What is adhesive disease and why does it occur? The first symptoms and methods of diagnosing adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity. Treatment and preventive measures.
The content of the article:- Causes of adhesive disease
- Main symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Surgery
- Folk remedies
- Diet
Adhesive disease is a pathological process in which connective tissue is formed between the peritoneal space and nearby internal organs. The disease develops after surgery, in some cases against the background of a chronic inflammatory process. Adhesions limit the mobility of organs and can cause dysfunction. In severe cases, it can cause difficulty conceiving a child or severe cardiovascular dysfunction.
Causes of adhesive disease development
With adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity, the formation of adhesions in the peritoneum is observed. This is a kind of protective reaction of the body that prevents serious complications. In order to protect healthy organs around the area with a pathological or inflammatory process, connective tissues are formed. They fill voids and perform a protective function. At first, these tissues have a loose structure, but over time they become denser and can ossify, forming adhesions.
The causes of adhesive disease are associated with pathologies of internal organs, which are combined with injuries received during surgery. The likelihood of formation of adhesions increases with the addition of infectious processes and blood. The cause may be inflammatory reactions affecting the intestines, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Connective tissue cords are also formed with congenital malformations of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, additional ligaments are formed, which fix and lead to bending of the intestinal loops with the subsequent development of the inflammatory process.
If the patient receives bruises to the soft tissues of the abdomen, adhesions may also form. This occurs as a result of hemorrhage in the peritoneal area, followed by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, the development of inflammation, stagnation of blood and lymph.
Important! In the vast majority of cases, adhesions are the result of surgery in the peritoneum or pelvic organs.The risk of developing adhesive disease increases during abdominal operations due to large incisions and trauma to soft tissues. The peritoneum comes into contact with air masses, surgical instruments, and the touch of a doctor. This provokes the development of inflammatory processes and the formation of adhesions. After minimally invasive procedures, the likelihood of such a complication is reduced.
The prognosis depends on the duration of the pathological process and its localization. Timely assistance prevents complications and improves the quality of life. If single adhesions are detected, the prognosis is predominantly favorable. Lack of therapy is fraught with complications - intestinal obstruction.
Main symptoms of adhesive disease
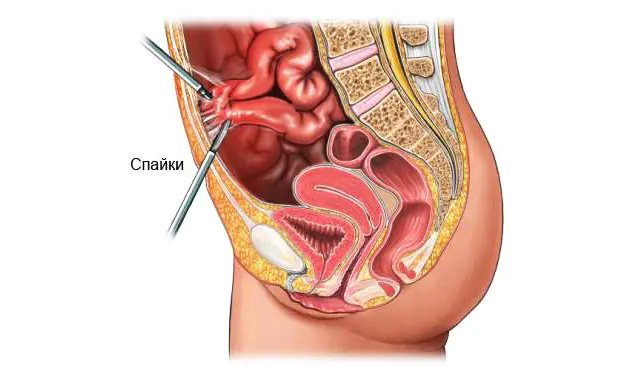
Adhesive intestinal disease (pictured above) has several variants of its course: latent, predominance of pain impulses, dyspeptic disorders, difficulty in intestinal patency.
In the latent form, there are no symptoms of adhesive disease. However, when the body’s compensatory functions are depleted, the pathology moves to the next stage.
The predominance of the pain syndrome is characterized by dull, aching pain that affects different parts of the abdominal region. Symptoms intensify after physical activity, if a healthy diet is not followed, and also under the influence of intestinal infections. In severe cases, intestinal obstruction develops. There are complaints of moderate nausea, heartburn, constipation, and diarrhea.
If dyspeptic disorders predominate, the patient's appetite is disturbed, the abdomen is swollen, constipation occurs, complaints of nausea and vomiting, heartburn, and cramping pain in the abdominal area.
With adhesive intestinal obstruction, a sharp, cramping pain in the lower abdomen occurs, nausea is replaced by vomiting, and there is no stool. The general condition is deteriorating, and weakness is troubling. Adhesions block the intestinal lumen, and blood circulation is disrupted. Lack of timely medical care is fraught with general intoxication, increased body temperature, and deterioration in general well-being.
Important! The development of adhesive obstruction is life-threatening and requires immediate surgical intervention.The long course of peritoneal adhesive disease causes extraintestinal manifestations: mood changes (increased irritability, aggressiveness, nervousness), kidney dysfunction with subsequent development of edema. The absorption of vitamins and microelements is impaired, resulting in the development of vitamin deficiency. Patients complain of impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system: heart rhythm is disturbed, fluctuations in blood pressure are observed.
Diagnosis of adhesive disease
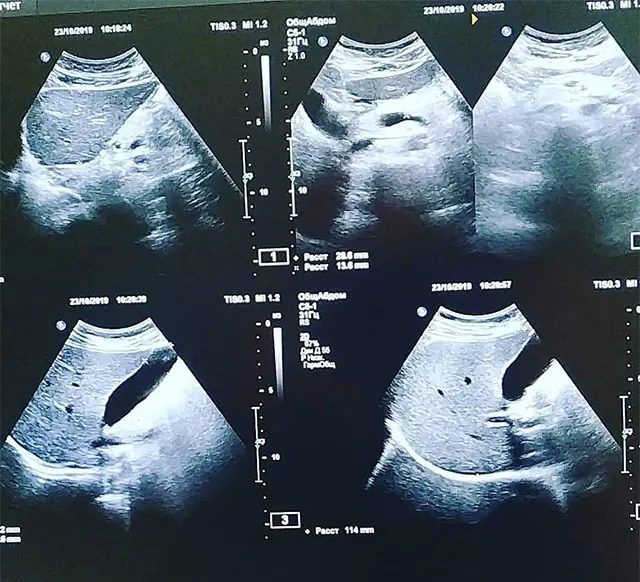
The decision on how to treat adhesive disease is made by the doctor after an in-person examination and interview of the patient, and a comprehensive examination.
Diagnosis of adhesive disease includes an in-person examination of the patient and palpation of the abdominal area. The pain is diffuse and intensifies even with slight pressure on the affected area.
The patient is also recommended:
- The primary method for identifying pathology is ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs to assess the functional and structural state of the peritoneal organs.
- Laboratory diagnostics (blood, urine, feces) in order to determine the general condition of the patient.
- X-ray to detect inflammatory exudate.
- Endoscopic diagnosis using FGDS procedures, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy, which allow you to assess the patency of organs and detect adhesions in the intestinal lumen.
- X-ray contrast diagnostics to detect the exact location of adhesions and intestinal obstruction.
To visually assess the condition of the peritoneal organs, the patient is prescribed a diagnostic operation - laparoscopy.
Methods for treating adhesive disease
Doctors use conservative and radical methods of therapy when identifying adhesions. Conservative treatment cannot cure the disease completely, but it can prevent the re-formation of adhesions and their complications. Therapy is aimed at reducing the feeling of pain. To do this, they use cleansing enemas (against the background of constipation and increased gas formation), and apply heat to the abdominal area. Elements of physiotherapy are also used: ultrasound, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis.
Medicines for adhesive disease
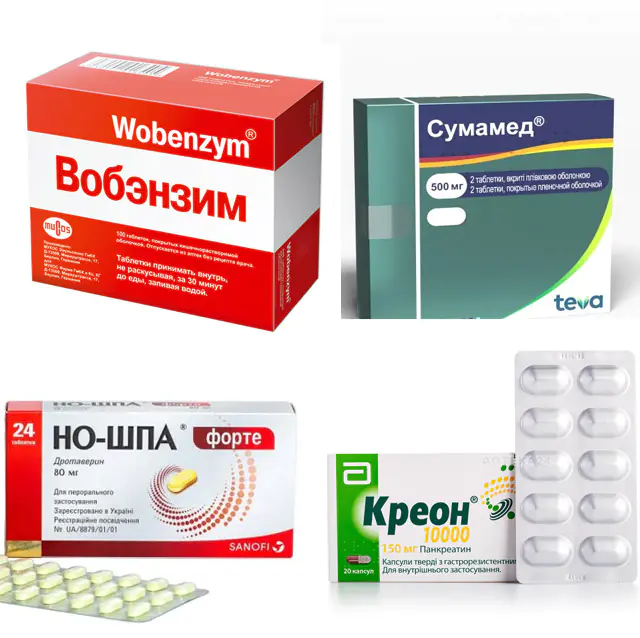
The selection of a drug treatment regimen for the disease is carried out by the doctor individually for each patient.
Effective drugs for the treatment of adhesive disease:
- Wobenzym. An enzyme preparation that breaks down fresh, thin adhesions. Available in the form of tablets for internal use. The pharmacological effect is based on the activity of the active ingredients: pancreatin, papain, bromelain, trypsin, lipase, amylase, chymotrypsin. The drug prevents complications and re-development of adhesive disease after surgery. The daily dosage is 5-10 tablets, divided into 3 doses throughout the day. After achieving a therapeutic effect, switch to a maintenance dose - 3-5 tablets per day. It is recommended to use the medicine 30 minutes before a meal, take it with a sufficient amount of liquid. Wobenzym can cause changes in the odor of stool and skin rashes. The cost of the drug is 520 rubles. (190 UAH). There are no exact structural analogues.
- Sumamed. A broad-spectrum antibiotic based on azithromycin, which is used to prevent infectious complications. Available in the form of tablets, capsules, powder for the preparation of suspension for internal use. Suppresses the production of protein compounds in pathogenic microorganisms. Effective against gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens. Contraindicated in patients with severe liver or kidney dysfunction, intolerance to macrolide antibiotics. The drug is taken 60 minutes before or 120 minutes after a meal. An overdose is fraught with temporary hearing loss, diarrhea, and vomiting. Therapy: rinse the stomach, use a sorbent and drugs for symptomatic treatment, selected by a doctor. Price — 410 rub. (150 UAH). Analogues: Azivok, Azikar, Azipol, Gynekit, Defense.
- No-Shpa. An antispasmodic that reduces the severity of pain. Available in the form of tablets and capsules for internal administration and solution for intramuscular administration. In case of intense pain, the patient is given an injection of No-Shpa, after which they switch to internal administration of tablets or capsules. Analogue - Drotaverine.
- Creon. An enzyme preparation that normalizes digestion and stimulates intestinal motility. Available in the form of 150 mg capsules for internal use. Contains amylase, pancreatin, lipase, protease. Restores digestion during partial resection of the stomach, can be used after surgical treatment of adhesive disease. Contraindicated in patients with intolerance to active substances, in acute cases and exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis. Half the recommended dose is used at the beginning of a meal, the rest - during the meal. The price of the drug is 340-700 rubles. (200 UAH). The drug has no exact structural analogues.
Surgical treatment of adhesive disease
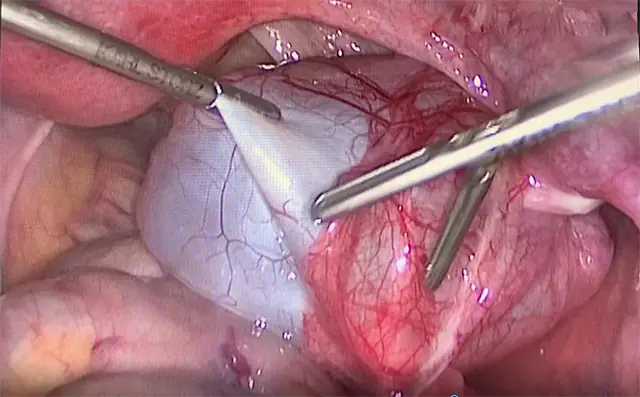
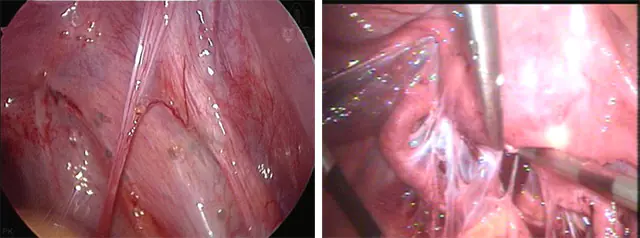
The photo shows abdominal adhesions – laparoscopic surgery
Surgery for adhesive disease is the main method of therapy, which is prescribed when an emergency condition is identified or regular exacerbations of the disease. The procedure is carried out according to indications: intestinal obstruction, chronic pain syndrome, severe dyspeptic disorders, difficulties in conceiving a child.
The surgical technique for adhesive disease is selected by the surgeon, taking into account the degree of progression and localization of the pathological process:
- Laparoscopy recommended if the number of adhesions is insignificant. The doctor gradually excises and separates them from the abdominal cavity using an atraumatic instrument.
- Bowel resection indicated if a certain area of the intestine is significantly damaged or twisted, tissue necrosis is observed. A section of intestine is removed and the rest is stitched together.
- Anastomoses (holes) This is done if there is extensive intestinal damage or obstruction. This workaround allows you to restore the passage of food and feces.
To prevent re-formation of adhesions during surgery, a number of measures are followed: do not allow the peritoneum to dry out, completely eliminate bleeding and immediately remove residual blood. During the procedure, the doctor makes a wide measurement and carefully ensures that foreign objects do not get into the peritoneum. To sew the edges of the wound, use a polymer thread. The use of antibiotics and antiseptics in powder form is not recommended.
During the recovery period after surgery, it is recommended to start moving as early as possible. Follow these recommendations:
- For 30 days, the patient should not lift weights, have sex, drink alcohol, or engage in strength sports that require significant stress.
- Refrain from visiting the sauna, bathhouse, sunbathing on the beach, or prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
72 hours after laparoscopy, the patient can begin performing therapeutic exercises under the supervision of a rehabilitation physician. Therapeutic exercise enhances motor activity and stimulates the work of the abdominal muscles. The selection of exercises is carried out on an individual basis.
Folk remedies for adhesive disease

Traditional treatment of adhesive disease is used as a complement to the main therapy recommended by the doctor. Such methods can be used during the recovery period after surgery to normalize the patient’s well-being, with prior agreement with the doctor.
Folk remedies for the treatment of adhesive disease:
- Wrap 3 tablespoons of flaxseed in cheesecloth and place in boiling water. Leave for 5 minutes, cool. Flax seeds are distributed over the lower abdominal area and left to act overnight.
- To reduce the symptoms of adhesions and inflammation, bergenia roots are poured with hot water, left for 7-9 hours and placed in the refrigerator. The resulting solution is diluted with water and used for douching.
- Centaury, sweet clover, coltsfoot are mixed in equal proportions, poured with boiling water and infused in a thermos for 4 hours. Drink 1/3 cup three times a day for 30 days.
- A tablespoon of dried St. John's wort herb is poured with boiling water and simmered over low heat for 10 minutes. Cool, take 1/3 cup three times a day. The course of treatment can be repeated several times a day. It is better to refrain from using St. John's wort in the summer, as the plant can cause hyperpigmentation.
Diet for adhesive disease
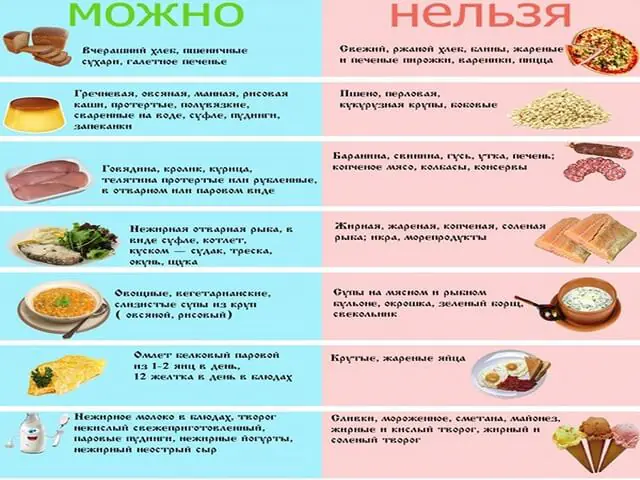
A diet for adhesive bowel disease involves eating food up to 4 times a day, in small portions. The food is chewed thoroughly and the portions are small.
It is allowed to consume low-fat meat and chicken broths, boiled fish, omelettes or hard-boiled eggs, vegetable broths, low-fat chicken fillets, fresh fruits (except grapes), cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal, rice).
When treating adhesive disease, it is necessary to maintain a drinking regime; the amount of fluid is calculated using the formula: 30 ml of water multiplied by the patient’s body weight.
It is recommended to exclude heavy foods that can cause increased gas formation. It is necessary to give up legumes, white cabbage, grapes, turnips, radishes, corn, milk, carbonated drinks, alcohol, fatty meat and fish, fast food, canned food, semi-finished products, pickles, smoked meats, semolina, flour products, baked goods, and sweets. In addition, avoid eating excessively hot or cold foods.
In the first 24 hours after surgery, it is allowed to consume weak broths, then light food with a puree-like consistency. After 3-4 days, boiled vegetables, meat, and porridge are introduced into the diet. The diet must be followed for less than 1 month.
For the prevention of adhesive disease it is recommended lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid hypothermia, give preference to moderate physical activity, and observe a work-rest regime. Long periods of hunger followed by overeating are unacceptable. It is necessary to normalize stool (at least once a day, and preferably 2 times), promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and undergo preventive examinations by a gastroenterologist. At the first signs of gastrointestinal diseases or adhesions, you should immediately contact an experienced specialist.
Video, what is adhesive disease, what are the dangers of surgical operations



