
In the summer, everyone strives to make the most of their vacation time and get a boost of health and vigor on the beach for the rest of the year. At the same time, many have heard both about the benefits and harms of tanning. We decided to figure out what is true and what is a myth.
1. The darker the tan, the more vitamin D
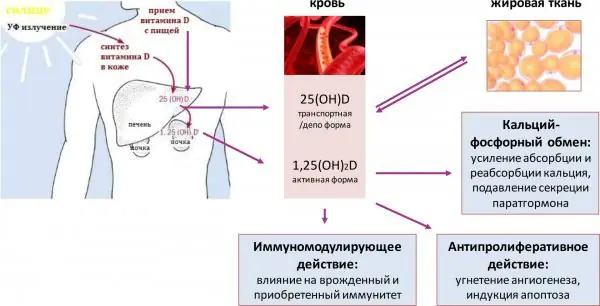
When ultraviolet rays hit the skin, they trigger the production of vitamin D. This is the only “non-standard” vitamin that not only comes to us with this or that product, but is also produced by the body under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. To get the daily requirement of vitamin D, it is enough to spend only 10-15 minutes in the sun. At the same time, bronzed skin becomes almost impenetrable, and the vitamin necessary for strengthening and growing bones is not produced. This is why people who try to be tanned all year round are faced with the problem of brittle bones earlier.
2. Brunettes can tan longer than blondes.
People with fair skin types are indeed much more prone to sunburn and, therefore, melanoma than dark-skinned people. Among Europeans, three phototypes are distinguished; in the classification, not only skin color, but also eye color is important.
So, the first type is light sensitive skin with freckles, light blue or green eyes, blond or red hair. Such people almost cannot sunbathe, but they can easily get sunburned. The safe time that people of this type can spend in the sun without protective cream is no more than 7 minutes. The second type is fair skin, few or no freckles, light eyes, light brown or brown hair. The tan does not apply well, at first the skin takes on a red tint and burns quite easily. You can be in the sun without sunscreen for no longer than 15 minutes.
The third type is dark skin, brown eyes, dark hair. The skin tans easily, and sunburn is rare for it. Without protection, you can sunbathe for up to 20 minutes.
3. Tanning accelerates aging
Aging of the body as a whole is a complex process on which tanning is unlikely to have any effect. However, when exposed to sunlight, processes similar to aging occur in the skin. In medicine, a special term “photoaging” even appeared. Scientists have calculated that one season of intense tanning ages the skin by 6 months. And if for the last 10 years you spent your summer holidays on the beach, then the first wrinkles may appear five years earlier than the date programmed by genes. The first sign of photoaging is pigment spots on the face and neck, which over time grow and darken. 1-2 days before visiting the beach or every 4 hours while in the sun, dermatologists recommend taking vitamin E capsules. It will help maintain elasticity and youthfulness of the skin.
4. Tanning leads to cancer and other diseases
Doctors have convincing evidence that excessive sun exposure can indeed cause skin cancer. However, if you use sunscreen and don't sunbathe to the point of blisters, there is no need to worry about such consequences.
Tanning is also often cited as a cause of mastopathy (breast disease). This myth is probably due to the fact that if mastopathy already exists but is asymptomatic, it can manifest itself after heavy sunbathing. Intense tanning can sometimes lead to hormonal imbalance and worsen the symptoms of the disease. Contrary to popular belief, the sun's rays do not directly affect breast tissue. The only danger is sunburn of the nipples and areolas (nipple area), which can lead to cracked nipples and even inflammatory changes in the mammary gland.
5. Certain foods will help enhance your tan.
A beautiful, even tan can really be achieved with some products. For example, carrots and apricots are rich in beta-carotene. Before going to the beach, it is recommended to drink a glass of freshly squeezed juice so that your tan goes on smoother and faster. Tomatoes will also help enhance the effect of tanning. They contain lycopene, a substance that stimulates melanin production. On the beach you can consume them in any quantity. Foods that will help you tan evenly include peaches, grapes, beets, melon, watermelon, tomatoes, spinach, sorrel, pumpkin, asparagus, broccoli, green vegetables, currants, citrus fruits, kiwi, bell peppers, wholemeal bread and oatmeal. . These products contain vitamins A, C, E, PP and folic acid, the lack of which can cause a “spotty” tan.
6. A number of medications can ruin your tan.
Those who combine sunbathing with taking antibiotics, hormonal contraceptives, tranquilizers, medications against allergies or high blood pressure are also at risk of getting sunburn spots. Another option is possible - photodermatitis or “sun allergy”: skin peeling off in layers. For diabetes, hypertension, mastopathy, gynecological diseases, disorders of the thyroid gland, chronic diseases of the liver and adrenal glands, it is better to sunbathe under the shade of an umbrella. This way you will receive the minimum dose of ultraviolet radiation necessary to boost your immunity and avoid harmful radiation.
7. It’s safe to sunbathe on a cloudy day.
There are two types of ultraviolet in the sun's rays: UV-A, the level of which is practically independent of the weather, and UV-B, which is necessary for the formation of vitamin D, its level actually decreases during cloudy weather. UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin, causing premature aging, wrinkles and allergic reactions. UVB rays penetrate only the top layer of the skin, but cause sunburn and provoke cancer. At the same time, clouds transmit up to 80% of ultraviolet radiation, so you can get sunburned even in cloudy weather. It is also worth remembering that beach umbrellas, like shade from palm trees, do not provide sufficient protection and do not save from scattered ultraviolet radiation: sand reflects up to 20% of the sun's rays. Regardless of the weather, when staying outdoors for a long time, it is recommended to use a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15.
8. It is impossible for already tanned skin to get sunburned.
Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the pigment melanin is produced in the skin; the intensity of the tan depends on its concentration. A basic tan is just the skin's reaction to ultraviolet light. Of course, melanin serves as a kind of barrier to dangerous UVA rays, but the skin still needs additional protection.
9. You don't need sunscreen if you swim a lot.
There is an opinion that water can provide protection from the sun, so those who bathe a lot do not need to use additional products. In fact, ultraviolet rays can penetrate to a depth of about one meter. Therefore, those who like to splash in the sea should apply sunscreen before entering the water, as well as after leaving it.
10. You need to prepare for the beach in the solarium
The possibility of getting sunburned is only slightly less for already tanned skin; such skin acquires a protection factor of no more than 5SPF, so the resulting tan is not good protection for long-term exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation. Tanning is a sign of damage to the skin from ultraviolet rays. Every time a person tans, he receives a new dose of these damages. Over time, they accumulate and contribute to accelerated skin aging and an increased risk of skin cancer.
11. A cream with a higher SPF protects your skin better.
Using sunscreens with a high SPF factor gives a sense of false security. In fact, the difference between the numbers indicating the protection factor is not that great. For example, a product with SPF 15 protects 93% of UVB rays from penetrating, and products with SPF 50-60 provide approximately 98% protection. Many sunscreens do not contain ingredients that provide comprehensive protection against both UVB and UVA rays, which have the highest penetrating power and reach the middle layers of the dermis. Experts advise applying sunscreen every 2 hours, regardless of SPF.
12. Waterproof products don’t need to be reapplied often.
Water-resistant sunscreens can only provide protection while swimming. However, even such preparations do not withstand prolonged bathing, so you will have to apply them again and again. You should also renew your protection if you dry yourself with a towel. The duration of action should be indicated on the products - 40-80 minutes. According to dermatologists, in fact, no product is completely waterproof.
A light tan on the skin looks very attractive, so in the summer women flock en masse to the beaches, and during the rest of the year they try to maintain it with other available means. But ultraviolet radiation is not only a beautiful golden skin tone, but also potential serious health problems if you sunbathe incorrectly. When choosing this or that type of tanning for yourself, consider the advantages and disadvantages of the method, study its features.
Why does skin tan?
Ultraviolet light entering the skin stimulates the oxidation of lipids (fats), which, in turn, provokes the accumulation of free radicals in the epidermal tissues. These compounds are harmful to the body, so it activates the protective function, beginning to actively synthesize melanin with the help of special cells - melanocytes. Under the influence of pigment, the skin darkens and roughens, becoming less susceptible to ultraviolet rays. It is also a powerful natural antioxidant that protects the deep layers of the dermis from the effects of free radicals.
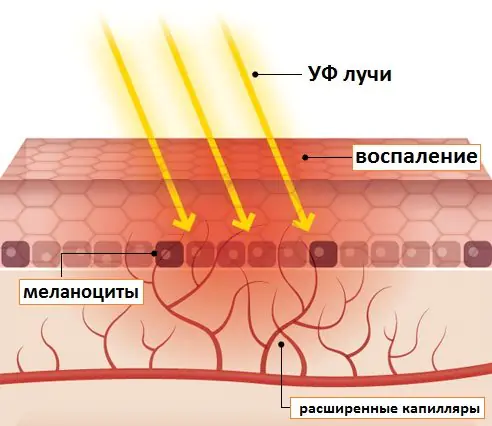
Ultraviolet radiation is divided into three types:
- UVA. It provokes photoaging, the appearance of fine wrinkles, dryness and flaking of the skin, and can cause a burn to the cornea.
- UVB. It is what is “responsible” for a beautiful tan, and with prolonged exposure to the sun or in a solarium, for burns and the development of cancer.
- UVC. It is most dangerous for the skin, but it is almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer.
The concentration of melanocytes in the skin is determined at the genetic level. The fewer there are, the faster and easier you burn, the more sensitive your skin is to the sun. There is no way to change this; the only way out is to use more powerful sunscreens.

Video: how a tan forms
Types of tanning
In addition to the “classic” option - natural sun tanning, the coveted golden skin tone can now be achieved in a solarium or with the help of special cosmetics. Each method has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, so the choice must be made wisely.
Natural solar
Formed on the skin under the influence of sunlight. Conventionally divided into sea and river. The first manifests itself faster due to the fact that the sun's rays at southern latitudes and near the equator fall on the ground at a smaller angle; accordingly, they have to overcome a smaller thickness of the atmosphere, which scatters them. Large areas of sea water and sand reflect ultraviolet radiation, further increasing the dose received by the skin. Salt water increases susceptibility to radiation, and it also contains iodine, which turns the skin a golden beige hue. Consequently, the risk of getting sunburned while vacationing at the seaside is much higher. And reflected radiation allows you to sunbathe, even while remaining in the shade.

Video: benefits of sun rays for skin
The tan obtained in temperate latitudes develops gradually. The radiation here is less strong; a significant part of it is absorbed, for example, by grass. A river tan can be recognized by a slight grayish undertone - the skin has time to react to radiation not only by synthesizing melanin, but also by thickening the superficial stratum corneum.

The sea tan also fades quickly. This is explained by the fact that the skin intensively irradiated with ultraviolet radiation dries out greatly, the body strives to quickly get rid of damaged epithelial cells and renew it.
Advantages of any natural tanning:
- The process of vitamin D synthesis is activated, phosphorus and calcium, which are necessary to maintain bone strength, are better absorbed.
- Improves well-being and mood. Tanning is subconsciously associated with summer and vacation, which cannot but evoke positive emotions. In addition, ultraviolet light promotes the production of serotonin (the hormone of happiness).
- Blood circulation in the body, metabolism, the process of removing waste and toxins, and the production of antibodies (to improve immunity) are stimulated.
- The ability to get rid of many dermatological diseases (acne, psoriasis) while they are still at an early stage and prevent their development. The sun provides superficial disinfection of the skin.
The process is not without its drawbacks:
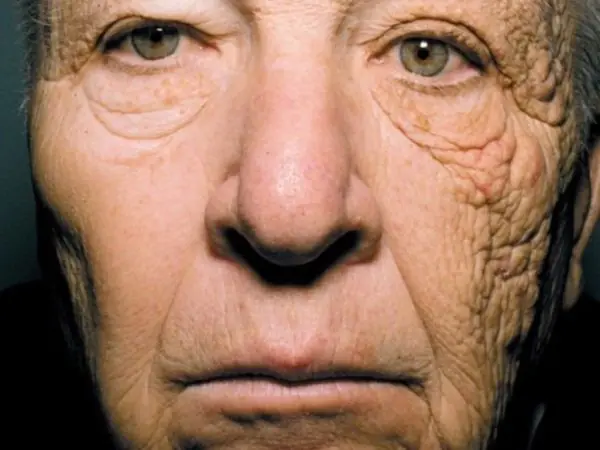
- Photoaging of the skin. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, it quickly loses moisture, peels off, wrinkles and age spots appear.
- Carcinogenicity. Ultraviolet radiation in excessive doses provokes the development of melanoma - skin cancer, which is extremely difficult to cure. Other serious skin diseases (photodermatitis, relapse of herpes) cannot be excluded.
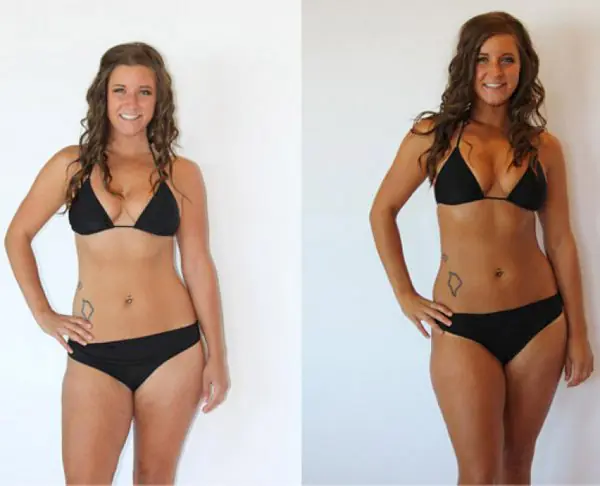
The first tan after sunbathing on dark skin appears within 2–3 hours. But this does not mean that you need to immediately spend so much time in the sun. It's much safer to break it up into 15-25 minute chunks. If the skin is light or thin, it is recommended to reduce the time to 5–7 minutes. The tan on her takes much longer to develop, it takes from 10–12 hours to several days. How quickly a tan fades depends on its intensity. The sea one noticeably fades after 1-3 months, the river one - after 2-5 months.
Video: the benefits and harms of natural tanning
In the solarium
The mechanism of tanning in a solarium is the same as in the sun. But the source of ultraviolet radiation is not its rays, but special lamps. The time spent under them and their power are calculated taking into account the skin phototype. The maximum duration of the procedure for burning dark brunettes is 12–15 minutes at full lamp power, for light-skinned blondes and redheads — 2–3 minutes at minimum power. For two intermediate phototypes - 4–10 minutes at average lamp power.

How the tan appears also depends on your skin type. If it is very light, almost milky, it will take 5-7 sessions at intervals of about a week to obtain and consolidate at least a light golden tint. For dark-skinned girls, 3-4 procedures are enough, no more than once a day. The recommended duration of a course of sessions in a solarium is 10–12 procedures, then you can maintain the achieved result by visiting it once a week for 2–3 minutes.
Video: rules for tanning in a solarium
The first positive result from visiting a solarium on any skin except the palest skin appears within 2–8 hours after the procedure. But it doesn’t last long, a day at most. With regular sessions, the skin will gradually accumulate melanin, the effect will become more lasting and pronounced. If you stop visiting, the tan goes away within 2–4 months.
The main advantages of a solarium:
- Affordable price and the opportunity to get a beautiful tan relatively quickly, regardless of the time of year and climate in the region.
- The effect on the body is similar to that of the sun - this applies to improved mood, vitamin D synthesis, and disease prevention.
- The ability to prepare your skin for a natural tan, reducing the risk of sunburn on the beach.
- Lamp radiation is only in the UVA and UVB range, and the percentage of the latter is less than in natural ultraviolet.

There are also many disadvantages:
- There is a higher probability of getting burns when you abuse a solarium - the radiation source is closer, the dose of ultraviolet radiation is greater. Allergic reactions are also possible.
- The photoaging process is more active than with natural tanning.
- If you are too enthusiastic, you will acquire a very dark tan, which looks unaesthetic and “rough.”
- Presence of contraindications for visiting. First of all, these are pregnancy, oncology, gynecological diseases.
- The need to use special cosmetics to protect the skin during the session, restore after it, and consolidate the achieved effect. All these funds are not cheap.
- Potential opportunity to pick up a fungus or other infection due to poor disinfection of the booth.

Video: advantages and disadvantages of artificial tanning
Self tanning
The main active component of auto-bronzants is dihydroxyacetone (a glycerol derivative, also obtained from beets and sugar cane). When it penetrates the superficial horn cells of the epidermis, a reaction begins with amino acids and proteins, resulting in the formation of melanoidin. This substance acts on the skin like paint, giving it a tan tint.
The result after applying self-tanning is noticeable within 3-5 hours, but it does not last long. According to manufacturers, the shade lasts 5–7 days; practice shows that after 2–4 days the natural skin color returns. The price of the product does not affect the duration of the effect.

- The ability to find the desired skin tone regardless of its phototype.
- No photoaging effect. The maximum that can be achieved by overusing the products is slight dehydration of the skin.

Disadvantages of cosmetics:
- Without practice, it is very difficult to apply cream or lotion evenly on the skin; the tan will appear in patches. And for the back area you will generally need the help of another person.
- Self-tanner is difficult to quickly remove if you are not satisfied with the result of application.
- The cream stains clothes. You should not get dressed for 10–15 minutes after application. Spots may remain on the white even when it dries.
- The vast majority of products do not contain an SPF factor and, accordingly, do not protect against ultraviolet radiation at all.
- Automotive bronzers are characterized by an unpleasant burning odor, which also develops on the skin.
- Contraindications for use include excessive dry skin, dermatological diseases, unhealed mechanical damage, allergies.
Video: how auto-bronzants work
Tanning: interesting facts
Tanning fashion comes and goes, and there is also a lot of debate about its benefits and harms. Some interesting facts about him:
- The fact that tanning visually “coarsens” one’s appearance was noticed back in ancient Egypt. Therefore, men, especially warriors, were depicted on frescoes with bronze skin, and women were light-skinned.
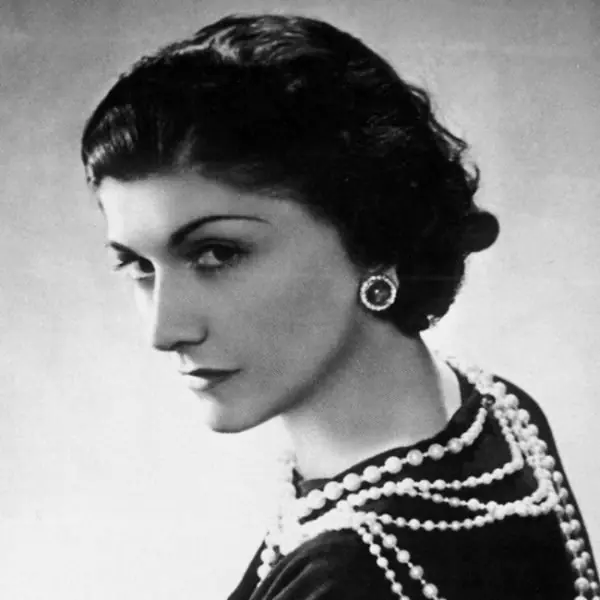
- Until the 20s of the 20th century, pale skin was considered a sign of aristocracy and sophistication; women carefully protected it from the sun. Tanning was considered the lot of peasants who constantly worked in the open air. The fashion for it was introduced by Coco Chanel, who inadvertently got tanned during her next vacation on the Mediterranean coast. The status of a cult fashion designer led to the fact that fans of her style quickly began to copy Chanel’s appearance. Thanks to her, more and more revealing swimsuits began to come into use, which ended with the invention of the bikini.



Staying in the sun has long ceased to be the only way to get a tan; now you can maintain a beautiful golden skin tone all year round. But, if you are planning to visit a solarium or apply self-tanning, keep in mind that such methods are not without their drawbacks. Sunbathing in the sun is also unsafe if you do not follow certain rules. Do not get carried away with sunbathing too much; some people are not given the chance to turn into a “chocolate bar” purely genetically.
During the holiday season, when many people head to the sea, we have prepared an article where we tell you in simple terms everything you need to know about tanning, sunburn, UV radiation, sunscreens and skin cancer. Read and once again do not expose yourself to unnecessary risks.
Summer is the time when many people take vacations and go away to bask in the sun. But if for some sunbathing is pure pleasure, for others it is a risk of experiencing pain and discomfort, which is called a sunburn.
I'm sure you already know that sunburn is the result of exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin and that you can prevent unpleasant consequences with the help of sunscreen. But what you may not know is that sunburn is nothing more than a protective reaction of the body, and that the effectiveness of aloe vera (popularly considered one of the best remedies for relieving burn symptoms) has not been proven at all.
Considering that sunburn is a fairly common phenomenon, it is surprising how many questions, myths and misconceptions it has acquired.
In this article we will explain to you what tanning, sunburn, sunscreens are and, most importantly, how to protect yourself from the development of cancerous tumors.
Why do some people tan while others instantly burn?
In short, sunburn is a reaction of skin cells to DNA damage caused by ultraviolet rays. Tanning and sunburn in themselves are not harmful to the body; it is only evidence that the DNA molecules have been damaged, which means that the likelihood of developing skin cancer has increased.
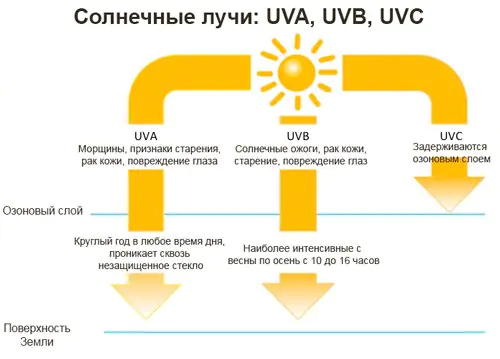
Ultraviolet (UV) is electromagnetic radiation that occupies the spectral range between visible and x-ray radiation. The sun emits several types of ultraviolet radiation.
Short wavelength UV (UV-C) is almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer. But the remaining two types (UV-A and UV-B) are able to penetrate the ozone layer.
For a long time, it was mistakenly believed that only UV-B could cause skin damage and cause DNA molecules to go into an excited state (this leads to mutations, genetic disorders and, as a result, the development of cancer).
More recently, scientists have found that although UVA does not cause burns, this type of radiation also causes cancer.
It is worth keeping in mind that our body has natural protection against ultraviolet radiation - a dark pigment called melanin. Melanin colors cells dark and reduces the harmful effects of radiation on the body.
Some people are born with elevated levels of melanin, which makes their skin darker and less vulnerable to UV damage. Others are forced to produce this pigment under the influence of small doses of radiation. The whole process takes from one to three days, and when it is completed, what we used to call a tan appears.
However, having a tan does not mean that your skin is completely protected from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation. People of all skin tones are susceptible to sunburn. It's just that those with less melanin are more likely to get burned.
Why sunburns are painful, itchy, and blistering
The body's first reaction to damage to DNA molecules from radiation is to kill the affected cells. This is necessary to prevent mutated cells from reproducing uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
If dead cells in the upper layers of the skin peel off without much difficulty (about a day after a sunburn), then the body has to clean out damaged cells in the deeper layers. There is a special mechanism for this.
When a cell dies, it releases a tiny piece of damaged genetic material. This signals neighboring cells to initiate a series of changes known as the inflammatory response.
This is the same reaction that the body triggers in response to an infection. Blood vessels dilate, increasing blood flow (resulting in a rise in temperature), and increased protein synthesis leads to itching and pain.
If a large number of cells are killed at once, a blister forms in their place. The body needs this in order to fill the damaged tissue with plasma and thus promote healing.
When and where are you more likely to get burned?
The time required to cause burns is proportional to the dose of ultraviolet radiation received by the skin. Accordingly, the more direct rays hit the skin, the greater the dose received.
That is, the closer to the equator, the higher the chance of getting sunburn. Likewise, the likelihood increases sharply during the summer, especially between 10:00 am and 2:00 pm. And UV radiation reaches its peak at noon.
Unfortunately, clouds block visible sunlight better than UV rays, so you can get burned even on a cloudy day.
In some cases—for reasons that are unclear—clouds can even increase the amount of ultraviolet light reaching the surface.
If you are at a high altitude, then the likelihood of getting burns is much higher, because in this case, solar radiation does not need to break through the entire atmospheric layer to reach you.
There are other factors that can increase your risk of getting burns. For example, being near snow, water, white sand, or other material that reflects UV will expose you to more radiation.
How to prevent burns
The answer is banal. Use sunscreen. This will not only prevent sunburn, but will also significantly reduce the risk of cancer cell formation.
Although with sunscreens, not everything is so simple. There is evidence that the active chemicals contained in creams have side effects and can cause poisoning. Therefore, today it is a very popular opinion that the best protection is creams based on minerals such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide.
Still, most dermatologists tend to believe that the benefits of chemical-based sunscreens outweigh the potential harm. Dermatologists also recommend using creams with a broad spectrum of protection (UVA and UVB protection) and an SPF of at least 30.
What is SPF in sunscreens?
SPF is an indicator of how long a cream can maintain its protective properties. That is, if the skin burns in 10 minutes without cream, then a cream with SPF equal to 30 can increase this period to 300 minutes.
It is also worth paying attention to the fact that SPF is a logarithmic indicator and after reaching a certain point (approximately 30), further increases in this value are unlikely to add additional protection.
How to use sunscreen
Experts recommend applying the cream at least 15 minutes before you are in the sun. You should repeat the procedure every two hours or immediately after you sweat or swim. Of course, there are a number of waterproof creams, but the rest are either washed off or lose their properties.
What to do if you are already burned
First, get out of the sun to prevent further damage and allow the body to begin its healing mechanism.
Secondly, to relieve pain, you can take a cold shower or use a moisturizer and anti-itch cream. If the pain is severe, it is acceptable to take painkillers.
Important! There is no evidence that aloe vera is the best treatment for burns.
Another good tip: if you get sunburned, drink more water. Sunburn is often accompanied by dehydration.
Sunburns begin to heal within a few days. It gets better in a couple of weeks. Still, it's worth remembering that cells with damaged DNA molecules accumulate and the more often you sunbathe or burn, the higher your risk of developing cancer.



