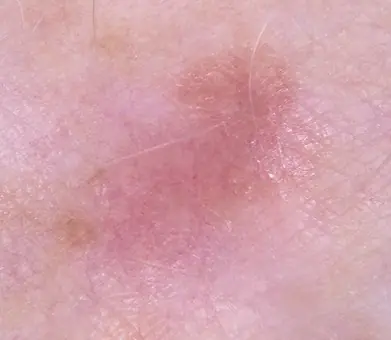
Skin lesions appear in people throughout their lives. There is a huge number of all kinds of moles, warts, papillomas, etc., and all these neoplasms have a different mechanism of occurrence. Some of them are considered benign and are not capable of causing harm to health. But sometimes tumors called melanoma arise, which means that healthy cells in the body have begun to degenerate into cancerous ones.
The incidence of cancer in the 21st century worries doctors and scientists around the world. One of the most terrible types of this disease is non-pigmented (amelanotic) melanoma - a cancerous tumor on the skin, which is very difficult to recognize in the first stages.
Amelanotic melanoma is much less common than other types of skin cancer. It is difficult to diagnose in a timely manner, due to its color, which does not differ from ordinary skin.
Characteristic features of development
Pigmentless melanoma is a cancerous lesion of the epidermis, which is characterized by rapid development and deepening into the inner layers of the skin. Amelanotic melanoma is characterized by an aggressive course and rapid spread of metastases. The reasons for its occurrence are not yet fully understood, but the main factor is considered to be a change in the DNA structures of melanocytes - the cells that produce the skin pigment melanin. Changes may be caused by exposure to ultraviolet rays, trauma to the nevus, or harmful chemical effects on the skin. Pigmentless melanoma is usually localized in open areas of the body: face, neck, shoulders and limbs.
This type of neoplasm occurs at the site of a mole, birthmark, or on unchanged skin. A distinctive feature of amelanotic melanoma is the lack of pigmentation of the tumor, which significantly complicates timely diagnosis. Due to the rapid spread of cancer cells through hematogenous and lymphogenous routes, the disease is often detected in late stages, in which case the treatment process is very difficult. The prognosis for life with this disease is often disappointing, since there are initially no visible symptoms.
The first symptom that a mole has begun to degenerate is a change in its color. Thus, the usual brown color inherent in a nevus begins to lighten, becoming pink or flesh-colored. Although there are many more symptoms that indicate malignancy, we will consider them below.
A protruding colorless formation found on the body should be examined by an oncologist
Common symptoms of amelanoma
Long-term observations of melanoma have shown that this disease is characterized by a wide variety of symptoms. In the initial stages of development, amelanoma resembles an insect bite.
- asymmetrical borders;
- elevation above skin level;
- hair loss from the surface of the mole;
- change from a homogeneous structure to a lumpy one;
- color change from dark to light;
- increase in the size of the mole;
- redness around the formation;
- the appearance of ulcers, peeling, bleeding;
- the appearance of a nodule on a thin stalk.
Finding at least one of the above symptoms is a reason to immediately contact an oncologist, so you will get a chance for a speedy and complete recovery.
Symptoms of the disease by stage
The main criterion by which the stage of development of the disease is determined is the thickness of the tumor and the rate of degeneration of atypical cells. The thinner the melanoma, the higher the patient's chances of survival.
- Stage 1. At the earliest stage, melanoma is located only in the upper layers of the dermis, the thickness of the neoplasm is less than 1 millimeter, and the contours are smooth. In some cases, a colorless, soft papilloma on a thin stalk may appear. Detection at this stage guarantees a high chance of curing a disease such as amelanoma. The survival rate is 99%.
- Stage 2. The tumor is also located in the upper layers of the skin, its thickness is about 1 millimeter, the borders are round, the neoplasm is symmetrical. At the second stage, a pedunculated nodule appears on the surface of the melanoma, which is easily injured by contact with tissue or mechanical impact. The survival rate is still high and is about 90%.
- Stage 3. At the third stage, the thickness of the formation can reach 4 millimeters. Metastases begin to spread to sentinel lymph nodes. There is pain in the affected area and bleeding. Life forecasts are significantly reduced and at this stage are less than 50%.
- Stage 4. The thickness of the formation is already more than 4 millimeters. Metastases actively spread throughout the body and affect such important organs as the lungs, liver, kidneys, brain and skeletal system. At this stage, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable; death occurs in 99% of cases.
A colorless formation with a loose surface may be melanoma
Timely diagnosis of non-pigmented melanoma and proper therapy are the key to a speedy recovery. The disease, detected in the early stages of development, can be successfully treated in most cases. A photo of the initial stage of non-pigmented melanoma will help you determine the presence of a tumor and have time to contact an oncologist before irreversible processes appear. Carry out self-examination regularly, and if necessary, consult a doctor immediately.
Typically, melanoma develops into a malignant tumor from a mole in 50-70% of cases. A non-pigmented neoplasm is characterized by the appearance of white tubercles that slowly grow in size. The bumps become uneven, dense, and resemble an insect bite.
Then, at an advanced stage, melanoma begins to itch, itch, cause discomfort and ultimately become unbearably painful. In later stages it bleeds and smells unpleasant. This is a dangerous symptom.
ABCDE visual testing is performed to determine the first symptoms of melanoma.
- A – asymmetry in shape. Spots, nodules, moles that are suspicious appear to have jagged edges in appearance.
- B – blurry borders and jagged edges.
- C – the color of a birthmark or neoplasm similar to melanoma is uneven and changes over time.
- D – size. Malignant neoplasms exceed 6 mm and gradually grow.
- E – development. As the patient’s condition worsens, the tumor changes, begins to itch, hurt, and begins to bleed.
If you have suspicious symptoms, it is important to go to a dermatologist or oncologist in time and develop the correct treatment option.
Types and forms
This unusual, rare type of disease comes in different types and forms. Amelanotic melanoma is insidious, camouflaged and not so easy to detect.

- Nodular is recognized as extremely dangerous; first, an elevation is formed, a small nodule that begins to grow quickly and rise above the skin. It metastasizes almost instantly, and the outcome of treatment is unfavorable. It mainly affects older people.
- Acral. It takes a long time to camouflage and takes on the appearance of a spot with blurred boundaries. Acral melanoma affects dark-skinned people, and the prognosis for survival is the most favorable.
- Spindle cell. Appears in the form of a dome, rising on the skin of the arms, legs, neck and head. The outcome is favorable if detected in the early stages.
- Epithelioid cell. The most common type. Oncologists diagnose it in 70% of cases, initially as a benign tumor. Then it can mutate into malignant and grow deeper, giving metastases.
How to detect amelanotic melanoma in the early stages
An apigmented tumor is difficult to diagnose, has an atypical appearance, is white in color, and is not pigmented.
A light tumor appears in the early stages of its course, when the disease is determined visually and suspicious elevations appear on the skin. Also, achromatic melanoma appears from moles and warts and can occur on any part of the body. It is difficult for an oncologist to identify from a large number of nevi which tumors to send for biopsy and examine.
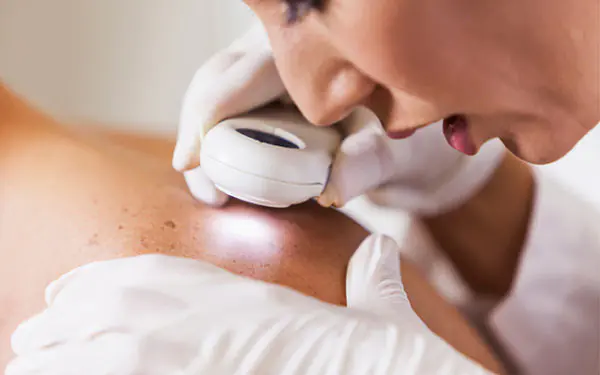
The main warning signs during the initial examination of the skin:
- The appearance of an unusual elevation instead of a flat spot.
- Warts and nevi begin to increase in size for no reason.
- The boundaries of the neoplasm blur and lose color.
It is difficult for a person to determine this type of clear cell cancer on his own; it is better to seek advice from a specialist.
A popular method in diagnosing the initial stage of the disease is dermatoscopy, when a suspicious cell is examined using polarized light on a portable device.
The oncologist is interested in the timing of detection of health problems, hereditary and genetic factors. After taking all the tests, the doctor makes a diagnosis, determines the stage and severity of the disease and prescribes treatment.
Localization zone
Pigmentless melanoma can appear anywhere on the human body, but primarily in those places that are influenced by external aggressive factors:
Stages
In oncology, there are 4 stages when the achromatic type of melanoma appears:
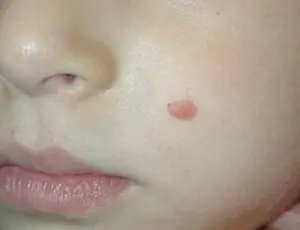
- The first stage is characterized by the appearance of painless lumps up to 1 mm, without pigment. This is the initial phase.
- At the second stage, the tubercle thickens, begins to grow deeper into the skin, becomes larger than 2 mm, but metastases do not appear.
- At the third stage, the lymphatic system begins to be affected, the lymph nodes begin to swell, and the neoplasm itself itches, bleeds and hurts. Damage to neighboring tissues occurs. The operation allows you to remove the tumor along with the adjacent area of skin within one centimeter.
- At the fourth stage, metastases already appear, the malignant nevus grows up to three centimeters. It becomes covered with growths, ulcers and can darken to black. Survival at this stage is practically zero: metastases spread quickly, especially when the disease is detected at the last stage.
Therefore, a visit to an oncodermatologist is prescribed so that the disease is not detected in an advanced form.
Treatment
The oncologist identifies the stage of the disease and prescribes treatment after diagnostics, a biopsy procedure, and histology.
First of all, surgery is performed and the tumor itself and healthy skin around it are removed. If the disease is detected at a late stage and the lymphatic system is affected, the inflamed lymph nodes are removed.
Radiation therapy is then prescribed to irradiate the area affected by metastases. Chemotherapy is also prescribed to stop the inexorably spreading process of metastasis to the brain and bones. At the last stage, even with the help of aggressive chemotherapy, it is difficult to completely cure the disease, since there is a likely risk of relapses. At the initial stage, the probability of a positive outcome and the prognosis of complete recovery within five years is 85%, and in the latter stage the chance is only 5%.
Prevention
Preventive actions will help prevent the formation of a malignant tumor:
- Apply sunscreen and cover bare areas of skin in the scorching sun. Do not sunbathe during dangerous hours when the sun is at its zenith.
- Use products with a high protection factor, even when it is cloudy outside.
- Do not visit the solarium often.
- Carry out self-diagnosis, examine moles yourself for the reason for changes in shape, size, color.
Subject to preventive measures and proper treatment by qualified specialists, the disease can be cured in the early stages with a high percentage of positive outcomes.

Melanoma is considered one of the most insidious human malignant tumors, the morbidity and mortality from which is steadily increasing from year to year.
They talk about it on TV, write in magazines and on the Internet. The interest of ordinary people is due to the fact that the tumor is increasingly being detected in residents of various countries, and the number of deaths is still high, even despite intensive treatment.
In terms of prevalence, melanoma lags significantly behind epithelial skin tumors (squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, etc.), according to various sources, accounting for 1.5 to 3% of cases, but it is much more dangerous. Over the 50 years of the last century, the incidence increased by 600%. This figure is enough to seriously fear the disease and look for the causes and methods of treating it.
What it is?
Melanoma is a type of cancer that affects melanocytes—pigment cells located in human skin. The disease has a high risk of rapid metastasis, which leads to the development of severe complications and, in severe cases, death of the patient. Every year, about 50 thousand new cases of melanoma are registered in the United States.
Melanoma is more susceptible to white-skinned older people (55-70 years old), but young people over 30 are also at risk of its occurrence. In almost all cases, the tumor is preceded by changes in the form of age spots, moles, dermatitis and other precancerous conditions. Melanoma is often detected at the metastatic stage, but even timely diagnosis often leaves no chance for a favorable outcome due to the extreme malignancy of the neoplasm.
The first link in the timely diagnosis of the disease is the patients themselves, since melanomas usually occur on open, visible areas of the skin. This is important because early detection and diagnosis of melanoma ensures rapid cure with minimal surgery.
Epidemiology
According to WHO, in 2000, more than 200,000 cases of melanoma were diagnosed worldwide and 65,000 melanoma-related deaths occurred.
In the period from 1998 to 2008, the increase in the incidence of melanoma in the Russian Federation was 38.17%, and the standardized incidence rate increased from 4.04 to 5.46 per 100 thousand population. In 2008, the number of new cases of skin melanoma in the Russian Federation amounted to 7,744 people. The mortality rate from melanoma in the Russian Federation in 2008 was 3159 people, and the standardized mortality rate was 2.23 people per 100 thousand population. The average age of melanoma patients diagnosed for the first time in their lives in 2008 in the Russian Federation was 58.7 years. The highest incidence was observed at the age of 75-84 years.
In 2005, the United States recorded 59,580 new cases of melanoma and 7,700 deaths due to this tumor. The SEER (The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) program notes that the incidence of melanoma increased 600% from 1950 to 2000.
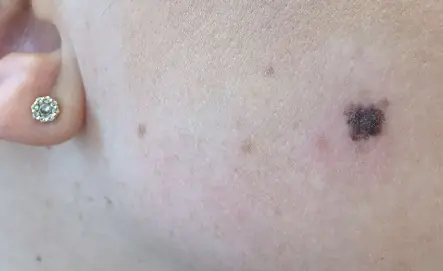
Causes of melanoma development
The reason for the formation of melanoma in the initial stage is the degeneration of melanocytes into malignant cells.
The main theory that explains this process is molecular genetics. Defects appear in the DNA molecule of the pigment cell. Further, under the influence of provoking factors, a gene mutation occurs, associated with a change in the number of genes, disruption of the integrity of chromosomes or their rearrangement. The changed cells acquire the ability to divide unlimitedly, as a result of which the tumor increases in size and metastasizes. These disorders can occur under the influence of unfavorable factors of internal and external properties or a combination of them.
Causes and risk factors:
- Prolonged exposure to the sun. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, including solariums, can cause the development of melanoma. Excessive sun exposure in childhood significantly increases the risk of disease. Residents of regions with increased solar activity (Florida, Hawaii and Australia) are more susceptible to developing skin cancer. Burns caused by prolonged exposure to the sun more than double the risk of developing melanoma. A visit to the solarium increases this indicator by 75%. The WHO Cancer Research Agency classifies tanning equipment as an "increased risk factor for skin cancer" and classifies tanning equipment as carcinogenic.
- Moles. There are two types of moles: normal and atypical. The presence of atypical (asymmetrical, raised above the skin) moles increases the risk of developing melanoma. Also, regardless of the type of moles, the more there are, the higher the risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor;
- Skin type. People with more delicate skin (characterized by light hair and eye color) are at increased risk.
- Anamnesis. If you have previously had melanoma or another type of skin cancer and are cured, your risk of developing the disease again increases significantly.
- Weakened immunity. The negative impact of various factors on the immune system, including chemotherapy, organ transplantation, HIV/AIDS and other immunodeficiency conditions, increases the likelihood of developing melanoma.
Heredity plays an important role in the development of cancer, including melanoma. Approximately one in ten patients with melanoma has a close relative who has or has had the disease. A strong family history includes melanoma in parents, siblings, and children. In this case, the risk of melanoma increases by 50%.
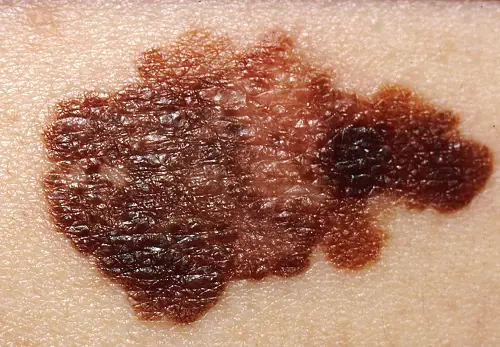
Classification
Clinical forms of the disease:
- Superficially spreading, or superficial. It is observed in 70% of patients, more often in women. This melanoma is characterized by a long period of benign growth. It grows into deeper layers after a long time and has a favorable prognosis.
- Nodular (nodular). Invasive variant of the tumor. It quickly grows deep into the skin and looks like a convex round bump. The pigmentation of such a formation is usually black, less often than other dark shades, or is not changed at all. Often, nodular melanoma is detected in elderly people on the limbs and trunk.
- Acrolentiginous. It develops on the surface of the skin and later grows deeper. A distinctive feature is the localization of symptoms - the tumor occurs on the palms, soles or under the nails. This melanoma appears more often in blacks and Asians.
- Lentiginous, or malignant lentigo. The neoplasm in appearance resembles a large flat birthmark. Nests of melanocytes form in the epithelial layer, from where they penetrate inside. It is more common in elderly women over 70 years of age on the face, neck and back of the limbs.
- Pigmentless (achromatic). It occurs quite rarely, in 5% of cases. Changed pigment cells lose the ability to synthesize pigment, so these formations are pink or flesh-colored. A non-pigmented tumor is considered as one of the varieties of the nodular form or is considered a manifestation of metastases on the skin.
Symptoms of melanoma in the initial stage
At the initial stage, melanoma (see photo) is no different from an ordinary mole. The main symptoms of the onset of the disease include the following:
- The mole began to grow and bleed and became darker;
- The mole began to itch.
These are the main symptoms that require immediate consultation with an oncologist. Also, do not postpone your visit if the number of moles suddenly increases sharply.
In the initial stage, the thickness of the formation does not exceed 1 mm. A mole that has just begun to degenerate is practically indistinguishable from an ordinary one. An already developing malignant neoplasm can have any size and shape, be weeping, covered with nodes, and bleed. The tumor has a dense consistency and often rises above the skin. The color can be black, brown, blue, gray. Not often, but there are cases when a melanoma lesion does not change color and remains light, similar to ordinary hypomelanosis.
Melanoma can occur in any area of the body. However, most often in women it is diagnosed on the lower leg, and in men - on the back. In older people, the tumor is more often localized on the face. In half of the cases, the formation develops on healthy skin, and in the remaining cases - on the site of pigmented nevi.
Melanoma on the iris of the eye looks like a dark spot of irregular shape; the subungual formation looks like a strip located under the nail plate on the cuticle.
Superficial forms tend to grow slowly, while nodular forms can go through several stages of development in a few weeks.
When a mole becomes malignant, changes can be observed:
- Increased pigmentation;
- Uneven color (presence of several shades);
- Shiny surface of the formation;
- Redness of the surrounding area;
- Blurred edges of the mole, jagged borders;
- Lack of hair;
- The lesion may exceed 5 mm;
- The appearance of nodular small papillomatous elements in the area of the nevus;
- Itching and burning.
As the formation grows and the stage moves to a more serious stage, a more pronounced clinical picture develops.
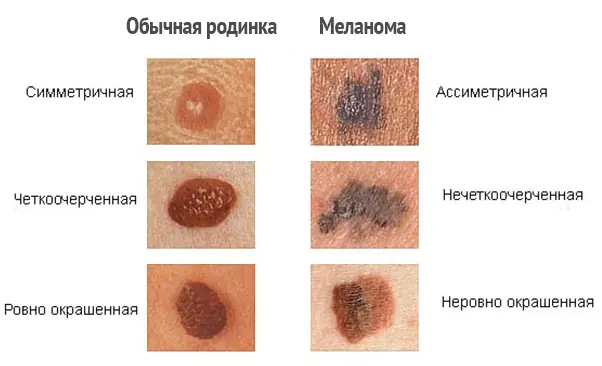
How to distinguish melanoma?
In order to correctly distinguish melanoma and notice the first signs of malignancy, it is necessary to distinguish skin formations, that is, to know the difference between freckles, moles, and nevi. Unfortunately, even many experts confuse these definitions with each other.
| Name | Description |
| Moles | Oval or round formations, dark brown or flesh-colored. The diameter of moles varies from 0.2 to 1 centimeter. As a rule, moles are flat, but sometimes they can rise above the level of the skin. |
| Freckles | Flat, light brown, rounded spots on the skin that darken in the sun and turn pale in winter. |
| Atypical or dysplastic nevi | Larger moles, with uneven edges and uneven coloring. |
| Malignant melanoma | Pigmented and non-pigmented formations on the skin, arising both independently (de novo) and on changed skin (that is, from previous moles). Melanoma develops from the pigment cells (melanocytes) of the skin. Further growing deeper, the tumor acquires the ability to metastasize through the lymphatic and blood vessels to any part of the body. |
Every pigmented formation, be it an old mole or a new nevus, in people over 20–30 years of age should be examined with suspicion of melanoma. In addition to periodic examinations by a dermatologist and oncologist, additional studies should be carried out.
Diagnostics
The quality of melanoma treatment and the prognosis of the disease directly depend on the early diagnosis of the lesion. To determine an oncological diagnosis, an oncologist performs a visual examination of the pathology area. A detailed examination of a malignant neoplasm is carried out using a dermatoscope, which is a special device for viewing pathology in an enlarged form.
In modern oncology clinics, digital dermatoscopes are used, which allow one to view a malignant neoplasm in a three-dimensional image on a monitor screen. An effective additional method for diagnosing melanoma is a blood test for cancer (tumor markers are specific proteins, the concentration of which increases with cancer).
All cancers undergo a biopsy at the final stage of examination. Cytological and histological studies of biological material taken from the primary cancer focus make it possible to establish a final diagnosis indicating the stage and form of oncology.
Photo: what melanoma looks like
Below are numerous photos that will help you understand what melanoma looks like in the initial as well as more advanced stages:
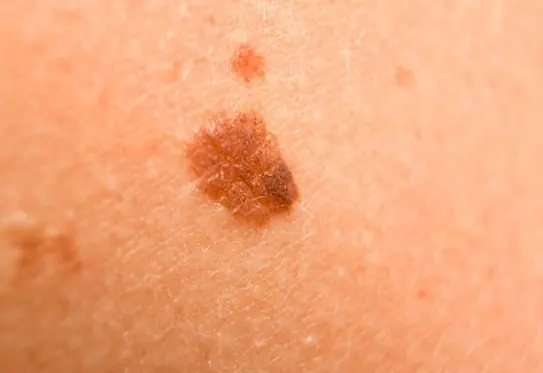
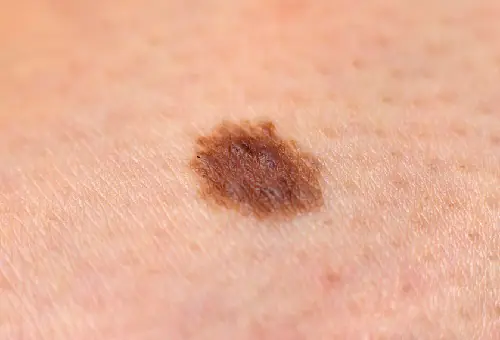
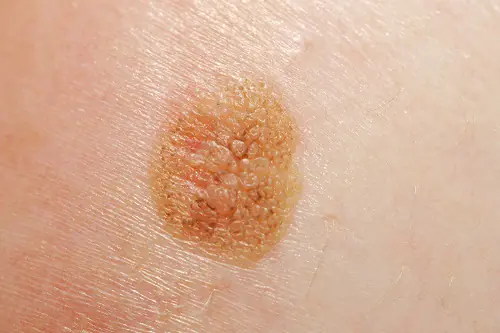
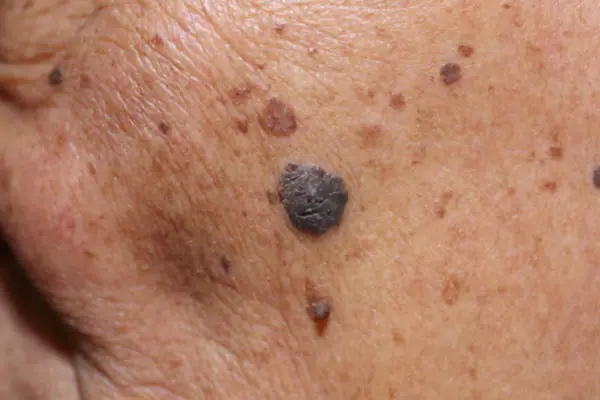
How to treat melanoma in the early stages
The main treatment method for early-stage melanoma in 2019 is surgical removal. Both for the primary tumor and for the treatment of relapses, sheath-fascial excision of the tumor is performed. The tumor is removed along with the adjacent area of apparently unchanged skin - depending on the stage, at a distance of 1 cm to 2-3 cm. Together with the tumor, the subcutaneous tissue is removed to the aponeurosis or fascia of the underlying muscle, followed by plastic surgery. Removal of the fascia itself is a controversial issue and is not accepted by some authors. If lymph nodes are affected, their resection is performed.
Indications for regional lymphadenectomy for primary cutaneous melanoma:
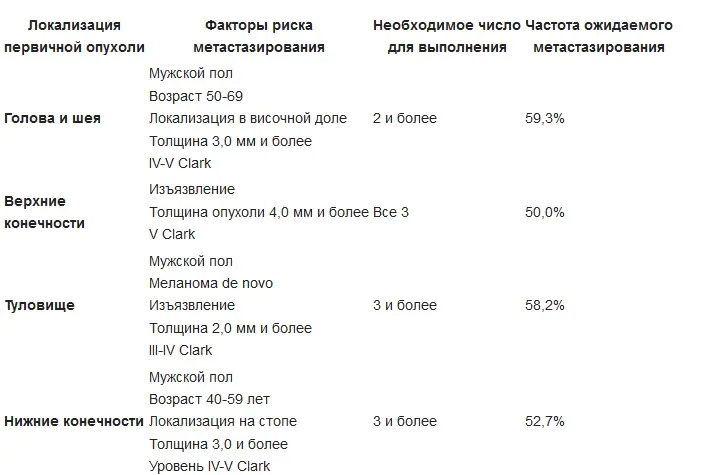
An option for surgical treatment may be Mohs surgery (Frederick Mohs) - surgical interventions under the control of a microscope, as well as laser sheath excision. Cryodestruction of melanoma is not used due to the fact that the level of invasion into the underlying tissue cannot be accurately determined.
Treatment of melanoma with metastases
The main methods of treating metastatic melanoma are polychemotherapy, immunotherapy and radiation therapy, which are usually used in combination.
Immunotherapy
- Interferon-alpha (IFN-A), interleukin 2 (IL-2) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). A study performed by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) showed that the use of interferon-alpha-2b at maximum tolerated doses provides a significant prolongation of disease-free interval and overall survival compared with no adjuvant therapy.
- Monoclonal antibodies. By prescribing immunotherapy drugs - ipilimumab and nivolumab - to patients with melanoma at stages III and IV, it was possible to achieve tumor reduction in 58% of cases, by more than a third, in the rest - to stop the growth of melanoma for a year. The study results were presented at the 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
- Radiation therapy - total focal dose - 4000...4500 rad. The optimal total dose is 10,000 rad. (Different protocols are different).
- Regional and systemic chemotherapy is used for generalization of the process: dacarbazine (DTIC), carmustine (BCNU), lomustine (CCNU), cisplatin, tamoxifen, cyclophosphamide, etc.
Gene therapy for melanoma is under research, aimed at introducing tumor suppressors p53 gene, p16INK4a, inactivation of the oncogenic signaling pathway - ras, - c-myc, etc.
Research led by Mikhail Nikiforov of the Roswell Park Cancer Institute is in the preclinical stage and shows that the enzyme guanosine monophosphate synthase (GMPS) can trigger the growth of melanoma and could become a target for new drugs against it. The role of GMPS in the development and metastasis of melanoma has now been studied. This enzyme can be blocked using the long-established antibiotic angustmycin A, also known as decoyinine. GMPS levels were found to be elevated in melanoma metastasis samples. Angustimin A is believed to have potential as a targeted therapy for tumors harboring the NRASQ61R or BRAFV600E gene mutation.
A new drug, Keytruda, which was approved by the FDA last year for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer, is undergoing further clinical trials. At this stage, the Sheba State Hospital in Israel is recruiting patients to participate in a clinical trial of the drug in the treatment of melanoma. Foreign patients can also take part in the studies.
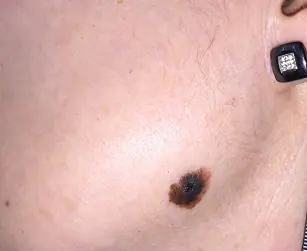
Patient monitoring
Patients who have completed radical surgical treatment should be followed up by an oncologist. Observation should be carried out according to the general rules - periodic examinations by a doctor, with control ultrasound examinations.
The rules for clinical observation of patients with melanoma are as follows:
- during preventive examinations, mandatory examination of the skin in the area of the removed tumor;
- mandatory palpation of lymph nodes - cervical, axillary, inguinal-femoral;
- additional ultrasound examination of lymph nodes;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs to exclude metastasis to internal organs;
- If necessary, bone scintigraphy and computed tomography of the brain are performed.
Prevention
Prevention of melanoma involves the use of a cream that protects against ultraviolet radiation and minimal exposure to direct sunlight. It is also necessary to regularly engage in self-examination. In order to answer the question of how long people live with melanoma, it is necessary to understand that it depends on the stage, location, size of the process and the activity of the body’s immune system.
Forecast
With initial and stage II melanoma without relapse, cure is possible; with relapse, the five-year survival rate is approximately 85%, stage III - 50%, stage V - up to 5%.
">