IN 1928 Adolf Windaus (Adolf Windaus) received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his studies of the composition of sterols and their relationship with vitamins. The fat-soluble substance he studied was vitamin D; however, the history of vitamin D and rickets, as its deficiency, actually dates back to antiquity, if you carefully study written sources and works of art.
IN 1919 Melanby (Mellanby), conducting experiments on dogs using cod liver, was the first to conclude that the cause of rickets was the lack of “auxiliary dietary factor.” Three years later, McCollum et al. found that cod liver oil, when heated and oxidized, cured rickets in rats. The new factor was named vitamin D, since it was the fourth vitamin discovered by that time.
At the same time, a completely different cure for rickets appeared in the form of UV light. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, the etiology of rickets was a lack of fresh air and sunlight, as well as a lack of exercise. In 1921, Hess and Unger observed a seasonality in rickets that paralleled seasonal variations in solar radiation. Regardless, Chick concluded that sunlight was as effective in curing rickets as cod oil.
IN 1919 Guldshinsky (Huldschinsky) came to the conclusion that artificial sunlight can act on rickets with the same success as natural light. By controlling diet and external UV exposure, he exposed children with severe rickets to a mercury-quartz lamp emitting UV rays and observed significant clinical and radiographic improvement, including fresh calcium deposits.
IN 1925 Hess and his collaborators isolated sitosterol from cotton seed oil, which had no effect on rickets in rats until it was irradiated with UV light. Since the discovery that irradiation of food, particularly whole milk, can impart anti-rickets properties, it has led to enormous advances in public health and has caused a rapid decline in the prevalence of rickets in children.
With amazing foresight, Hess hypothesized that cholesterol in the skin was activated by UV radiation and became antirachitic. The complete photochemical and thermal reaction steps in the vitamin D mechanism were finally elucidated in 1955 by Velluz. The exact sequence of steps leading to photoproduction of cutaneous cholecalciferol is outlined in a review by Holik in 1980.
A) Functions of Vitamin D. Vitamin D regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. Its main role is to increase the influx of calcium into the bloodstream by absorbing calcium and phosphorus from the intestines and reabsorbing calcium in the kidneys, allowing for normal bone mineralization and muscle function. This vitamin affects serum alkaline phosphatase levels and also inhibits T cell proliferation and dendritic cell maturation along with effects on keratinocyte function.
Vitamin D deficiency leads to impaired bone mineralization, which causes bone softening pathologies, in particular rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, and possibly contributes to the development of osteoporosis. Deficiency may result from dietary intake of the vitamin combined with inadequate sun exposure, as well as from diseases that limit its absorption or conditions that impair the conversion of vitamin D into active metabolites, such as liver or kidney disease.
Those most prone to low levels of the vitamin are the elderly, residents of high latitudes with long winter periods, obese individuals and all persons with dark skin pigmentation living in high latitudes.
Toxicity due to excess vitamin D may manifest in the form of hypercalciuria or hypercalcemia, the latter causing muscle weakness, lethargy, headache, confusion, anorexia, irritability, nausea, vomiting and bone pain and can potentially lead to complications such as kidney stones and kidney disease. failure. The effects of chronic toxicity include the above symptoms in combination with constipation, anorexia, abdominal cramps, polydipsia, polyuria, back pain and hyperlipidemia.
Symptoms may also include calcification followed by hypertension and cardiac arrhythmia (due to a shortened refractory period). Although information on the effects of high doses of vitamin D is limited, 10,000 IU per day is considered a safe upper dose limit for adults. The chronic toxic dose for adults is more than 50,000 IU/day.
There are two main sources of vitamin D: food and skin. When a vitamin is supplied from outside, through food or food additives, it is absorbed in the small intestine. Natural food sources rich in vitamin D include certain types of fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, catfish, cod, sardines and eels, as well as butter, margarine, yogurt, liver, liver oil and egg yolk, but At least in the United States, most dietary vitamin D comes from fortified foods, particularly cereals, milk, and orange juice.
An 8-ounce glass of fortified milk, for example, typically contains 100 IU of the vitamin, only a fraction of the adequate daily intake for adults. To get their daily dose of the vitamin, most Americans take vitamin D supplements, either alone, with calcium, or in a multivitamin.
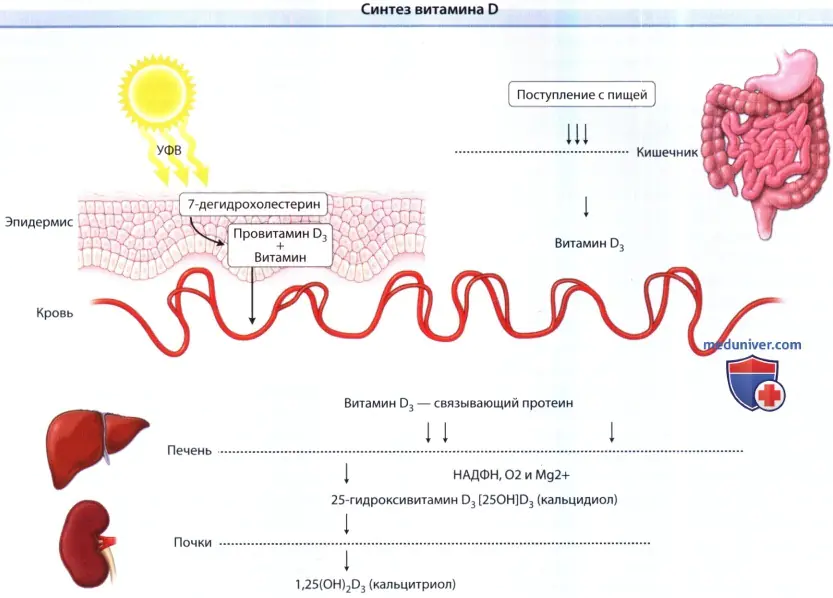
b) Biochemistry of vitamin D. As a result of exposure to UVB on the skin, the precursor of vitamin D3 (7-dehydrocholesterol, a precursor of cholesterol) is quickly converted into provitamin D3, which, through the process of isomerization, is spontaneously transformed into vitamin D3 and enters the blood on a binding protein, combining with dietary D2 (erogocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol) absorbed from the intestines. Having reached the liver, they undergo passive hydroxylation in the endoplasmic reticulum of hepatocytes, and this process requires NADPH, O2 and Mg 2+ .
The resulting product, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [25(OH)D3 (calcidiol)], accumulates in hepatocytes and, as needed, enters the plasma through the proximal renal tubules, where it is acted upon by 25(OH)D-1-a-hydroxylase, an enzyme , whose activity is increased by parathyroid hormone and low PO levels4 2- . In people with kidney disease, conversion of vitamin D to its active form may not occur. After this conversion, 1,25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3 (calcitriol)] enters the blood, which binds to the carrier protein in the plasma (VDBP protein) and is transported to various target organs.
V) Spectrum of action for the formation of vitamin D in the skin. Action spectrum studies show that light wavelengths most effective for photosynthesis of vitamin D in the skin are between 295 and 300 nm, which, ironically, are also most often responsible for photocarcinogenesis. Optimal synthesis occurs in a very narrow band of the UVB spectrum between 295 and 300 nm, with the peak of isomerization occurring at 297 nm. With a UVB index of at least 3, which is observed daily in the tropics and almost never in high latitudes, adequate amounts of vitamin D3 are synthesized in the skin after 10-15 minutes of sun exposure of the face, arms, hands or back without applying sunscreen at least twice in Week.
In Boston, the level of sun exposure from November to February is not sufficient to produce significant amounts of vitamin D in the skin. The supply of UVB for vitamin D synthesis depends on all of the factors that determine the UV index, including time of day, cloud cover, smog, shade, reflection from nearby water surfaces, sand or snow, latitude, altitude and time. of the year. Of course, individual factors also play a role, such as age (vitamin D production decreases in people over 70), body mass index, clothing, and the amount of skin exposed to the sun. Individuals with high levels of melanin in their skin need longer exposure to the sun than those with lower levels of melanin to synthesize the same amount of vitamin D.
According to Holick, when a person's entire body is exposed to sunlight in the amount of one minimum erythemal dose, at least 10,000-25,000 units of vitamin D are synthesized. Vitamin D production in the skin occurs within minutes and reaches a maximum even before the skin turns pink. Exposure to the sun for long periods of time does not usually result in vitamin D toxicity. Within 20 minutes of sun exposure for fair-skinned individuals (within 1-3 hours for pigmented skin), the concentration of vitamin D precursors produced by the skin reaches equilibrium and excess vitamin D simply decomposes as quickly as it is synthesized.
Vitamin D synthesis: Vitamin D is synthesized in the epidermis under the influence of UVB and is also adsorbed in the intestine.
It is then delivered by a carrier protein to the liver, where it undergoes 25-hydroxylation.
The resulting metabolite, calcidiol, is the main circulating form of vitamin D.
The last stage of synthesis mainly occurs in the proximal tubules of the kidneys under the action of 25(OH) D-1-α-hydroxylase, an enzyme whose activity is increased by parathyroid hormone and low PO levels4 2- .
The process of 1-α-hydroxylation is also thought to occur in the periphery, such as in the skin, where vitamin D is a promoter of differentiation.
Vitamins are essential substances that enter the human body with food. And only one is an exception - it is produced by epidermal cells under the influence of ultraviolet radiation when a person is in the sun. What vitamin can human skin synthesize? What are its functions?
Description
Human skin can produce vitamin D. It regulates calcium and phosphorus levels. A sufficient amount of it in the blood promotes the proper development of skeletal bones, prevents the occurrence of rickets and osteoporosis, and reduces the incidence of diabetes, acute respiratory infections, and obesity.
The synthesis of vitamin D has been studied for at least 100 years: since the discovery of a certain fat-soluble component found in fish oil in 1913. Its influence on the treatment of rickets was colossal, which identified fish oil as a panacea and stimulated further study of the unknown chemical compound.
The classification defines vitamin D as fat-soluble, but it is actually a prohormonal steroid. It is synthesized in the layers of the epidermis from provitamins, the main part of which is formed from cholesterol present in the body (7-dehydrocholesterol), a precursor of cholecalciferol, and is partially extracted from food (ergoterol, stigmaterol and sitosterol). The hormone acts as an active derivative of vitamin D - 1.25 dioxycholecalciferol, or calcitriol, which is synthesized by the kidneys from provitamins produced in the skin or ingested with food.
Vitamin D contains 6 forms of stearins. The main physiological role is played by 2 of them:
- D2 (ergocalciferol). Synthesized in plants. A person receives it by eating mushrooms, milk, fish, and this compound is absorbed in the intestines with the participation of bile enzymes. If bile production is impaired, the absorption of the vitamin also deteriorates.
- D3 (cholecalciferol). Produced by the human epidermis from dehydrocholesterol with the participation of ultraviolet light.
These are identical substances, externally they are white crystals, highly soluble in organic solvents and fat, stable when exposed to high temperatures. The D3 form is more important for the body than D2, but often the concepts are generalized and vitamin D is mentioned in general. Both are regarded as equivalent and interchangeable.
It has been scientifically proven that vitamin D exerts its effect only after binding to target receptors. Similar VDR receptors are present in many tissues of the human body (lungs, cells of the immune system, gonads).
Functions
The specific effect of a chemical compound such as Vitamin D is to maintain the level of calcium in the blood serum, regulating the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the intestines or from bone tissue. It promotes the accumulation of the first macronutrient in the bones, thereby preventing their softening.
Vitamin D is a kind of “signal button” that triggers a physiological response to changes in calcium levels in the bloodstream. In the intestines it stimulates the production of the protein carrier of the macronutrient, and in the kidney tissue and muscles it stimulates the reabsorption of Ca++ ions.
More and more evidence is accumulating that in addition to the classical skeletal function, 1.25 dioxycholecalciferol performs many other functions:
- It stimulates the production of an active substance by macrophages - cathelicidin, which has antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal properties.
- Regulates the division and differentiation of immune cells.
- Controls the process of creating a skin antibacterial barrier, an innate immune skin response to attack by microorganisms from the outside.
A large number of VDR receptors have been found in the brain, especially in areas responsible for cognitive properties (thalamus, cortex). A proportional dependence of the probability of developing cognitive impairment on the level of the active form of vitamin D in the blood was revealed. This is especially true for older people, who for this reason have an increased risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, senile dementia, and depression. In addition, with age, the skin's ability to synthesize cholecalciferol decreases significantly, which can lead to hypovitaminosis D.
Cholecalciferol preparations are included in the therapeutic course of treatment of multiple sclerosis, since this chemical compound is involved in the regeneration of the protective sheaths of nerve fibers.
The contribution of calcitriol to reproductive function is important. It is involved in the connection between the embryo and the endometrium. In addition, vitamin receptors are present in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and placenta. At the stage of pregnancy planning and infertility, it is important to identify and correct possible vitamin D deficiency.
The cause-and-effect relationship between the level of vitamin D in the body and impaired insulin secretion, the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, obesity, arterial hypertension, and myocardial infarction has been scientifically confirmed.
The “non-calcium” effects of vitamin D also include inhibition of cell division and stimulation of cell differentiation. Vitamin D in the skin is actively involved in the process of renewal of its cellular elements, the formation of the stratum corneum, while simultaneously suppressing hyperproliferation. It also plays a certain role in the development of certain types of carcinomas and autoimmune pathologies.
The amount of vitamin is normal
The amount of vitamin D is measured in micrograms (mcg) or international units (IU):
Pregnant and lactating women have higher daily values.
Given the multiple noncalcemic functions of this compound, average dosages are likely to be revised in the future. In addition, widespread hypovitaminosis D is detected in the world, associated with the environmental situation and a decrease in the quality of life.
Sources
There are 3 known sources of vitamin D: food, special dietary supplements and UV radiation. Let's look at them in more detail.
Ultraviolet
Back in the mid-17th century, the scientist Glisson noted that the incidence of rickets among children (infants) of farmers was much higher in high mountain areas. They do not see the sun most of the time and are indoors, hiding from rainy and cold weather. At the same time, they received a sufficient amount of butter, milk and meat in their diet.
Almost all people replenish their vitamin D stores (more than 90%) through exposure to ultraviolet light. Under the influence of UV radiation the following reactions occur:
- In the epidermis, previtamin D3 is converted into provitamin D3.
- Further, through thermal isomerization, it is converted into cholecalciferol (form D3) and enters the skin vessels and the general bloodstream.
The effective wavelength under which this process occurs in the human epidermis covers the spectral range of 255–330 nm with an average value of 295 nm.
Interestingly, such rays reach the Earth’s surface precisely during the period of time when experts do not recommend sunbathing (from 11.00 to 15.00). However, exposure to the open sun for only 15–20 minutes is enough for 250 mcg of the vitamin cholecalciferol (suberythemal amount) to be synthesized in the skin. Provided there is a sufficient amount of ultraviolet radiation, the body’s needs for this chemical compound are completely covered.
The development of vitamin D deficiency is uncommon. It is mainly affected by residents of the Far North, where the polar night lasts for many months, or by infants. Vitamin deficiency mainly develops in the autumn-winter period.
The production of cholecalciferol depends on certain factors:
The older a person is, the lower the ability of his skin to synthesize cholecalciferol.
Nutrition
Food is only a minor source of vitamin D, since our diet, whatever it may be, is almost always poor in its content.
This chemical compound is present in milk, fish oil, eggs, nettles, and parsley. However, as practice shows, even the above products may contain only small amounts of this compound and such doses are not able to eliminate the human need:
Nutritional supplements
In many countries, the diet includes foods artificially fortified with vitamin D: juices, cereals, bread, milk and its derivatives. In addition, there are a number of medications that contain vitamin D (multivitamin complexes and nutritional supplements). You should take this remedy only on the recommendation of a specialist.
Food supplements are available in the form of suspensions, capsules, tablets (for example, Calcefediol, Ergocalciferol, Cholecalciferol). It is not advisable to combine the use of such drugs with active sun exposure - symptoms of hypervitaminosis may develop (toxicosis, thirst, constipation, weight loss).
The important thing is that vitamin D deficiency cannot be corrected instantly; it is a long and difficult process. Therefore, do not take things to extremes, do not neglect sunbathing and walks in the fresh air. Remember that window glass and walls are an insurmountable barrier to ultraviolet radiation.
The skin is the largest organ in the human body and is a litmus test for the general condition of the entire organism. It can be used to judge the presence of malfunctions and diseases, lack of minerals and vitamins. In particular, dull skin with numerous inflammatory foci may indicate hypovitaminosis, which is quite common in our cold country. Even in the summer during the gardening season, together with food, we receive only 20–30% of the necessary vitamins, and in the period from autumn to spring much less, so we cannot do without additional “feeding”. Let's figure out how a lack of vitamins affects the appearance and health of the skin, how natural vitamins differ from synthetic analogues, what natural yeast complexes are and what their benefits are for the skin.
It is important to know that you cannot stock up on vitamins for future use - they are not stored in tissues as reserves. The body itself synthesizes only two vitamins D and K, and even then in small quantities. Meanwhile, for normal life functions we need at least 13 vitamins, and we can only get them from the outside - with food or pharmaceutical drugs. When vitamins enter the body, they are consumed extremely quickly, and water-soluble ones (C, P, PP, group B) are excreted along with the liquid within a couple of days. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly replenish your “vitamin bins”.
How to recognize hypovitaminosis: symptoms on the skin
Acne (acne). Acne occurs as a result of increased sebum production, blockage and subsequent inflammation of the sebaceous glands. The main reasons are metabolic disorders due to hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, infectious and chronic diseases, deficiency of vitamins and microelements. In case of serious skin lesions on the face and/or body, it is not worth treating with vitamins alone. Due to the large “bouquet” of reasons, a doctor must diagnose hypovitaminosis. In addition, the specialist will determine the deficiency of a specific element or vitamin group.
Dry skin. Peeling and even cracking of the skin is caused by dehydration and lack of sebum (also due to improper functioning of the sebaceous glands). Violation of the water-salt balance occurs due to functional failures in the kidneys and diseases of the central nervous system. Vitamin D is responsible for the regulation of kidney function; vitamins B6 and B12 are required for normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Rosacea (rosacea). Bright redness of the skin with inflamed tubercles occurs due to the fact that the blood vessels in the facial area become highly sensitive to external irritants. The main cause of the disease is considered to be photodegradation of vitamins A and C - beneficial elements decompose under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, with a lack of nutrition, collagen tissue is destroyed, and nearby vessels become inflamed. The mechanism is not fully understood, but doctors note that it is long-term intake of vitamins A and C that improves the condition of reddened skin and restores the functioning of blood vessels.
Pigmentation. The main pigment of the human body is the protein melanin; skin color depends on its quantity and distribution. If there is an excess accumulation of pigment, dark spots appear; if there is a deficiency, hypopigmentation develops in the form of light areas. The culprits are free radicals, which disrupt the functioning of melanocytes (the cells that produce melanin). Antioxidant vitamins A, C, E, as well as trace elements selenium, zinc, copper, manganese bind free radicals and restore the functioning of melanocytes. By taking vitamin-mineral complexes with an antioxidant effect, it is possible to smooth out the contrast between healthy and damaged areas of the skin and even completely get rid of age spots.
How to treat skin: synthetic or natural vitamins?
A balanced diet with fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs is good, but over the past decades the amount of vitamins and minerals in foods has decreased significantly. For example, since the mid-1960s, the vitamin A content in oranges and apples has decreased threefold (data from the Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences), that is, today you need to eat three fruits instead of one in order to deliver the daily dose of retinol to the body. In addition, the amount of active elements decreases during storage - by the beginning of spring, vegetables, fruits and root vegetables lose at least 30% of their vitamins, and greens lose 60% in just one day.
To make up for the deficiency, we go to the pharmacy for synthetic multivitamins, in which the active substances retain their properties until the end of the expiration date. However, some researchers call artificial drugs “dummies.” The main argument is the different chemical composition of synthetic and natural substances. Indeed, pharmaceutical laboratories reproduce vitamin formulas only partially, whereas for complete absorption the entire set of components is needed. For example, orange vitamin C contains seven isomers of ascorbic acid, while the synthetic version contains only one isomer. The situation is the same with vitamin E - out of eight natural tocopherols, only one is reproduced in laboratories. As a result, even the most “famous” synthetic vitamins are absorbed by a maximum of 15%. Pharmaceutical companies are not at all concerned about this state of affairs - technologies for the synthesis of complete formulas are available, but the expensive process is simply unprofitable.
The theory of the uselessness of synthetic vitamins is discussed in detail in the book “Vitaminology”. Moreover, author Katherine Price considers artificial drugs dangerous: according to her research, vitamin A is synthesized using acetone and formaldehyde, B1 is released from coal tar, and PP from nylon fibers. Proponents of synthetics argue that many vitamins are obtained from natural products - for example, PP from orange peel, and B12 from bacteria similar to the microflora of the human intestine. But, as a rule, components isolated from natural products are the prerogative of expensive complexes from well-known brands.
And yet, it is possible to treat the skin for hypovitaminosis without overpaying and without relying on the honesty of manufacturers. Nature itself contains a 100% natural complex of vitamins and minerals - brewer's yeast. Yeast also has an advantage over fresh fruits and vegetables - like synthetics, its components remain active for a long time.
Yeast complexes – beauty from within
Yeast is a mass of microscopic single-celled fungi. These mushrooms live almost everywhere: in food, drinks, air - we can say that they are always nearby. More than half of yeast consists of complete protein, that is, it is a source of easily digestible amino acids. It also contains fats, carbohydrates and RNA (ribonucleic acid), which prevents the destruction of living cells and premature aging of the body. As for vitamins, yeast is the most valuable natural accumulator of B vitamins and vitamin PP. They also contain vitamins D, K, H, E and minerals - calcium, magnesium, chromium, potassium, zinc, phosphorus, iron and many others. There are useful elements for all human organs and tissues, including the “components of beauty” - skin, hair, nails.
For medicinal purposes and for health prevention, dry brewer's yeast is usually used (this form is convenient for the production of tablets). Opponents of yeast treatments say the pills are useless because they are made from “dead” yeast cultures. Indeed, there is no living fungus in dry yeast, but this is precisely the main value. During the manufacturing process, live fungi are inactivated, after which the yeast loses its ability to ferment and does not cause disorders in the digestive tract. In addition, when the shell is partially destroyed, the fungal biocomplex becomes maximally accessible and is 100% absorbed by the body. Another myth is that yeast increases weight. In fact, the saying “grows by leaps and bounds” is about bread, not about a person. The fungus does not cause hormonal disruptions, but rather normalizes metabolism. When the body returns to normal, intestinal function improves and, accordingly, appetite increases - eating without measure can give you extra pounds, but yeast is not directly to blame for this.
Enriched yeast with sulfur: maximum benefits for the skin
Since yeast is easily digestible, other beneficial microelements, such as sulfur, can be delivered to the body along with it. As a recognized beauty mineral, it effectively fights skin aging - it simulates the synthesis of natural keratin and collagen, making the skin firm and elastic. In addition, sulfur normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands, eliminating the very causes of dry skin and acne.
Naturally, brewer's yeast, even in tandem with sulfur, is not a miracle pill. To get a visible result, a couple of pills is not enough. All health-improving medications should be taken in long courses according to the manufacturers' instructions. For greater effect, taking tablets can be combined with specialized external treatments, which are often included in the same product line along with yeast: foams, creams, lotions.
Avoid counterfeits
Alas, multivitamins and yeast complexes are counterfeited in the same way as popular medicines. At best, you will get ordinary chalk, at worst, toxic chemicals. To avoid getting a “dummy” or dangerous product, buy vitamins and yeast in pharmacies, on branded websites and in large specialized online stores.