What you need to know about angina? Causes and symptoms of the disease. Diagnosis, first aid for angina pectoris, drug treatment. Prevention of illness.
The content of the article:- What is angina
- Reasons for development
- Main symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Urgent Care
- Medicines
- Prevention
Angina pectoris is a clinical syndrome that has been the leading cause of sudden death in developed countries for many years. The pathology is a manifestation of insufficient oxygen supply to myocardial tissue (the middle muscular layer of the heart, constituting the bulk of its mass), but is not associated with necrosis of muscle cells. Familiarization with the first signs of the disease and methods of emergency care will allow you to avoid the most harmful consequences of the pathology.
What is angina?
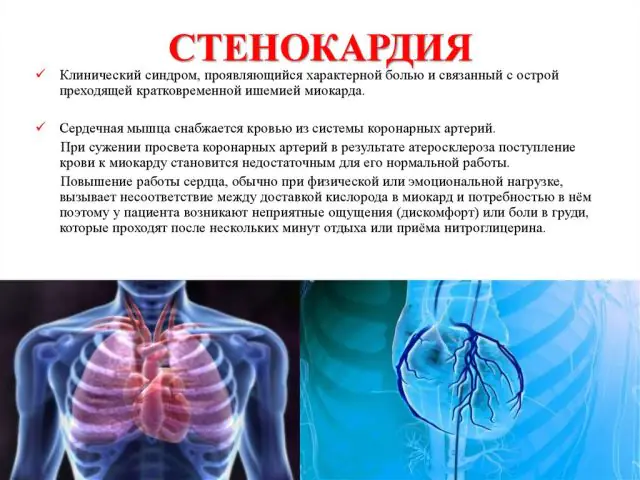
Angina pectoris is a dangerous disease, the likelihood of symptoms of which increases significantly every day. In Russia alone, periodic chest pain is the norm for 3 million people, and as studies show, this is only 40% of all cases, because most patients do not even know about their disease. Against the backdrop of growing mortality rates from a sudden attack of angina (by 3% over 10 years), cardiologists around the world call for taking responsibility for your own health.
Symptoms of angina pectoris are the most common form of coronary heart disease (CHD). The etiology of the disease is closely related to lack of oxygen. Thus, an increase in tissue demand for oxygen during physical activity, but the supply is disrupted for various reasons, leads to burning or pressing pain in the chest.
The amount of oxygen required for normal functioning varies depending on the heart rate, organ contractility and other indicators. But insufficient blood supply is often caused by narrowing of the arteries, spasms, and embolism.
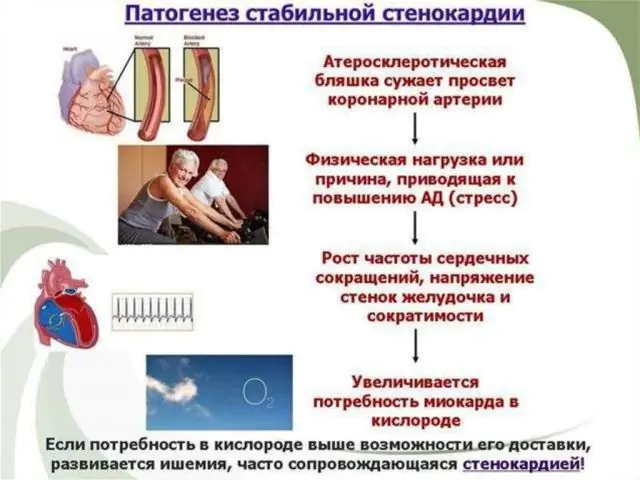
Pathogenesis of angina
Discomfort can occur both during physical activity and in a stressful situation. In addition, signs of angina may also appear at rest, which is typical mainly for older people.
Depending on the body’s need for oxygen, a group of WHO experts proposed classifying angina by type:
- stress pathologywhen symptoms appear after physical or emotional stress;
- rest pathology (variant) - lack of oxygen in the myocardium is felt even while the patient is resting.
Up to 20% of people over 65 suffer from this disease. If angina pectoris is not treated, then in 5.5% of acute conditions it will end in death. However, people in the younger age group are also susceptible to the disease (up to 5% of people over 45).
The mortality rate in men is 3 times higher, and although over the past 10 years, with the help of early diagnosis and developed treatment methodology, the number of deaths has decreased significantly, it is not possible to completely get rid of the disease.
Important! The patient's condition can also be aggravated due to hypoxia or anemia, and in acute cases it is provoked by them.Causes of angina development
The nature of the disease, as already noted, is directly related to insufficient oxygen supply to the myocardium. The mechanism for the occurrence of specific pain during angina pectoris is simple: during physical activity or emotional stress, the heart muscle contracts more actively, and narrowed vessels do not allow a sufficient amount of oxygen-enriched blood to flow.
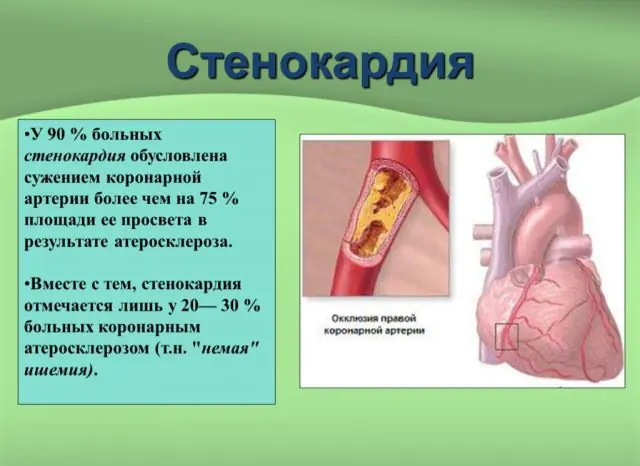
The main cause of angina is atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. The narrowing of the arterial lumens is caused by the accumulation of cholesterol on the walls.
Another cause of pathology is vascular spasms of various natures. While myocardial oxygen demand can be predicted depending on the level of physical activity, contraction is not a static indicator.
If the cause of angina is vascular atherosclerosis, then its manifestations are unsystematic. It has only been established that a greater number of attacks occur in the first half of the day, which is associated with increased vascular tone at this time.
Risk factors for diagnosing angina pectoris are:
- genetic predisposition or congenital abnormalities of the cardiovascular system;
- insufficient physical activity or, on the contrary, excessive exercise;
- tendency to bad habits - alcoholism and smoking;
- emotional overstrain.
Main symptoms of angina
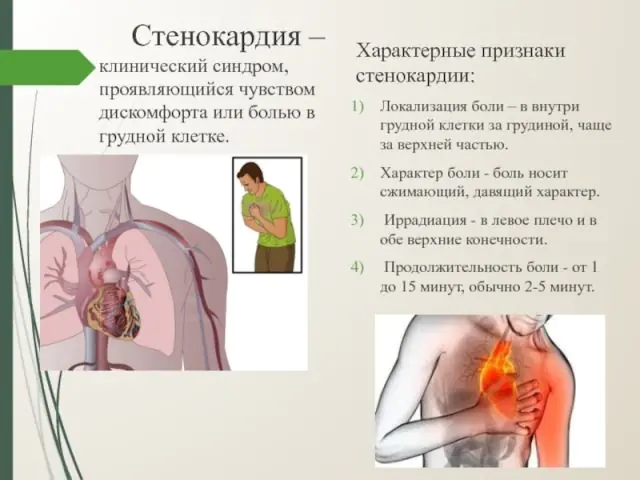
Insufficient oxygen supply to the myocardium leads to a decrease in the acid level of the blood and an increase in the amount of lactate. An electrocardiogram in this case will show a decrease in the contractile capabilities of the left ventricle.
In this case, the patient may feel both mild pain and severe compression that cannot be ignored. The pain can radiate to the left arm, and often to the back, jaw and teeth. A sign of angina can even be pain radiating to the inner surface of the right arm.
During acute attacks, there is an increased level of diastolic pressure in the left ventricle, which in turn causes congestion in the lungs. The first sign of acute angina, in addition to chest pain, is shortness of breath. Sometimes, after belching or vomiting, symptoms may decrease or disappear altogether.
As a rule, patient complaints are quite vague, so it is quite difficult to differentiate the pathology. In addition, after an attack, physical examinations will not show any abnormalities.
Classification of angina according to the nature of the development of the clinical picture:
- Stable pathology - symptoms do not progress for 2 or more months.
- Unstable pathology - difficult to predict dynamics of attacks, an increase in their frequency or the manifestation of disturbances at rest. An unstable pathology also includes the appearance of the first sign of angina, indicating the maturation of the disease.
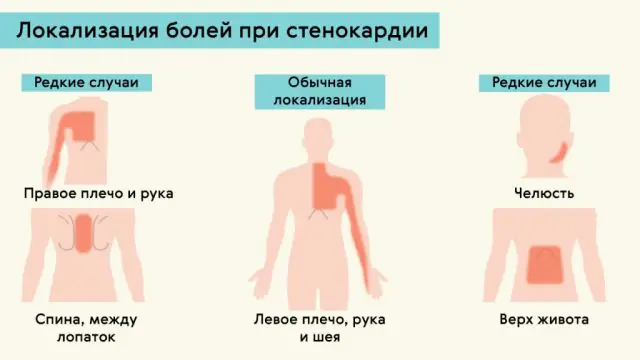
Scheme of localization of pain during angina pectoris
Stable angina is divided into classes according to the severity of symptoms:
- Violations appear with prolonged or sudden physical activity;
- Painful sensations appear with minor physical activity (climbing stairs, climbing a mountain, brisk walking), as well as after eating;
- The pathology manifests itself even after walking 100 m on level ground;
- Even at rest, the patient feels compression in the chest area.
Diagnosis of angina pectoris

An acute painful attack requires emergency treatment for angina pectoris. However, systematic treatment requires an accurate diagnosis. The patient's life history and disease history must be collected and analyzed. It is necessary to describe to the doctor in detail the nature of pain during angina pectoris, the frequency of occurrence and previous pain provocations.
It is also necessary to undergo a number of laboratory tests:
- Electrocardiogram. Prescribed in the presence of symptoms typical of the pathology. This method of research at rest is not always informative. In 30% of patients no abnormalities will be recorded, and in 70% signs of a heart attack may be detected. But at the time of an attack, an ECG will show reversible ischemic changes in the system.
- Stress test. Refers to the method of specific diagnosis of angina pectoris. Patients with typical pain are referred for a stress test. The disadvantage of testing is the inability to use it for patients with unstable dysfunction, as well as reduced sensitivity in women under 55 years of age.
- Coronary angiography. Prescribed when the stress test results are positive. The main task of angiography is to determine the location of vascular damage. In 70% of cases, narrowing affects insufficient supply to the myocardium, but at the same time, this diagnostic method is not informative if the cause of the pathology is vasospasm or thrombosis.
To visualize the patient’s condition, additional instrumental studies may be prescribed: electron beam computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, multi-slice computed tomographic coronary angiography.
Emergency care for angina pectoris
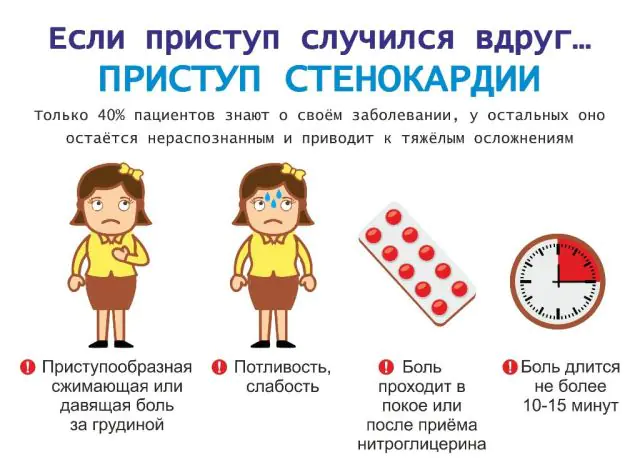
Pathogenesis of an attack in angina pectoris
When diagnosing angina, treatment recommendations should be made exclusively by a doctor. The key points of competent therapy are providing assistance for angina pectoris, as well as avoiding situations that cause attacks. As soon as the patient has discomfort in the chest, it is necessary to stop the development of the attack.
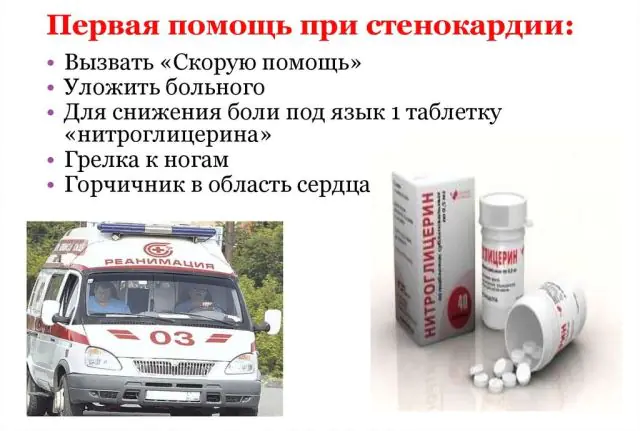
Emergency care for angina pectoris consists of sequentially performing a number of actions:
- Stop all physical activity.
- Sit down in a comfortable chair.
- Place a Nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue. The package costs only 8 hryvnia, 19 rubles and should be in the first aid kit of every core.
- If the pain does not go away within 5 minutes, you must call an ambulance. It is permissible to take a second tablet.
After the attack is over, you need to consult a doctor, he will tell you how to treat angina in the future.
Important! During an attack, you should never take a horizontal position.Medicines for the treatment of angina pectoris
Metoprolol for the treatment of angina pectoris
Patients are required to be sent for treatment of the underlying disease that has caused insufficient oxygen supply to the body, and also include physical activity (up to a threshold level) lasting at least 30 minutes in their daily routine.
Treatment of angina pectoris with the help of pharmacological agents is aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing oxygen starvation of the myocardium. At the time of an attack, the most effective remedy, as already noted, is Nitroglycerin.
During the interictal period, prophylactic drugs for angina pectoris may be prescribed:
- Antiplatelet - acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel. Aspirin is the most affordable product in the series; in Ukraine, tablets cost 6 hryvnia, and in Russia - 16 rubles.
- Beta blockers - Celiprolol, Carvedilol, Metoprolol. Tablets with the active ingredient Metoprolol cost from 12 hryvnia, 58 rubles.
- Calcium channel blockers — Nifedipine and its analogues Amlodipine, Felodipine. A package of Nifedipine costs 12 hryvnia, 40 rubles, analogues will cost a little more.
If the patient’s condition worsens while taking medications for angina pectoris, then revascularization is prescribed (blood supply is improved surgically).
Prevention of angina

It is not enough to know how to treat angina; patients must strictly follow the doctor’s therapeutic recommendations, as well as independently identify and eliminate risk factors in their environment.
Basic measures to prevent new attacks:
- Normalization of cholesterol in the blood by improving nutrition and following the recommendations of the attending physician. Patients are advised to reduce the amount of animal fats in the diet and increase the consumption of vegetables.
- Monitor the condition of the cardiovascular system. At home, you can systematically measure your blood pressure level, taking measures to normalize it in case of deviations.
- Give up bad habits - smoking, alcohol.
- Normalize your weight and move more in the fresh air; the level of physical activity should be agreed with your doctor.
- Avoid emotional stress, both positive and negative.
How to treat angina pectoris - watch the video:
Angina is a set of clinical symptoms indicating a lack of oxygen in the myocardium. A prolonged attack characterized by chest pain can develop into a myocardial infarction. And if a person does not receive emergency care for angina, sudden cardiac death is possible. Prognosis worsens with age. Carefully following all the recommendations of the attending physician and avoiding risk factors improves the chances of living without chest pain and allows you to keep the pathology under control.



