the hospital, as there is always a risk of contracting the gastrointestinal tract with severe types of infections.



